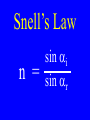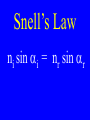* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Psc CH-17 Reflection
Architectural lighting design wikipedia , lookup
Gravitational lens wikipedia , lookup
Light pollution wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Photopolymer wikipedia , lookup
Doctor Light (Kimiyo Hoshi) wikipedia , lookup
Bioluminescence wikipedia , lookup
Chapter 17 Reflection & Refraction Reflection •When light rays bounce back off of a medium boundary Refraction •The bending of light rays when passing from one medium to another Ray •A straight line path representing the direction of a light wave Regular Reflection •Reflection off of a smooth surface which results in reflected wave that are parallel Regular Reflection •Produce good images • Mirrors give regular reflections Diffuse Reflection • Reflection off of a rough surface which results in reflected waves that are not parallel Diffuse Reflection • Because light waves are scattered all over the place, no image can be seen Law of Reflection •The angle of reflection equals the angle of incident Law of Reflection a b b = a Normal Optical Density • How fast light passes through a substance as compared to the speed of light in a vacuum. Optical Density •As optical density increases, the speed in which light passes decreases Index of Refraction (n) •Ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to the speed of light in a material Indices of Refraction •Vacuum: n = 1.00 •Air: n = 1.0003 •Water: n = 1.33 •Ethanol: n = 1.36 Indices of Refraction •Crown glass: n = 1.52 •Quartz: n = 1.54 •Flint glass: n = 1.61 •Diamond: n = 2.42 Speed of Light in Other Substances nsub = c vsub Speed of Light in Other Substances vsub = c nsub Solve for the speed of light in each of the following: water (n = 1.33) crown glass (n = 1.52) diamond (n = 2.42) Solve for the speed of light in a substance with an optical density of 1.50: Snell’s Law •The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence over the sine of the angle of refraction is constant for any substance Snell’s Law n = sin ai sin ar Snell’s Law ni sin ai = nr sin ar Snell’s Law ai n1 = air ar n2 = water Draw a model with a light ray passing from one medium to another more optically dense medium. Include reflection & refraction A light ray from air (nair = 1.00) & strikes glass (nglass = 1.52) with an incident angle of o 30.0 . Calculate the angle of refraction: A light ray from air (nair = 1.00) strikes glass (nglass = 1.61) with an o incident angle of 36.9 . Calculate the angle of refraction: A light ray from air (nair = 1.00) & strikes diamond (ndiamd = 2.42) with an incident angle o of 45.0 . Calculate the angle of refraction: A light ray incident from air (nair = 1.00) at o 45.0 passes into an unknown substance at o 30.0 . Calculate its index of refraction: Total Internal Reflection • When light passes from a more optically dense substance to a less optically dense one, the angle of refraction > the angle of incident b a Total Internal Reflection (TIR) •When the angle of o refraction 90 , total internal reflection occurs. Calculate the angles where TIR occurs when light passes from the following to air: water (n = 1.33) crown glass (n = 1.52) diamond (n = 2.42) Applications & Effects • Prisms • Fiber Optics • Mirages • Red Sunsets • Rainbows Prisms • When light pass through a prism the various wavelengths of light are dispersed or separated into a spectrum Prisms Fiber Optics • A light wave can pass through a thin glass thread surrounded by a reflective substance. Even if the glass thread is bent, the wave passes through as it reflects off the sides. Mirages •Light refracted from a far away source looks closer Mirages Sunsets & Rises • Sunlight is refracted as it strikes the atmosphere at great angles bending light towards Earth Sunsets • Because different wavelengths are refracted differently, colors change Sunsets Rainbows • Sunlight is refracted & reflected by rain droplets dispersing the light into a spectrum Rainbows Rainbows Rainbows fall o from 40 – 42 from incident Rainbows Rainbows fall o from 40 – 42 from incident A light ray from water (nw = 1.33) & strikes diamond (ndiamd = 2.42) with an incident angle o of 53.0 . Calculate the angle of refraction: Answer the questions at the end of Chapter 16 Answer the questions at the end of Chapter 17 A light ray from water (nw = 1.33) & strikes glass (nglass = 1.51) with an incident angle of o 53.0 . Calculate the angle of refraction: Calculate the angle of total internal reflection of pukon with n = 3.00 An incident ray from air strikes quartz (n = 1.50) at an angle of o 30 from normal. Calculate: refl & refr