Powerpoint version
... protein fibers are interwoven in this matrix: collagen, elastin, fibronectin. Secreted by cells Desmosomes – “Rivets” to anchor adjacent cells that are not touching ...
... protein fibers are interwoven in this matrix: collagen, elastin, fibronectin. Secreted by cells Desmosomes – “Rivets” to anchor adjacent cells that are not touching ...
Tissue- Collection of cells working together to perform a function
... Gastric juice (water, enzymes, HCl) chemically digests food. Pepsin begins the break down of protein into amino acids. Mucus is secreted by stomach cells to protect cells from gastric juice. ...
... Gastric juice (water, enzymes, HCl) chemically digests food. Pepsin begins the break down of protein into amino acids. Mucus is secreted by stomach cells to protect cells from gastric juice. ...
Multiple Choice: Choose the one best answer to each question
... d) All of above have hydroxyls and are good targets IF the kinase is specific for that protein and residue 25) a) True/b) False: All living cells have a membrane potential (mV) but only excitable cells can create and send action potentials down their length. 26) a) True/b) False: All cells have sili ...
... d) All of above have hydroxyls and are good targets IF the kinase is specific for that protein and residue 25) a) True/b) False: All living cells have a membrane potential (mV) but only excitable cells can create and send action potentials down their length. 26) a) True/b) False: All cells have sili ...
BHS 150.2 Biochemistry Date: 02/08/13, 1st hour Notetaker: Laurel
... Q1: Receptor mechanism of action for glucagon and insulin. Know mechanisms for final exam. Q2: Think about glycogen synthetase, glycogen phosphatase, pyruvate kinase, and the effects of high levels of insulin. Insulin activates a phosphatase, which removes a phosphate group. Activates things to stor ...
... Q1: Receptor mechanism of action for glucagon and insulin. Know mechanisms for final exam. Q2: Think about glycogen synthetase, glycogen phosphatase, pyruvate kinase, and the effects of high levels of insulin. Insulin activates a phosphatase, which removes a phosphate group. Activates things to stor ...
Review F14
... 14. Draw the process of exocytosis. 15. What is the difference between and permeable and semi permeable membrane? What kind is a cell membrane? 16. Why is it dangerous to have a really high fever? 17. What do plants need to accomplish photosynthesis? Draw a diagram showing how plants get the needed ...
... 14. Draw the process of exocytosis. 15. What is the difference between and permeable and semi permeable membrane? What kind is a cell membrane? 16. Why is it dangerous to have a really high fever? 17. What do plants need to accomplish photosynthesis? Draw a diagram showing how plants get the needed ...
Cell Transport notes
... A solute moves through the interior of a protein ( facilitated diffusion) It is a two-way transport The net direction of movement at a given time depends on how many molecules or ions of the solute are making random contact with vacant binding sites in those proteins ...
... A solute moves through the interior of a protein ( facilitated diffusion) It is a two-way transport The net direction of movement at a given time depends on how many molecules or ions of the solute are making random contact with vacant binding sites in those proteins ...
BIOMOLECULES UNIT 3 Chemistry Review: Atoms
... Made of amino acids containing carbon, nitrogen, hydrogen, oxygen, sulfur. Have 4 covalent bonds, and one variable “R” group. Protein structures are 3 dimensional, and their folding patterns are unique. Denaturing a protein destroys its pattern and its ability to function properly. EX: snake venom- ...
... Made of amino acids containing carbon, nitrogen, hydrogen, oxygen, sulfur. Have 4 covalent bonds, and one variable “R” group. Protein structures are 3 dimensional, and their folding patterns are unique. Denaturing a protein destroys its pattern and its ability to function properly. EX: snake venom- ...
Multiple Choice: Choose the one best answer to each question
... d) All of above have hydroxyls and are good targets IF the kinase is specific for that protein and residue 25) a) True/b) False: All living cells have a membrane potential (mV) but only excitable cells can create and send action potentials down their length. 26) a) Trueb) Fa/lse: All cells have sili ...
... d) All of above have hydroxyls and are good targets IF the kinase is specific for that protein and residue 25) a) True/b) False: All living cells have a membrane potential (mV) but only excitable cells can create and send action potentials down their length. 26) a) Trueb) Fa/lse: All cells have sili ...
Control of cellular homeostasis: organelles take
... in the regulation of cellular metal levels and suggest novel therapeutic avenues in Wilson’s disease, a liver disease that stems from mutational inactivation of ATP7B. ...
... in the regulation of cellular metal levels and suggest novel therapeutic avenues in Wilson’s disease, a liver disease that stems from mutational inactivation of ATP7B. ...
Document
... Cell surface receptors: G protein coupled; ion-channel linked; receptor tyrosine kinase linked; receptors with intrinsic enzymatic activity Second messengers: inside the cell—effector molecules of cell signaling Signaling: protein kinases; GTP-binding proteins with GTPase activity can function as mo ...
... Cell surface receptors: G protein coupled; ion-channel linked; receptor tyrosine kinase linked; receptors with intrinsic enzymatic activity Second messengers: inside the cell—effector molecules of cell signaling Signaling: protein kinases; GTP-binding proteins with GTPase activity can function as mo ...
Synthetic bile acid derivatives induce apoptosis through a c
... Recently, we have reported that a synthetic derivative of ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA), HS1183, and those of chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA), HS-1199 and HS-1200, induced apoptosis in human breast carcinoma cells through a p53-independent pathway. Here, we present that the synthetic bile acid derivative ...
... Recently, we have reported that a synthetic derivative of ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA), HS1183, and those of chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA), HS-1199 and HS-1200, induced apoptosis in human breast carcinoma cells through a p53-independent pathway. Here, we present that the synthetic bile acid derivative ...
Hepatocyte growth factor receptor B-2837-3_2
... Receptor tyrosine kinase that transduces signals from the extracellular matrix into the cytoplasm by binding to hepatocyte growth factor/HGF ligand. Regulates many physiological processes including proliferation, scattering, morphogenesis and survival. Ligand binding at the cell surface induces a ...
... Receptor tyrosine kinase that transduces signals from the extracellular matrix into the cytoplasm by binding to hepatocyte growth factor/HGF ligand. Regulates many physiological processes including proliferation, scattering, morphogenesis and survival. Ligand binding at the cell surface induces a ...
Bio 201, Fall 2010 Test 3 Study Guide Questions to be able to
... 3. What is pectin, what are its chemical properties and how do they contribute to the function of the middle lamella? 4. Why are there cations in the middle lamella? 5. Why do fruits and vegetables get mushy? 6. What is the series of connections between the molecules involved in the extracellular ma ...
... 3. What is pectin, what are its chemical properties and how do they contribute to the function of the middle lamella? 4. Why are there cations in the middle lamella? 5. Why do fruits and vegetables get mushy? 6. What is the series of connections between the molecules involved in the extracellular ma ...
Assist.lec. Rafah Saleem Mitochondrion:: In cell biology, a
... most of the cell's supply of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), used as a source of chemical energy. Mitochondria have been implicated in several human diseases, including mitochondrial disorders and cardiac dysfunction, and may play a role in the aging process. ...
... most of the cell's supply of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), used as a source of chemical energy. Mitochondria have been implicated in several human diseases, including mitochondrial disorders and cardiac dysfunction, and may play a role in the aging process. ...
幻灯片 1
... •Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) Covered with ribosomes (causing the "rough" appearance) which are in the process of synthesizing proteins for secretion or localization in membranes. ...
... •Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) Covered with ribosomes (causing the "rough" appearance) which are in the process of synthesizing proteins for secretion or localization in membranes. ...
STAAR Review 1
... with one phosphate group, is formed. c. Energy is released, which can be used by the cell. d. Energy is lost in the process. ...
... with one phosphate group, is formed. c. Energy is released, which can be used by the cell. d. Energy is lost in the process. ...
11 Signal Transduction
... • Each TK adds a phosphate from an ATP to a tyrosine on the tail of the other polypeptide • The receptor is fully activated as a result ...
... • Each TK adds a phosphate from an ATP to a tyrosine on the tail of the other polypeptide • The receptor is fully activated as a result ...
Cell Structures and Their Functions - GCG-42
... Their membranes fuse with the cell membrane and release contents to the exterior of the cell ...
... Their membranes fuse with the cell membrane and release contents to the exterior of the cell ...
Biochemistry Chapter 11 [10-2-13].
... b. also has intracellular domain for signal transd. 2. when ligand bindscauses conformational change 3. polar molecules-cannot diffuse across membrane 4. pathway of signal transd. Has 2 major effects: a. rapid effects on ion levels or activation/inhibition of enzymes b. slower changes in the rate o ...
... b. also has intracellular domain for signal transd. 2. when ligand bindscauses conformational change 3. polar molecules-cannot diffuse across membrane 4. pathway of signal transd. Has 2 major effects: a. rapid effects on ion levels or activation/inhibition of enzymes b. slower changes in the rate o ...
Endocrine System: Overview
... Most physiological systems are located in specific locations in the body. The endocrine system does not fit this description. Explain why not. ...
... Most physiological systems are located in specific locations in the body. The endocrine system does not fit this description. Explain why not. ...
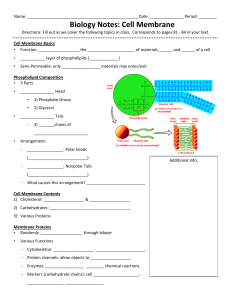
Biology Notes: Cell Membrane
... - Cytoskeleton: __________________ ______________________ - Protein channels: allow objects to __________________ - Enzymes: _________________ ________ chemical reactions - Markers (carbohydrate chains): cell ____________________; ________________ _________________ ...
... - Cytoskeleton: __________________ ______________________ - Protein channels: allow objects to __________________ - Enzymes: _________________ ________ chemical reactions - Markers (carbohydrate chains): cell ____________________; ________________ _________________ ...
asdfs
... line up with their hydrophillic heads to the outside and their hydrophobic tails toward the center bilayer ...
... line up with their hydrophillic heads to the outside and their hydrophobic tails toward the center bilayer ...
Lipid signaling

Lipid signaling, broadly defined, refers to any biological signaling event involving a lipid messenger that binds a protein target, such as a receptor, kinase or phosphatase, which in turn mediate the effects of these lipids on specific cellular responses. Lipid signaling is thought to be qualitatively different from other classical signaling paradigms (such as monoamine neurotransmission) because lipids can freely diffuse through membranes (see osmosis.) One consequence of this is that lipid messengers cannot be stored in vesicles prior to release and so are often biosynthesized ""on demand"" at their intended site of action. As such, many lipid signaling molecules cannot circulate freely in solution but, rather, exist bound to special carrier proteins in serum.


















![Biochemistry Chapter 11 [10-2-13].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001491986_1-28945f6beadb86fb208c56f0103a35db-300x300.png)