PE and KE
... Kinetic Energy • Energy of matter in motion. • Measured by how much work is done to put an object in motion or to rest. • The faster the object moves, the more kinetic energy. ...
... Kinetic Energy • Energy of matter in motion. • Measured by how much work is done to put an object in motion or to rest. • The faster the object moves, the more kinetic energy. ...
Redox Reactions: Transferring Electrons
... whatever gizmo you have it hooked up to When a reaction transfers an electron from one substance to another we call it an “Oxidation-Reduction” reaction or Redox for short. If a substance is losing the electron it is being oxidized If a substance is gaining, it is being reduced. ...
... whatever gizmo you have it hooked up to When a reaction transfers an electron from one substance to another we call it an “Oxidation-Reduction” reaction or Redox for short. If a substance is losing the electron it is being oxidized If a substance is gaining, it is being reduced. ...
AP Chemistry Summer Study Guide
... Gamma Ray: 0 protons, mass number = 0, Low ionizing ability, high energy Halogen: Elements in group 17. Form halides as ions Hydrogen Bonding: Strong dipole that results when H is bonded to F, O, or N Indirect relationship: Relationship between two variables where when one changes, the other changes ...
... Gamma Ray: 0 protons, mass number = 0, Low ionizing ability, high energy Halogen: Elements in group 17. Form halides as ions Hydrogen Bonding: Strong dipole that results when H is bonded to F, O, or N Indirect relationship: Relationship between two variables where when one changes, the other changes ...
1 - Georgetown ISD
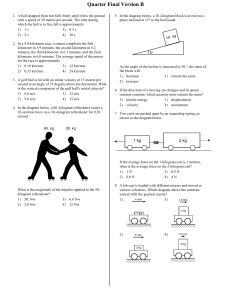
... 3. The figure above shows a rough semicircular track whose ends are at a vertical height h. A block placed at point P at one end of the track is released from rest and slides past the bottom of the track. Which of the following is true of the height to which the block rises on the other side of the ...
... 3. The figure above shows a rough semicircular track whose ends are at a vertical height h. A block placed at point P at one end of the track is released from rest and slides past the bottom of the track. Which of the following is true of the height to which the block rises on the other side of the ...
R - physicsinfo.co.uk
... For questions 1–10, in Section A, select one answer from A to D and put a cross in the box and then If you change your mind, put a line through the box mark your new answer with a cross . ...
... For questions 1–10, in Section A, select one answer from A to D and put a cross in the box and then If you change your mind, put a line through the box mark your new answer with a cross . ...
Physics around 1900
... ‘black light’ may be concentrated by metals well polished zinc steel glow-worms (soon confirmed by Muraoka in Kyoto) ...
... ‘black light’ may be concentrated by metals well polished zinc steel glow-worms (soon confirmed by Muraoka in Kyoto) ...
A wave that DOES NOT require a medium through which to travel.
... Two hypotheses concerning light and polarization (two outdated models) 1. Light is a mechanical vibration that travels through an elastic medium. This medium is completely transparent and has exactly zero mass. This medium is called ether. 2. A light wave is some new type of vibration that does not ...
... Two hypotheses concerning light and polarization (two outdated models) 1. Light is a mechanical vibration that travels through an elastic medium. This medium is completely transparent and has exactly zero mass. This medium is called ether. 2. A light wave is some new type of vibration that does not ...
Document
... (higher in frequency and energy), we get Xrays. With their high energies, X-rays can be used to image our insides. • As the shortest wavelengths and the highest energies, we have gamma rays. Gamma ...
... (higher in frequency and energy), we get Xrays. With their high energies, X-rays can be used to image our insides. • As the shortest wavelengths and the highest energies, we have gamma rays. Gamma ...
S4. Building Blocks of the Universe Agenda Lunar Reconnaissance
... • What is the exclusion principle? • Two fermions of the same type cannot occupy the same quantum state at the same time. (This principle does not apply to bosons.) • How is the exclusion principle important to our existence? • The exclusion principle explains the different energy levels in atoms, w ...
... • What is the exclusion principle? • Two fermions of the same type cannot occupy the same quantum state at the same time. (This principle does not apply to bosons.) • How is the exclusion principle important to our existence? • The exclusion principle explains the different energy levels in atoms, w ...
Lecture 27
... has an index of refraction of 1.5. It is arranged (in air) so that one 2cm side is parallel to the ground, and the other to the left. You direct a laser beam into the prism from the left. At the first interaction with the prism surface, all of the ray is transmitted into the prism. ...
... has an index of refraction of 1.5. It is arranged (in air) so that one 2cm side is parallel to the ground, and the other to the left. You direct a laser beam into the prism from the left. At the first interaction with the prism surface, all of the ray is transmitted into the prism. ...
Two valence electrons.
... atoms. When elements are listed in order according to the number of protons (called the atomic number), repeating patterns of physical and chemical properties identify families of elements with similar properties. ...
... atoms. When elements are listed in order according to the number of protons (called the atomic number), repeating patterns of physical and chemical properties identify families of elements with similar properties. ...