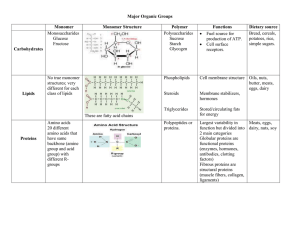
Biochemistry Learning Targets and Essential Vocabulary name describe
... Biochemistry Learning Targets and Essential Vocabulary ...
... Biochemistry Learning Targets and Essential Vocabulary ...
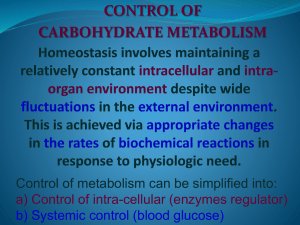
Control of intra-cellular (enzyme regulator)
... The ideal enzyme for regulatory intervention is one whose quantity or catalytic efficiency dictates that the reaction it catalyzes is slow relative to all others in the pathway ...
... The ideal enzyme for regulatory intervention is one whose quantity or catalytic efficiency dictates that the reaction it catalyzes is slow relative to all others in the pathway ...
Key: Biomolecule Study Guide 1) In animals, excess carbohydrates
... They must fit the molecules that they interact with (Lock and Key) 10) What does it mean to say an enzyme is “denatured”? It has changed its 3-D shape 11) What are 2 ways to denature an enzyme? Change the temperature or pH ...
... They must fit the molecules that they interact with (Lock and Key) 10) What does it mean to say an enzyme is “denatured”? It has changed its 3-D shape 11) What are 2 ways to denature an enzyme? Change the temperature or pH ...
邵吉民_Signal_and_dis
... desensitization: decreased response to ligand stimulation up regulation: increase in number of receptors hypersensitivity: increased response to ligand stimulation, or self-activation without ligands ...
... desensitization: decreased response to ligand stimulation up regulation: increase in number of receptors hypersensitivity: increased response to ligand stimulation, or self-activation without ligands ...
Learning Objectives Chapter 10
... Requires a carrier protein in the membrane. The protein undergoes a conformational change that allows molecule to be released on the other side: like enzymes, exhibits saturation kinetics. Example: glucose transporters, which are acted upon by insulin 10. What is a gated channel, examples? Transmemb ...
... Requires a carrier protein in the membrane. The protein undergoes a conformational change that allows molecule to be released on the other side: like enzymes, exhibits saturation kinetics. Example: glucose transporters, which are acted upon by insulin 10. What is a gated channel, examples? Transmemb ...
Practice Questions
... In the experiment in which heterokaryons were made by fusing mouse and human cells, (1) what happened to the mouse and human membrane proteins after several hours and (2) what property of membranes did this demonstrate? 1) They intermixed and became homogeneous around the membrane 2) That they were ...
... In the experiment in which heterokaryons were made by fusing mouse and human cells, (1) what happened to the mouse and human membrane proteins after several hours and (2) what property of membranes did this demonstrate? 1) They intermixed and became homogeneous around the membrane 2) That they were ...
Intracellular signalling
... FIGURE 15.10. The PDGF receptor, like other growth factor receptors, activates the GTPase Ras and therefore the MAP kinase cascade. ...
... FIGURE 15.10. The PDGF receptor, like other growth factor receptors, activates the GTPase Ras and therefore the MAP kinase cascade. ...
PowerPoint 簡報
... potentially regulating intracellular signaling. In addition to engaging in proteinprotein interactions, several PDZ domains including those of syntenin, CASK, Tiam1 and FAP are capable of binding to the phosphoinositide PIP2. PIP2-PDZ domain binding is thought to control the association of PDZ domai ...
... potentially regulating intracellular signaling. In addition to engaging in proteinprotein interactions, several PDZ domains including those of syntenin, CASK, Tiam1 and FAP are capable of binding to the phosphoinositide PIP2. PIP2-PDZ domain binding is thought to control the association of PDZ domai ...
TYPES OF RECEPTORS
... Receptors that are kinases or bind kinases: When a signaling chemical binds to the membrane receptor protein on the outside of the cell, this triggers a change in the 3D conformation of that protein, which in turn, triggers a chemical reaction on the inside of the cell. ...
... Receptors that are kinases or bind kinases: When a signaling chemical binds to the membrane receptor protein on the outside of the cell, this triggers a change in the 3D conformation of that protein, which in turn, triggers a chemical reaction on the inside of the cell. ...
1 Which of the following are the smallest cells? A) human ovum B
... 23 The following molecules freely pass through a cell membrane except which one? A) ...
... 23 The following molecules freely pass through a cell membrane except which one? A) ...
Product: Cat. No.: Lot No.: Synonyms: Size: Storage: Usage: Product
... growth factor (HGF), platelet derived growth factor (PDGF), and c-Kit receptors. Also known as Ruk (regulator of ubiquitous kinase) and SETA (SH3 domain-containing gene expressed in tumorigenic astrocytes), CIN85 is an ubiquitously expressed adaptor protein with three SH3 domains. It interacts with ...
... growth factor (HGF), platelet derived growth factor (PDGF), and c-Kit receptors. Also known as Ruk (regulator of ubiquitous kinase) and SETA (SH3 domain-containing gene expressed in tumorigenic astrocytes), CIN85 is an ubiquitously expressed adaptor protein with three SH3 domains. It interacts with ...
The ins and outs of sphingolipid synthesis
... Subsequent to its formation by 3KSR, sphinganine can either be acylated by dihydroceramide synthase (DHCerS, see Reaction vi below), or phosphorylated by sphingosine kinase (SK) to form sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P), an important bioactive lipid mediator [16]. SKs were originally identified in yeast ...
... Subsequent to its formation by 3KSR, sphinganine can either be acylated by dihydroceramide synthase (DHCerS, see Reaction vi below), or phosphorylated by sphingosine kinase (SK) to form sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P), an important bioactive lipid mediator [16]. SKs were originally identified in yeast ...
Nanodevices
... the cell membrane. Enclosed within these proteins are transmembrane conduction pores which selectively allow transfer of specific ions down their concentration gradients at a rate at > 10-fold greater free diffusion in solution. 2. Access to the conducting pore can be open or closed (channel gating) ...
... the cell membrane. Enclosed within these proteins are transmembrane conduction pores which selectively allow transfer of specific ions down their concentration gradients at a rate at > 10-fold greater free diffusion in solution. 2. Access to the conducting pore can be open or closed (channel gating) ...
cell signalling
... What are receptors? Receptors are proteins and modified proteins (such as lipoproteins and glycoproteins) on the cell surface membrane (part of the glycocalyx) that respond to a specific signal and have a complementary shape to the signal ...
... What are receptors? Receptors are proteins and modified proteins (such as lipoproteins and glycoproteins) on the cell surface membrane (part of the glycocalyx) that respond to a specific signal and have a complementary shape to the signal ...
protein - Hagan Bayley
... Figures mainly from Bruce Alberts et al. “Molecular Biology of the Cell” Also a good text for organelles ...
... Figures mainly from Bruce Alberts et al. “Molecular Biology of the Cell” Also a good text for organelles ...
Cell Communication (Plan)
... • Small, nonprotein, water-soluble molecules or ions. • Rapidly diffuse throughout the cell. Two of the most important are cyclic AMP and Ca2+. Others DAG & IP3 (membrane-derived ) ...
... • Small, nonprotein, water-soluble molecules or ions. • Rapidly diffuse throughout the cell. Two of the most important are cyclic AMP and Ca2+. Others DAG & IP3 (membrane-derived ) ...
The complex life of simple sphingolipids
... phytosphingosine) to which a fatty acid is attached by an amide bond to carbon 2 (Fig 1). The simplest sphingolipid, ceramide (Merrill, 2002), functions both as a key player in cell signalling and as the precursor of more complex sphingolipids. In contrast to complex sphingolipids, which contain a h ...
... phytosphingosine) to which a fatty acid is attached by an amide bond to carbon 2 (Fig 1). The simplest sphingolipid, ceramide (Merrill, 2002), functions both as a key player in cell signalling and as the precursor of more complex sphingolipids. In contrast to complex sphingolipids, which contain a h ...
A mutant defective in enzyme
... 1. Muscle protein responds to conditions such as starvation, trauma, burns and septicemia, by undergoing massive degradation. Of the amino acids released, most important as a source of fuel are branched-chain amino acids? What are they? (3 %)What enzyme involved in the first step in their degradatio ...
... 1. Muscle protein responds to conditions such as starvation, trauma, burns and septicemia, by undergoing massive degradation. Of the amino acids released, most important as a source of fuel are branched-chain amino acids? What are they? (3 %)What enzyme involved in the first step in their degradatio ...
050907
... • When the hormone vasopressin stimulates cleavage of phosphatidylinositol 4,5bisphosphate by hormone-sensitive phospholipase C, two products are formed. What are they? Solubility? ...
... • When the hormone vasopressin stimulates cleavage of phosphatidylinositol 4,5bisphosphate by hormone-sensitive phospholipase C, two products are formed. What are they? Solubility? ...
plasmodium protein kinases: from database mining to the search for
... that no malarial PK clustered with the tyrosine kinase (TK) group; and (iv) that no members of the dualspecificity protein kinase (MAPKK) family (a subgroup of the STE group) are present in the P. falciparum genome. In addition, a novel, apparently Plasmodium-specific family of 18 genes encoding pro ...
... that no malarial PK clustered with the tyrosine kinase (TK) group; and (iv) that no members of the dualspecificity protein kinase (MAPKK) family (a subgroup of the STE group) are present in the P. falciparum genome. In addition, a novel, apparently Plasmodium-specific family of 18 genes encoding pro ...
Document
... • Insulin, glucagon, grehlin, leptin etc control glucose, lipids and metabolism • The renin-angiotensin/aldosterone system controls blood pressure • Hormones control reproduction • And probably many other examples, which show the importance of hormones in normal life and development. ...
... • Insulin, glucagon, grehlin, leptin etc control glucose, lipids and metabolism • The renin-angiotensin/aldosterone system controls blood pressure • Hormones control reproduction • And probably many other examples, which show the importance of hormones in normal life and development. ...
BIOL 201: Cell Biology and Metabolism
... G-Alpha is in a GDP bound state. When it interacts with the activated receptors, it undergoes its own conformational change, kicking out GDP from the binding site o Activated receptor acts as a Guanine Exchange Factor This allows GTP to interact with G-Alpha. When GTP binds, the G-Protein falls apar ...
... G-Alpha is in a GDP bound state. When it interacts with the activated receptors, it undergoes its own conformational change, kicking out GDP from the binding site o Activated receptor acts as a Guanine Exchange Factor This allows GTP to interact with G-Alpha. When GTP binds, the G-Protein falls apar ...
Lipid signaling

Lipid signaling, broadly defined, refers to any biological signaling event involving a lipid messenger that binds a protein target, such as a receptor, kinase or phosphatase, which in turn mediate the effects of these lipids on specific cellular responses. Lipid signaling is thought to be qualitatively different from other classical signaling paradigms (such as monoamine neurotransmission) because lipids can freely diffuse through membranes (see osmosis.) One consequence of this is that lipid messengers cannot be stored in vesicles prior to release and so are often biosynthesized ""on demand"" at their intended site of action. As such, many lipid signaling molecules cannot circulate freely in solution but, rather, exist bound to special carrier proteins in serum.