* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Properties of Light
Holiday lighting technology wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Bicycle lighting wikipedia , lookup
Architectural lighting design wikipedia , lookup
Gravitational lens wikipedia , lookup
Light pollution wikipedia , lookup
Daylighting wikipedia , lookup
Photopolymer wikipedia , lookup
Doctor Light (Kimiyo Hoshi) wikipedia , lookup
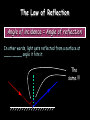
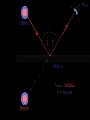
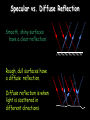
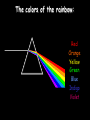
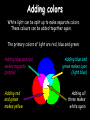
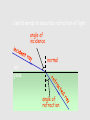
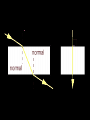
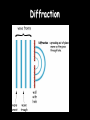
Light 1) 2) 3) 4) Properties of light Reflection Colors Refraction Part 1 – Properties of Light Light travels in straight lines: Laser Light travels VERY FAST – around 300,000 kilometres per second. At this speed it can go around the world 8 times in one second. Light travels much faster than sound. For example: 1) Thunder and lightning start at the same time, but we will see the lightning first. 2) When a starting pistol is fired we see the smoke first and then hear the bang. We see things because they reflect light into our eyes: Homework Luminous and non-luminous objects A luminous object is one that produces light. A non-luminous object is one that reflects light. Luminous objects Reflectors Shadows Shadows are places where light is “blocked”: Rays of light Properties of Light summary 1) Light travels in straight lines 2) Light travels much faster than sound 3) We see things because they reflect light into our eyes 4) Shadows are formed when light is blocked by an object Part 2 - Reflection Reflection from a mirror: Normal Reflected ray Incident ray Angle of incidence Angle of reflection Mirror The Law of Reflection Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection In other words, light gets reflected from a surface at ____ _____ angle it hits it. The same !!! Image - is a position in space where all the reflected light appears to diverge from. Images formed by plane mirrors are virtual 1.The image formed by a plane mirror is Virtual Image – not real therefore can not be caught on a screen – Images are formed in locations where light does not actually reach – Rays do not actually cross at the point behind the mirror. • They only appear to have originated there. 2.The object distance (often represented by the symbol do) is equal to the image distance (often represented by the symbol di). 3.Dimensions of the image are the same as the dimensions of the object . 4. The image is upright 5. Left right reversal – The image is laterally reversed. Specular vs. Diffuse Reflection Smooth, shiny surfaces have a clear reflection: Rough, dull surfaces have a diffuse reflection. Diffuse reflection is when light is scattered in different directions Reflection off of smooth surfaces such as mirrors or a calm body of water leads to a type of reflection known as specular reflection. Reflection off of rough surfaces such as clothing, paper, and the asphalt roadway leads to a type of reflection known as diffuse reflection. Color White light is not a single color; it is made up of a mixture of the seven colors of the rainbow. We can demonstrate this by splitting white light with a prism: This is how rainbows are formed: sunlight is “split up” by raindrops. The colors of the rainbow: Red Orange Yellow Green Blue Indigo Violet Adding colors White light can be split up to make separate colors. These colours can be added together again. The primary colors of light are red, blue and green: Adding blue and red makes magenta (purple) Adding red and green makes yellow Adding blue and green makes cyan (light blue) Adding all three makes white again Seeing color The color an object appears depends on the colors of light it reflects. For example, a red book only reflects red light: White light Only red light is reflected A pair of purple trousers would reflect purple light (and red and blue, as purple is made up of red and blue): Purple light A white hat would reflect all seven colours: White light Using colored light If we look at a colored object in colored light we see something different. For example, consider a football kit: Shirt looks red White light Shorts look blue In different colours of light this kit would look different: Red light Shirt looks red Shorts look black Shirt looks black Blue light Shorts look blue Refraction is the bending of light when the light passes from one medium to another. air glass Useful words to describe refraction of light angle of incidence air glass normal angle of refraction Examples of refraction of light Bent chopstick • The chopstick appears bent because of refraction The bending occurs because the speed in which light travels through a substance depends on the substance's density. In air light travels at about 186,000 miles per second but in water light travels only about 140,000 miles per second (see chart below). Since light travels slower in water than in air, water is said to have a greater optical density than air. ‘When hunting a fish under water, you should aim your spear directly at the fish.’ Do you agree? Yes, of course. No, because the fish is actually located somewhere else. No, because size of objects changes when they are put under water. “The Inverse Square Law” The Energy we receive is inversely proportional to the square of the distance. Diffraction Diffraction is the apparent bending of waves around small obstacles and the spreading out of waves past small openings. POLARIZATION Only transvers e waves may become polarized. •Sun glasses reduce the glare of bright light using the phenomenon of polarization