Particles reactions - Teaching Advanced Physics
... varieties of matter…. The key feature is that positrons are the antiparticles of electrons. When matter and antimatter meet, they can mutually annihilate. The energy in their masses has been unlocked: Erest = mc2 at work. What is the point of this? Destroying the electrons and positrons is just the ...
... varieties of matter…. The key feature is that positrons are the antiparticles of electrons. When matter and antimatter meet, they can mutually annihilate. The energy in their masses has been unlocked: Erest = mc2 at work. What is the point of this? Destroying the electrons and positrons is just the ...
Basics of Electron Storage Rings
... - Equation of motion is usually a differential equation with respect to time t, however, we are usually interested not in time but particle trajectory along a path. We, therefore, write down equations of motion with respect to distance s (=t). ...
... - Equation of motion is usually a differential equation with respect to time t, however, we are usually interested not in time but particle trajectory along a path. We, therefore, write down equations of motion with respect to distance s (=t). ...
Activity 1 Solutions: Introduction to Physics 104
... spark has reached the radio. b) How did energy from the separated charges on the Wimshurst machine reach the radio? There is no direct electrical connection between the Wimshurst machine and the radio. Energy produced by the spark (the source) traveled in electromagnetic waves across the room to the ...
... spark has reached the radio. b) How did energy from the separated charges on the Wimshurst machine reach the radio? There is no direct electrical connection between the Wimshurst machine and the radio. Energy produced by the spark (the source) traveled in electromagnetic waves across the room to the ...
Tuesday, Nov. 25, 2014
... – You can prepare a one 8.5x11.5 sheet (front and back) of handwritten formulae and values of constants for the exam • None of the parts of the solutions of any problems • No derived formulae, derivations of equations or word definitions! ...
... – You can prepare a one 8.5x11.5 sheet (front and back) of handwritten formulae and values of constants for the exam • None of the parts of the solutions of any problems • No derived formulae, derivations of equations or word definitions! ...
Slide 1
... a battery of very high voltage V in series with a very large resistance R. Such approximation would supply a current V/R into any load that has a resistance much smaller than R. ...
... a battery of very high voltage V in series with a very large resistance R. Such approximation would supply a current V/R into any load that has a resistance much smaller than R. ...
Electric & Gravitational Fields and Electric Potentials
... – The result is lines start from a positive charge and end at a negative charge ...
... – The result is lines start from a positive charge and end at a negative charge ...
Special Theory of Relativity
... “I had a better grasp of things when physics dealt mostly with falling bodies.” ...
... “I had a better grasp of things when physics dealt mostly with falling bodies.” ...
Measuring the speed of light
... for introducing the fixed factor 1/1000 into the hardware between the modulator and the socket, is that a relatively simple oscilloscope can be used for the task. After determination of the modulation frequency, the two other sockets (femit -fsync and frec -fsync ) are connected to the two input cha ...
... for introducing the fixed factor 1/1000 into the hardware between the modulator and the socket, is that a relatively simple oscilloscope can be used for the task. After determination of the modulation frequency, the two other sockets (femit -fsync and frec -fsync ) are connected to the two input cha ...
Light and Color
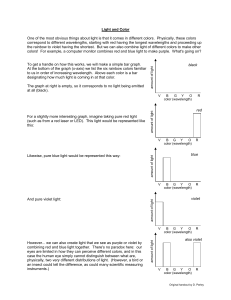
... One of the most obvious things about light is that it comes in different colors. Physically, these colors correspond to different wavelengths, starting with red having the longest wavelengths and proceeding up the rainbow to violet having the shortest. But we can also combine light of different colo ...
... One of the most obvious things about light is that it comes in different colors. Physically, these colors correspond to different wavelengths, starting with red having the longest wavelengths and proceeding up the rainbow to violet having the shortest. But we can also combine light of different colo ...