Charge
... Capacitors are electrical devices used to store electrical energy. They are not to be confused with batteries which create electrical energy via chemical reaction. The structure of a capacitor is shown on the next slide. Essentially, electrons are pumped onto one of the metal plates shown and pushe ...
... Capacitors are electrical devices used to store electrical energy. They are not to be confused with batteries which create electrical energy via chemical reaction. The structure of a capacitor is shown on the next slide. Essentially, electrons are pumped onto one of the metal plates shown and pushe ...
Name: Midterm Review (Part II) Fill in the blanks (Chapter 6.1 – 6.3
... When atom is the ground state, what must happen for the atom to be in an excited state? Your notes What must happen for this atom to return to ground state?p. 142 Would an electron have to absorb or release energy to jump from the second energy level to the third energy level?p. 142-143 How light is ...
... When atom is the ground state, what must happen for the atom to be in an excited state? Your notes What must happen for this atom to return to ground state?p. 142 Would an electron have to absorb or release energy to jump from the second energy level to the third energy level?p. 142-143 How light is ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC)
... The linear and nonlinear optical response of metal nanoparticles is specified by oscillations of the surface electrons in the Coulomb potential formed by the positively charged ionic core. This type of excitation is called the surface plasmon (SP)[2]. In 1908 Mie proposed a solution of Maxwell’s equ ...
... The linear and nonlinear optical response of metal nanoparticles is specified by oscillations of the surface electrons in the Coulomb potential formed by the positively charged ionic core. This type of excitation is called the surface plasmon (SP)[2]. In 1908 Mie proposed a solution of Maxwell’s equ ...
On a possibility of moving with the speed greater than the speed of
... The problem is that a detailed description of the phenomenon requires the quantummechanical development of relativistic gravitational theory. In our approach, it was assumed that the photon-field interaction is consistent with conservative properties of the field. Consequently, a deceleration effect ...
... The problem is that a detailed description of the phenomenon requires the quantummechanical development of relativistic gravitational theory. In our approach, it was assumed that the photon-field interaction is consistent with conservative properties of the field. Consequently, a deceleration effect ...
PPT
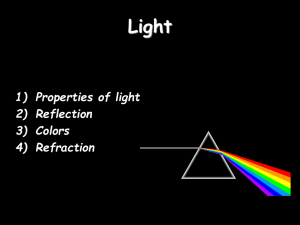
... = detecting light that has been reflected off the object's surface light = electromagnetic wave; “visible light”= those electromagnetic waves that our eyes can detect “wavelength” of e.m. wave (distance between two successive crests) determines “color” of light wave hardly influenced by object if ...
... = detecting light that has been reflected off the object's surface light = electromagnetic wave; “visible light”= those electromagnetic waves that our eyes can detect “wavelength” of e.m. wave (distance between two successive crests) determines “color” of light wave hardly influenced by object if ...
Charges forces and fields
... (c) a charge of 2 C and one of 15 C separated by 1.5 m (d) an alpha particle (charge = 2e) and a gold nucleus (charge = 79e) when they are separated by 3.6x10-14 m 2. Calculate the electric field intensity at the following places (a) half way between two plates separated by 0.5 cm when a p.d of 3000 ...
... (c) a charge of 2 C and one of 15 C separated by 1.5 m (d) an alpha particle (charge = 2e) and a gold nucleus (charge = 79e) when they are separated by 3.6x10-14 m 2. Calculate the electric field intensity at the following places (a) half way between two plates separated by 0.5 cm when a p.d of 3000 ...
Energy - Types of Energy
... If you double the mass, you double the kinetic energy. If you increase the speed of a moving object you increase the kinetic energy. BUT… If you double the speed, you quadruple the kinetic energy. This is why even if you are slightly above the speed limit, you increase the kinetic energy of a moving ...
... If you double the mass, you double the kinetic energy. If you increase the speed of a moving object you increase the kinetic energy. BUT… If you double the speed, you quadruple the kinetic energy. This is why even if you are slightly above the speed limit, you increase the kinetic energy of a moving ...
The interaction of electrons with a uniform magnetic field. A... field couples to the electronic motion, and to the electron...
... momentum L = 3. This means that the states with J = 2, 3, and 4 are all possible. This gives for the case of n = 2 electrons 5 + 7 + 9 = 21 options. (Note that in this case, (2L + 1)(2S + 1) = 21.) However, Hund’s third rule tells us that the lowest energy is obtained for J = |L − S| = 2, and theref ...
... momentum L = 3. This means that the states with J = 2, 3, and 4 are all possible. This gives for the case of n = 2 electrons 5 + 7 + 9 = 21 options. (Note that in this case, (2L + 1)(2S + 1) = 21.) However, Hund’s third rule tells us that the lowest energy is obtained for J = |L − S| = 2, and theref ...
Radiation from accelerated charged particles
... The electromagnetic radiation emitted when the charged particles are accelerated radially (v a) is called synchrotron radiation It is produced in the synchrotron radiation sources using bending magnets undulators and wigglers ...
... The electromagnetic radiation emitted when the charged particles are accelerated radially (v a) is called synchrotron radiation It is produced in the synchrotron radiation sources using bending magnets undulators and wigglers ...
Section 2 Models of the Atom
... kinetic energy (of photoelectrons ejected from the surface) is the difference between the photon energy and the work function of the metal. maximum kinetic energy of a photoelectron KEmax = hf – hft maximum kinetic energy = (Planck’s constant frequency of incoming photon) – work function ...
... kinetic energy (of photoelectrons ejected from the surface) is the difference between the photon energy and the work function of the metal. maximum kinetic energy of a photoelectron KEmax = hf – hft maximum kinetic energy = (Planck’s constant frequency of incoming photon) – work function ...
PowerPoint Notes
... kinetic energy (of photoelectrons ejected from the surface) is the difference between the photon energy and the work function of the metal. maximum kinetic energy of a photoelectron KEmax = hf – hft maximum kinetic energy = (Planck’s constant frequency of incoming photon) – work function ...
... kinetic energy (of photoelectrons ejected from the surface) is the difference between the photon energy and the work function of the metal. maximum kinetic energy of a photoelectron KEmax = hf – hft maximum kinetic energy = (Planck’s constant frequency of incoming photon) – work function ...