The variable and conserved interfaces of modeled olfactory receptor
... of the OR model. We observed that out of 36 hypervariable residues ~whose variability value is more than one standard deviation above the average variability in the TM segments!, in the entire OR protein, 26 are in the three variable helices, most of which ~20 residues! are on the predicted inner su ...
... of the OR model. We observed that out of 36 hypervariable residues ~whose variability value is more than one standard deviation above the average variability in the TM segments!, in the entire OR protein, 26 are in the three variable helices, most of which ~20 residues! are on the predicted inner su ...
Fatty Acid Biosynthesis
... • AcetylCoA carboxylase is under allosteric regulation. Citrate is a positive effector and palmitoyl CoA is a negative effector. ...
... • AcetylCoA carboxylase is under allosteric regulation. Citrate is a positive effector and palmitoyl CoA is a negative effector. ...
Sylabus
... Knows the consequences of an improper diet including a longtime starvation as well as the intake of an excess-calories meals and unbalanced diet; Knows the consequences of vitamins and minerals deficiency or excess in the organism; Knows the biochemical pathways of the communication between cells, b ...
... Knows the consequences of an improper diet including a longtime starvation as well as the intake of an excess-calories meals and unbalanced diet; Knows the consequences of vitamins and minerals deficiency or excess in the organism; Knows the biochemical pathways of the communication between cells, b ...
Title Effect of Glutamine Analogs on Glutaminase Formation in
... The formation of asparaginase of Escherichiacoli was not increased when a complex medium or an amino acid free medium were supplemented with L-asparagine (24). Only among species of Pseudomonashas there been evidence of a marked inducible formation of asparaginase by asparagine or aspartic acid (25) ...
... The formation of asparaginase of Escherichiacoli was not increased when a complex medium or an amino acid free medium were supplemented with L-asparagine (24). Only among species of Pseudomonashas there been evidence of a marked inducible formation of asparaginase by asparagine or aspartic acid (25) ...
Supplemental notes in pdf
... controlled more acutely by hormonal signaling through receptor proteins. Two of these hormones are insulin and glucagon which we have discussed numerous times throughout the course. Another important signaling pathway we introduce here is one that controls inter-organ metabolic flux through a subfam ...
... controlled more acutely by hormonal signaling through receptor proteins. Two of these hormones are insulin and glucagon which we have discussed numerous times throughout the course. Another important signaling pathway we introduce here is one that controls inter-organ metabolic flux through a subfam ...
"Allosteric Activation of Kinases: Design and Application of RapR
... of mutants, application of pharmacological inhibitors, and down-regulation of kinase expression by siRNA or genetic modifications. Down-regulation and overexpression of kinases enable targeted control, but do not provide temporal control. Application of pharmacological inhibitors allows excellent te ...
... of mutants, application of pharmacological inhibitors, and down-regulation of kinase expression by siRNA or genetic modifications. Down-regulation and overexpression of kinases enable targeted control, but do not provide temporal control. Application of pharmacological inhibitors allows excellent te ...
13synthesis
... lipids) they transferred to different cell membranes by Golgi apparatus in form of vesicles. ...
... lipids) they transferred to different cell membranes by Golgi apparatus in form of vesicles. ...
BCHM 463 Supplemental Problems for Friday, April 2, 2004 1. Write
... Rxn 3: phosphofructo kinase: ATP is an allosteric inhibitor; AMP, ADP, F2,6P, and other compounds overcome this inhibition and therefore serve as activators Rxn 10: pyruvate kinase: product inhibition by ATP (allosteric); FBP acts as an allosteric activator 11. Xylose has the same structure as gluco ...
... Rxn 3: phosphofructo kinase: ATP is an allosteric inhibitor; AMP, ADP, F2,6P, and other compounds overcome this inhibition and therefore serve as activators Rxn 10: pyruvate kinase: product inhibition by ATP (allosteric); FBP acts as an allosteric activator 11. Xylose has the same structure as gluco ...
pdf file
... upon addition of respiratory substrates to mitochondria. It is shown that the rate and extent of membrane potential generated by succinate (plus rotenone) addition to mitochondria were unaffected by treatment with 5 lM (20 nmol/mg prot) AEA. ADP addition at the steady-state caused an atractyloside a ...
... upon addition of respiratory substrates to mitochondria. It is shown that the rate and extent of membrane potential generated by succinate (plus rotenone) addition to mitochondria were unaffected by treatment with 5 lM (20 nmol/mg prot) AEA. ADP addition at the steady-state caused an atractyloside a ...
Insulin mRNA to Protein Kit Student Handout
... • The ribosome synthesizes a precursor form of insulin, known as preproinsulin. • Preproinsulin is processed to become mature, functional insulin as it proceeds through the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus, moving toward the cell membrane where it can be secreted from the cell. • When th ...
... • The ribosome synthesizes a precursor form of insulin, known as preproinsulin. • Preproinsulin is processed to become mature, functional insulin as it proceeds through the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus, moving toward the cell membrane where it can be secreted from the cell. • When th ...
INTRODUCTION - international journal of advances in
... quickly then the reestablishment and recovery occurs but if reperfusion is followed itself by irreversible damage. Depressed function and energy production during ischemia The onset of ischemia there is a decline in developed pressure and increase in the enddiastolic pressure that is linked with reg ...
... quickly then the reestablishment and recovery occurs but if reperfusion is followed itself by irreversible damage. Depressed function and energy production during ischemia The onset of ischemia there is a decline in developed pressure and increase in the enddiastolic pressure that is linked with reg ...
Lecture Notes Ch21
... – A product of a reaction acts as a negative regulator – An end product binds with the first enzyme in a sequence when sufficient product is present ...
... – A product of a reaction acts as a negative regulator – An end product binds with the first enzyme in a sequence when sufficient product is present ...
enzyme
... Competitive Inhibition: The inhibitor competes with the substrate or coenzyme for the binding site on the active center by forming an enzyme inhibitor complex EI. Inhibition can be made ineffective by excess substrate, as is the case for inhibition of succinate dehydrogenase by malonate. ...
... Competitive Inhibition: The inhibitor competes with the substrate or coenzyme for the binding site on the active center by forming an enzyme inhibitor complex EI. Inhibition can be made ineffective by excess substrate, as is the case for inhibition of succinate dehydrogenase by malonate. ...
NUCLEOTIDE METABOLISM
... NUCLEOTIDE METABOLISM Mark Rush Nucleotides serve various metabolic functions. For example, they are: ...
... NUCLEOTIDE METABOLISM Mark Rush Nucleotides serve various metabolic functions. For example, they are: ...
Role of basic character of α-sarcin`s NH2-terminal β
... fungal natural killers characterized by their exquisite ribonucleolytic specificity against ribosomes and their ability to cross cellular membranes in the absence of any known protein receptor [1,2]. These toxic proteins cleave just a single phosphodiester bond of the large rRNA fragment, located at ...
... fungal natural killers characterized by their exquisite ribonucleolytic specificity against ribosomes and their ability to cross cellular membranes in the absence of any known protein receptor [1,2]. These toxic proteins cleave just a single phosphodiester bond of the large rRNA fragment, located at ...
Chapter 26
... made by carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II (CPS II) – This is a cytosolic enzyme (whereas CPS I is mitochondrial and used for the urea cycle) – Substrates are HCO3-, glutamine (not NH4+), 2 ATP – In mammals, CPS-II can be viewed as the committed step in pyrimidine synthesis – Bacteria have but one CP ...
... made by carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II (CPS II) – This is a cytosolic enzyme (whereas CPS I is mitochondrial and used for the urea cycle) – Substrates are HCO3-, glutamine (not NH4+), 2 ATP – In mammals, CPS-II can be viewed as the committed step in pyrimidine synthesis – Bacteria have but one CP ...
BIO 322_Rec_4part1_Spring 2013
... • Fatty acyl-CoAs are high energy compounds – hydrolysis to free FA + acetyl CoA ∆G’º= -31kj/mol •Formation of FA-CoA is made favorable by the hydrolysis of two high energy bonds in ATP. Pyrophosphate hydrolized by inorganic phosphatase ...
... • Fatty acyl-CoAs are high energy compounds – hydrolysis to free FA + acetyl CoA ∆G’º= -31kj/mol •Formation of FA-CoA is made favorable by the hydrolysis of two high energy bonds in ATP. Pyrophosphate hydrolized by inorganic phosphatase ...
Ocimum sanctum Induced hepatic damage R.Bhuvaneswari Dr.K.Jegatheesan
... Toxicity of chemicals majorly affects all kinds of plants and animals. Excess of any kind of compounds will be harmful to life [1].Liver plays a major role in detoxification and is generally the major site for intense metabolism[2].It is also a site of biotransformation, of toxic compounds were conv ...
... Toxicity of chemicals majorly affects all kinds of plants and animals. Excess of any kind of compounds will be harmful to life [1].Liver plays a major role in detoxification and is generally the major site for intense metabolism[2].It is also a site of biotransformation, of toxic compounds were conv ...
R-lipoic acid inhibits mammalian pyruvate
... Aging is the single largest risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, which in turn are the leading cause of death of individuals over the age of 65 years. In part, this risk is due to a profound loss of vasomotor function of the major conduit arteries, primarily because of lower levels of endothelia ...
... Aging is the single largest risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, which in turn are the leading cause of death of individuals over the age of 65 years. In part, this risk is due to a profound loss of vasomotor function of the major conduit arteries, primarily because of lower levels of endothelia ...
Other Pathways of Carbohydrate Metabolism Gluconeogenesis
... The Glyoxylate Pathway In plants, acetyl-CoA can be converted to oxaloacetate 2Acetyl-CoA + 2NAD+ + FAD → oxaloacetate + 2CoA + 2NADH + FADH2 + 2H+ involves enzymes of mitochondrion and glyoxysome ...
... The Glyoxylate Pathway In plants, acetyl-CoA can be converted to oxaloacetate 2Acetyl-CoA + 2NAD+ + FAD → oxaloacetate + 2CoA + 2NADH + FADH2 + 2H+ involves enzymes of mitochondrion and glyoxysome ...
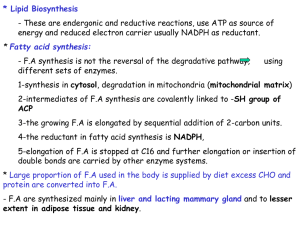
fatty acids synthesis
... donated by the original acetyl CoA, which are found at the methyl-group end of the fatty acid.] .The major fatty acid synthesized de novo is palmitic acid. Summary of fatty acid synthesis ...
... donated by the original acetyl CoA, which are found at the methyl-group end of the fatty acid.] .The major fatty acid synthesized de novo is palmitic acid. Summary of fatty acid synthesis ...
Fundamentals of Biochemistry. Life at the Molecular Level. 3rd Edition Brochure
... Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2242601/ ...
... Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2242601/ ...
Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
... Glucagon, a pancreatic hormone, signals low blood sugar and lowers the level of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate in the liver. This stimulates gluconeogenesis and the production of glucose. ...
... Glucagon, a pancreatic hormone, signals low blood sugar and lowers the level of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate in the liver. This stimulates gluconeogenesis and the production of glucose. ...
Lecture 35 - Lipid Metabolism 1
... Homemade soap is made from animal fat Soap is made from fatty acids through a process called saponification. Fatty acids are amphipathic molecules that break up grease by partitioning the fat and water into micelles. Saponification neutralizes the fatty acid carboxylate group with Na+, however, Mg2 ...
... Homemade soap is made from animal fat Soap is made from fatty acids through a process called saponification. Fatty acids are amphipathic molecules that break up grease by partitioning the fat and water into micelles. Saponification neutralizes the fatty acid carboxylate group with Na+, however, Mg2 ...
Cell-to-cell communication Transduction pathways
... •usually not bound to carrier protein •do not readily diffuse across membrane •bind to membrane receptor •H-R complex triggers production of 2nd messenger cAMP, cGMP (cyclic nucleotide monophosphates) IP3 (inositol phospholipids) Ca2+ ions •rapid, short-lived responses; usually metabolic ...
... •usually not bound to carrier protein •do not readily diffuse across membrane •bind to membrane receptor •H-R complex triggers production of 2nd messenger cAMP, cGMP (cyclic nucleotide monophosphates) IP3 (inositol phospholipids) Ca2+ ions •rapid, short-lived responses; usually metabolic ...
Lipid signaling

Lipid signaling, broadly defined, refers to any biological signaling event involving a lipid messenger that binds a protein target, such as a receptor, kinase or phosphatase, which in turn mediate the effects of these lipids on specific cellular responses. Lipid signaling is thought to be qualitatively different from other classical signaling paradigms (such as monoamine neurotransmission) because lipids can freely diffuse through membranes (see osmosis.) One consequence of this is that lipid messengers cannot be stored in vesicles prior to release and so are often biosynthesized ""on demand"" at their intended site of action. As such, many lipid signaling molecules cannot circulate freely in solution but, rather, exist bound to special carrier proteins in serum.