CSM 101 Fall 2010 Timeline
... Excited electrons from the antenna complex resonance energy to the reaction center. From there pheophytin is reduced by electrons in photosystem II. Plastoquinone (PQ) receives electrons from photosystem II and carries them across the lumen side of the thylakoid and delivers them to more electronega ...
... Excited electrons from the antenna complex resonance energy to the reaction center. From there pheophytin is reduced by electrons in photosystem II. Plastoquinone (PQ) receives electrons from photosystem II and carries them across the lumen side of the thylakoid and delivers them to more electronega ...
Week 4:
... Fermentation: when oxygen is taken away, yields only the energy associated with glycolysis (2ATP) and yields one of several products that are generally harmful to living organisms at high concentrations: e.g. ethanol, lactic acid. Tuesday 4/26: We mentioned the terms oxidation, reduction, and “redox ...
... Fermentation: when oxygen is taken away, yields only the energy associated with glycolysis (2ATP) and yields one of several products that are generally harmful to living organisms at high concentrations: e.g. ethanol, lactic acid. Tuesday 4/26: We mentioned the terms oxidation, reduction, and “redox ...
4 Krebs ETC
... • Cristae contain molecules that make up the electron transport system utilized in aerobic respiration • Electron transport system consists of 4 complexes that receives a pair of electrons then transfers the electrons to the next complex – Cytochrome complex 3 and 4 are membrane bound proteins ...
... • Cristae contain molecules that make up the electron transport system utilized in aerobic respiration • Electron transport system consists of 4 complexes that receives a pair of electrons then transfers the electrons to the next complex – Cytochrome complex 3 and 4 are membrane bound proteins ...
respiratory chain
... such as coenzyme Q and cytochrome C. b) Each carrier of electron transport chain can receive electrons from the more electronegative donor and can subsequently donate electrons to the next more electropositive carrier in the chain. Finally electrons combine with oxygen and protons to form water and ...
... such as coenzyme Q and cytochrome C. b) Each carrier of electron transport chain can receive electrons from the more electronegative donor and can subsequently donate electrons to the next more electropositive carrier in the chain. Finally electrons combine with oxygen and protons to form water and ...
Electron Transport
... Electron Transport - continued The protons (H+) then diffuse back down their concentration gradient through ATP synthase This flow of protons causes the formation of ATP ...
... Electron Transport - continued The protons (H+) then diffuse back down their concentration gradient through ATP synthase This flow of protons causes the formation of ATP ...
Biology 123 SI-Dr. Raut`s Class Session 10
... that particular molecule is reduced. When the electrons move on to the next molecule, the first molecule is oxidized. Therefore the electron transport chain is a series of redox reaction, with oxygen getting oxidized at the end. When the electrons combine with ½ O2, two hydrogen atoms join ½ O2 to m ...
... that particular molecule is reduced. When the electrons move on to the next molecule, the first molecule is oxidized. Therefore the electron transport chain is a series of redox reaction, with oxygen getting oxidized at the end. When the electrons combine with ½ O2, two hydrogen atoms join ½ O2 to m ...
EXAM III KEY - the Complex Carbohydrate Research Center
... ADP stimulate the consumption of O2 until the ADP is all utilized. However when uncouplers, such as 2,4-dinitrophenol, are membrane-soluble compounds which allow the unrestricted transfer of protons across the mitochondrial membrane, thereby destroying the proton gradient. Thus, it was concluded tha ...
... ADP stimulate the consumption of O2 until the ADP is all utilized. However when uncouplers, such as 2,4-dinitrophenol, are membrane-soluble compounds which allow the unrestricted transfer of protons across the mitochondrial membrane, thereby destroying the proton gradient. Thus, it was concluded tha ...
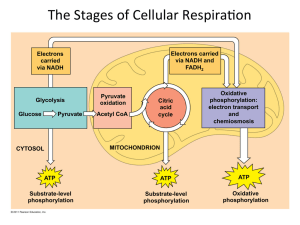
Energy Transfer and Glycolysis Cellular Respiration • Remember
... 2. Pyruvate Oxidation: occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion 3. Kreb Cycle: occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion 4. Electron Transport and Chemiosmosis: occur on the cristae (the inner mitochondrial membrane) Energy Transfer There are two main types Substrate-Level Phosphorylation: an e ...
... 2. Pyruvate Oxidation: occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion 3. Kreb Cycle: occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion 4. Electron Transport and Chemiosmosis: occur on the cristae (the inner mitochondrial membrane) Energy Transfer There are two main types Substrate-Level Phosphorylation: an e ...
Pyruvate to Acetyl Coenzyme A (Acetyl CoA)
... Chemiosmosis) Location: Inner mitochondrial membrane of mitochondria ...
... Chemiosmosis) Location: Inner mitochondrial membrane of mitochondria ...
The Stages of Cellular RespiraWon
... (citric acid cycle) Cristae or inner membrane: electron transport chain and oxida3ve phosphoryla3on ...
... (citric acid cycle) Cristae or inner membrane: electron transport chain and oxida3ve phosphoryla3on ...
Cell Respiration Exam - Data Analysis and Essay Markscheme
... small space between membranes allows protons to be accumulated / concentrated; 3 max ...
... small space between membranes allows protons to be accumulated / concentrated; 3 max ...
Transport of molecules into a bacterial cell
... – What is the greediest electron hog we know? Molecular oxygen. – In Electron transport, electrons are passed to oxygen so that these metabolic processes can continue with more glucose. – Electron carriers in membrane are reversibly reduced, then reoxidized as they pass electrons (or Hs) to the next ...
... – What is the greediest electron hog we know? Molecular oxygen. – In Electron transport, electrons are passed to oxygen so that these metabolic processes can continue with more glucose. – Electron carriers in membrane are reversibly reduced, then reoxidized as they pass electrons (or Hs) to the next ...
Stage 4 Digestion: Electron Transport Chain
... Stage 4 Digestion: Electron Transport Chain - ETC Interconnected proteins - named by Roman numerals (on large graphic on back of page) - embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane ETC Jobs 1. Dehydrogenases: Removal of H from NADH and FADH Separation into a high energy electron e- & H+ 2. Proton p ...
... Stage 4 Digestion: Electron Transport Chain - ETC Interconnected proteins - named by Roman numerals (on large graphic on back of page) - embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane ETC Jobs 1. Dehydrogenases: Removal of H from NADH and FADH Separation into a high energy electron e- & H+ 2. Proton p ...
Document
... (as it would be for the last round of oxidation of a 3 carbon FA), this oxidation would produce a formal group, which is cannot be cleaved by thiolase from the FA chain. ...
... (as it would be for the last round of oxidation of a 3 carbon FA), this oxidation would produce a formal group, which is cannot be cleaved by thiolase from the FA chain. ...
Digestion and Respiration MMHS Anatomy Chitraroff
... Digestion and Respiration MMHS Anatomy Chitraroff ...
... Digestion and Respiration MMHS Anatomy Chitraroff ...
The Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle Acetyl-coenzyme A is oxidized to CO 2
... concentration is high) and carry them to the matrix side, thereby destroying the proton gradient that couples electron transport and the ATP synthase. In mitochondria treated with uncouplers, electron transport continues, and protons are driven out through the inner membrane. However, they leak back ...
... concentration is high) and carry them to the matrix side, thereby destroying the proton gradient that couples electron transport and the ATP synthase. In mitochondria treated with uncouplers, electron transport continues, and protons are driven out through the inner membrane. However, they leak back ...
Phototropic bacteria - useful organisms for class experiments
... physiology), have been used extensively in research to provide ‘model systems’ in the study of photosynthetic reaction centres, electron transport, ion translocation, ATP synthesis, pigment biosynthesis, membrane-protein assembly and cell mobility. In undergraduate class experiments they provide use ...
... physiology), have been used extensively in research to provide ‘model systems’ in the study of photosynthetic reaction centres, electron transport, ion translocation, ATP synthesis, pigment biosynthesis, membrane-protein assembly and cell mobility. In undergraduate class experiments they provide use ...
Oxidative phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation (or OXPHOS in short) is the metabolic pathway in which the mitochondria in cells use their structure, enzymes, and energy released by the oxidation of nutrients to reform ATP. Although the many forms of life on earth use a range of different nutrients, ATP is the molecule that supplies energy to metabolism. Almost all aerobic organisms carry out oxidative phosphorylation. This pathway is probably so pervasive because it is a highly efficient way of releasing energy, compared to alternative fermentation processes such as anaerobic glycolysis.During oxidative phosphorylation, electrons are transferred from electron donors to electron acceptors such as oxygen, in redox reactions. These redox reactions release energy, which is used to form ATP. In eukaryotes, these redox reactions are carried out by a series of protein complexes within the inner membrane of the cell's mitochondria, whereas, in prokaryotes, these proteins are located in the cells' intermembrane space. These linked sets of proteins are called electron transport chains. In eukaryotes, five main protein complexes are involved, whereas in prokaryotes many different enzymes are present, using a variety of electron donors and acceptors.The energy released by electrons flowing through this electron transport chain is used to transport protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane, in a process called electron transport. This generates potential energy in the form of a pH gradient and an electrical potential across this membrane. This store of energy is tapped by allowing protons to flow back across the membrane and down this gradient, through a large enzyme called ATP synthase; this process is known as chemiosmosis. This enzyme uses this energy to generate ATP from adenosine diphosphate (ADP), in a phosphorylation reaction. This reaction is driven by the proton flow, which forces the rotation of a part of the enzyme; the ATP synthase is a rotary mechanical motor.Although oxidative phosphorylation is a vital part of metabolism, it produces reactive oxygen species such as superoxide and hydrogen peroxide, which lead to propagation of free radicals, damaging cells and contributing to disease and, possibly, aging (senescence). The enzymes carrying out this metabolic pathway are also the target of many drugs and poisons that inhibit their activities.