Agonism with the omega-3 fatty acids α-linolenic acid
... Forty-eight hours following transfection with FLAG-GPR120-S or FLAG-GPR120-L, HEK293 cells were washed three times in ice cold PBS and lysed at 4 °C in RIPA buffer (50 mM Tris–HCl, 150 mM NaCl, 5 mM EDTA, 1% Nonidet P-40, 0.5% sodium deoxycholate, 0.1% SDS, 10 mM NaF, 10 mM Na2HPO4, pH 7.4) plus pro ...
... Forty-eight hours following transfection with FLAG-GPR120-S or FLAG-GPR120-L, HEK293 cells were washed three times in ice cold PBS and lysed at 4 °C in RIPA buffer (50 mM Tris–HCl, 150 mM NaCl, 5 mM EDTA, 1% Nonidet P-40, 0.5% sodium deoxycholate, 0.1% SDS, 10 mM NaF, 10 mM Na2HPO4, pH 7.4) plus pro ...
Classification and substrate head-group specificity of membrane
... clusters are formed (Fig. 3). The largest cluster consists of acyl-CoA specific Δ9 FDs (FD-A). The only other cluster that contains experimentally characterized desaturases is the FD-C cluster, which contain the characterized bi-functional acyl-lipid-specific Arabidopsis thaliana Δ7/Δ9 desaturases (AD ...
... clusters are formed (Fig. 3). The largest cluster consists of acyl-CoA specific Δ9 FDs (FD-A). The only other cluster that contains experimentally characterized desaturases is the FD-C cluster, which contain the characterized bi-functional acyl-lipid-specific Arabidopsis thaliana Δ7/Δ9 desaturases (AD ...
Transmitter Release
... Transmitter is released in individual “bundles” of about 5,000-10,000 molecules These “transmitter bundles” are stored in organelles called synaptic vesicles The unit synaptic potential results from release of the contents of a single synaptic vesicle Transmitter is “sucked into” vesicles by an acti ...
... Transmitter is released in individual “bundles” of about 5,000-10,000 molecules These “transmitter bundles” are stored in organelles called synaptic vesicles The unit synaptic potential results from release of the contents of a single synaptic vesicle Transmitter is “sucked into” vesicles by an acti ...
Short transmembrane domains with high
... Fig. 1. Geometric features of TMDs in metazoan type II Golgi and plasma membrane proteins. (A) Average volume of amino acids of Type II Golgi and plasma membrane protein TMDs. Values are mean 6 2 s.e.m. calculated in a window of five amino acids at each position in the TMD for all proteins in the da ...
... Fig. 1. Geometric features of TMDs in metazoan type II Golgi and plasma membrane proteins. (A) Average volume of amino acids of Type II Golgi and plasma membrane protein TMDs. Values are mean 6 2 s.e.m. calculated in a window of five amino acids at each position in the TMD for all proteins in the da ...
Dinazyme C/S
... Involves movement of electrons from one molecule to another. In biological systems we usually see the removal of hydrogen from the substrate. Enzymes in this class are called dehydrogenases. Ex., alcohol dehydrogen-ase catalyzes reactions of the type R-CH2OH + A → R-CHO + H2A, where A is an acceptor ...
... Involves movement of electrons from one molecule to another. In biological systems we usually see the removal of hydrogen from the substrate. Enzymes in this class are called dehydrogenases. Ex., alcohol dehydrogen-ase catalyzes reactions of the type R-CH2OH + A → R-CHO + H2A, where A is an acceptor ...
The Carboxyl-Terminal Region of Protein C Is
... and 380, which is immediately before the frameshift mutation. Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells stably transfected with the different constructs were pulse-labeled with [35 S]Met and chased for up to 6 hours. None of the truncated variants were efficiently secreted from CHO cells (Fig 2A). The prote ...
... and 380, which is immediately before the frameshift mutation. Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells stably transfected with the different constructs were pulse-labeled with [35 S]Met and chased for up to 6 hours. None of the truncated variants were efficiently secreted from CHO cells (Fig 2A). The prote ...
Regulation of carbohydrate metabolism
... 2. conversion of glucose to triacylglycerols in liver and adipose tissue (lipogenesis) ...
... 2. conversion of glucose to triacylglycerols in liver and adipose tissue (lipogenesis) ...
Full_ppt_ch21
... – A product of a reaction acts as a negative regulator – An end product binds with the first enzyme in a sequence when sufficient product is present ...
... – A product of a reaction acts as a negative regulator – An end product binds with the first enzyme in a sequence when sufficient product is present ...
Regulation of secondary metabolism in fungi
... It should also be noted that the onset of patulin—forming enzymes by P. urticae can be delayed for hours by provision of too great a concentration of nitrogen source (2). ...
... It should also be noted that the onset of patulin—forming enzymes by P. urticae can be delayed for hours by provision of too great a concentration of nitrogen source (2). ...
Intermediary Metabolism of Carbohydrate, Protein, and Fat
... The further metabolism of glucose 6-phosphate in the glycolytic pathway begins with its conversion to fructose 6-phosphate by phosphoglucose isomerase (Fig. 1). Phosphofructokinase then catalyzes the phosphorylation of fructose 6-phosphate to fructose 1,6-bisphosphate. Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate is c ...
... The further metabolism of glucose 6-phosphate in the glycolytic pathway begins with its conversion to fructose 6-phosphate by phosphoglucose isomerase (Fig. 1). Phosphofructokinase then catalyzes the phosphorylation of fructose 6-phosphate to fructose 1,6-bisphosphate. Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate is c ...
Catalogue Code: BA0125 Pack Size: 400 assays
... the high-energy donor molecule ATP, to their specific substrates. Kinases are known to regulate the majority of cellular processes. The largest group of this family is the protein kinases. So far, 518 different kinases have been identified in humans and up to 30% of human proteins are modified by th ...
... the high-energy donor molecule ATP, to their specific substrates. Kinases are known to regulate the majority of cellular processes. The largest group of this family is the protein kinases. So far, 518 different kinases have been identified in humans and up to 30% of human proteins are modified by th ...
Enzymes lII: Clinical Applications
... because the mitochondrial isoenzyme of AST is released in addition to the corresponding cytoplasmic isoenzyme. The amount of enzyme released into the plasma from an injured tissue is usually much greater than can be accounted for on the basis of tissue enzyme concentration and magnitude of injury. L ...
... because the mitochondrial isoenzyme of AST is released in addition to the corresponding cytoplasmic isoenzyme. The amount of enzyme released into the plasma from an injured tissue is usually much greater than can be accounted for on the basis of tissue enzyme concentration and magnitude of injury. L ...
Fatty Acid Synthesis
... Acetate is subsequently transferred to a cysteine thiol of the Condensing Enzyme domain. ...
... Acetate is subsequently transferred to a cysteine thiol of the Condensing Enzyme domain. ...
MOA slides - Epilepsy
... In receptor function studies1 • Perampanel inhibits function of AMPA receptors at concentrations that have no effect on NMDA receptor function Effect on AMPA receptor function 50% inhibition at 93 nMa ...
... In receptor function studies1 • Perampanel inhibits function of AMPA receptors at concentrations that have no effect on NMDA receptor function Effect on AMPA receptor function 50% inhibition at 93 nMa ...
The Binding Site for the @r Subunits of Heterotrimeric G Proteins on
... observed using GST-PARKfusion proteins,and we have FIG. 1. Analysis of BARK1 carboxyl-terminal truncations. reported previously (15) that Py specifically binds toPARK1 within thelarge carboxylthird of the enzyme. Using the GSTa, schematic representation of wild-type PARK1 (construct I ) and six carb ...
... observed using GST-PARKfusion proteins,and we have FIG. 1. Analysis of BARK1 carboxyl-terminal truncations. reported previously (15) that Py specifically binds toPARK1 within thelarge carboxylthird of the enzyme. Using the GSTa, schematic representation of wild-type PARK1 (construct I ) and six carb ...
Biochimie
... DAG:DAG transacylase (DGTA) utilize diacylglycerol (DAG), a central lipid intermediate, for direct incorporation into the TAG molecule. The candidate genes for PDAT are identifiable in some algal genomes; as for DGTA, no gene candidates have been identified in either higher plants or algae. The TAG as ...
... DAG:DAG transacylase (DGTA) utilize diacylglycerol (DAG), a central lipid intermediate, for direct incorporation into the TAG molecule. The candidate genes for PDAT are identifiable in some algal genomes; as for DGTA, no gene candidates have been identified in either higher plants or algae. The TAG as ...
17. Amino acids are precursors of many specialized biomolecules
... feedback inhibition (no covalent modifications yet revealed). • Deoxyribonucleotides are derived from ribonucleotides at the NDP level, with the catalysis of ribonucleotide reductase, which contains a chain of electron carriers, uses free radicals, and being regulated for both substrate specificity ...
... feedback inhibition (no covalent modifications yet revealed). • Deoxyribonucleotides are derived from ribonucleotides at the NDP level, with the catalysis of ribonucleotide reductase, which contains a chain of electron carriers, uses free radicals, and being regulated for both substrate specificity ...
Malonyl-CoA: the regulator of fatty acid synthesis and oxidation
... In the catabolic state with no food intake, the liver generates ketones by breaking down fatty acids. During the nocturnal fast or longer starvation periods, this protects the brain, which cannot oxidize fatty acids. In 1977, we published a study in the JCI noting the surprising realization that mal ...
... In the catabolic state with no food intake, the liver generates ketones by breaking down fatty acids. During the nocturnal fast or longer starvation periods, this protects the brain, which cannot oxidize fatty acids. In 1977, we published a study in the JCI noting the surprising realization that mal ...
Lipids and Carbohydrates
... carbonyl group (a carbon double bonded to oxygen), and the spatial arrangement of atoms around the carbons. Sugars naturally favor the form of carbon rings but are often portrayed in diagrams in the linear form for comparison. The most common carbohydrate sugar is glucose, a molecule used for energy ...
... carbonyl group (a carbon double bonded to oxygen), and the spatial arrangement of atoms around the carbons. Sugars naturally favor the form of carbon rings but are often portrayed in diagrams in the linear form for comparison. The most common carbohydrate sugar is glucose, a molecule used for energy ...
AMINOACID METABOLISM
... MECHANISM – Transfer of aminogroup to PLP. Transfer of amino group from Pyridoxamine phosphate to keto acid ...
... MECHANISM – Transfer of aminogroup to PLP. Transfer of amino group from Pyridoxamine phosphate to keto acid ...
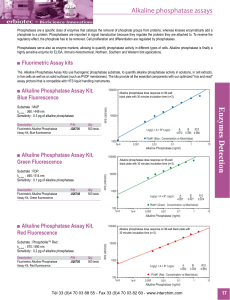
Enzymes Detection
... system can be used directly to screen for drugs that alter cellular metabolism involving FFA or that alter the behavior of enzymes that either produce or use FFA. ADIFAB2 is a high affinity version of the original ADIFAB probe. It is formed by acrylodan labeling the Leu72 to Ala mutant of the Intest ...
... system can be used directly to screen for drugs that alter cellular metabolism involving FFA or that alter the behavior of enzymes that either produce or use FFA. ADIFAB2 is a high affinity version of the original ADIFAB probe. It is formed by acrylodan labeling the Leu72 to Ala mutant of the Intest ...
Biomarkery a mechanismy toxicity
... MFO: principle enzymes: cytochromes P450 (CYPs) - haem-containing enzymes (superfamily of more than 150 genes) - several classes and subclasses (different substrate specificity; structure ...) Cytochrome P450 1A (CYP1A) – basic for detoxification of hydrophobic environmental contaminants Cytochrome ...
... MFO: principle enzymes: cytochromes P450 (CYPs) - haem-containing enzymes (superfamily of more than 150 genes) - several classes and subclasses (different substrate specificity; structure ...) Cytochrome P450 1A (CYP1A) – basic for detoxification of hydrophobic environmental contaminants Cytochrome ...
MIBCB Syllabus
... The course will be mainly through correspondence. Students will be sent the study material of each topic by email (or CD) every 21 days, and the students will send back the answers back. The answers are assessed. There will be some virtual classes; one professor will take a class on a particular top ...
... The course will be mainly through correspondence. Students will be sent the study material of each topic by email (or CD) every 21 days, and the students will send back the answers back. The answers are assessed. There will be some virtual classes; one professor will take a class on a particular top ...
Lipid signaling

Lipid signaling, broadly defined, refers to any biological signaling event involving a lipid messenger that binds a protein target, such as a receptor, kinase or phosphatase, which in turn mediate the effects of these lipids on specific cellular responses. Lipid signaling is thought to be qualitatively different from other classical signaling paradigms (such as monoamine neurotransmission) because lipids can freely diffuse through membranes (see osmosis.) One consequence of this is that lipid messengers cannot be stored in vesicles prior to release and so are often biosynthesized ""on demand"" at their intended site of action. As such, many lipid signaling molecules cannot circulate freely in solution but, rather, exist bound to special carrier proteins in serum.