Lecture 9: Cell signaling
... cortisol, calciferol (Vitamin D), and testosterone. Eicosinoids: derivatives of arachidonic acid including prostaglandins, leukotrienes, and thromboxanes B. Gasses: Nitric oxide (NO) and carbon monoxide ...
... cortisol, calciferol (Vitamin D), and testosterone. Eicosinoids: derivatives of arachidonic acid including prostaglandins, leukotrienes, and thromboxanes B. Gasses: Nitric oxide (NO) and carbon monoxide ...
BIO 330 Cell Biology Lecture Outline Spring 2011 Chapter 14
... Second messengers Signal transduction Membrane vs. intracellular receptors Peptide vs. hydrophobic ligands C. Binding between receptors and ligands Ligands bind their cognate receptors at the binding site Receptor is “occupied” when ligand is bound Amount of receptor binding is proportional to conce ...
... Second messengers Signal transduction Membrane vs. intracellular receptors Peptide vs. hydrophobic ligands C. Binding between receptors and ligands Ligands bind their cognate receptors at the binding site Receptor is “occupied” when ligand is bound Amount of receptor binding is proportional to conce ...
Endocrine System 1 - Napa Valley College
... - activation of G protein activates Phospholipase C enzyme in the cell membrane - phospholipase C cleaves a membrane phospholipid - forms 2 second messengers: diacylglycerol (DAG) inositol triphosphate (IP3) D. Stimulation of Hormone Secretion 1. neural - by neurons that synapse on endocrine cells 2 ...
... - activation of G protein activates Phospholipase C enzyme in the cell membrane - phospholipase C cleaves a membrane phospholipid - forms 2 second messengers: diacylglycerol (DAG) inositol triphosphate (IP3) D. Stimulation of Hormone Secretion 1. neural - by neurons that synapse on endocrine cells 2 ...
a. The three-step process by which an external signal is converted
... c. The IP3 pathway is a tyrosine kinase specific pathway. Signals are first received by tyrosine kinase and a dimer forms and is phosphorylated by ATP. This phosphorylation activates an enzyme, phospholipase C, which targets a phospholipid in the membrane and cleaves off a molecule of IP3. IP3 then ...
... c. The IP3 pathway is a tyrosine kinase specific pathway. Signals are first received by tyrosine kinase and a dimer forms and is phosphorylated by ATP. This phosphorylation activates an enzyme, phospholipase C, which targets a phospholipid in the membrane and cleaves off a molecule of IP3. IP3 then ...
1 OVERVIEW OF EXTRACELLULAR SIGNALING A. Steps of
... OVERVIEW OF EXTRACELLULAR SIGNALING A. Steps of extracellular communication 1. synthesis of signaling molecule 2. Release of signaling molecule 3. Transport of the signal to the target cell 4. Detection of the signal by a specific receptor protein 5. Change in cellular metabolism or gene expression ...
... OVERVIEW OF EXTRACELLULAR SIGNALING A. Steps of extracellular communication 1. synthesis of signaling molecule 2. Release of signaling molecule 3. Transport of the signal to the target cell 4. Detection of the signal by a specific receptor protein 5. Change in cellular metabolism or gene expression ...
Hormonal Control
... heart, eyes, muscles, digestive system to prepare body for “fight or flight” response ...
... heart, eyes, muscles, digestive system to prepare body for “fight or flight” response ...
Slide 1
... Contains enzymes that modify, sort, and package macromolecules to transport to other parts of the cell and especially for secretion ...
... Contains enzymes that modify, sort, and package macromolecules to transport to other parts of the cell and especially for secretion ...
Cell Communication II
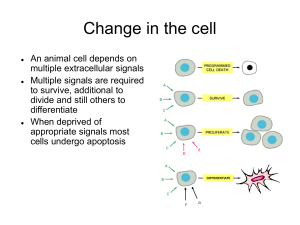
... An animal cell depends on extracellular signals to differentiate. Without extracellular signals the cell will die ...
... An animal cell depends on extracellular signals to differentiate. Without extracellular signals the cell will die ...
JAK/STAT signalling • Binding of cytokines (small protein ligands) to
... Only switched on in response to a signal (applies to signalling proteins and to genes) Enzymes that phosphorylate other proteins The idea that DNA makes RNA which makes protein An intermediate in sign ...
... Only switched on in response to a signal (applies to signalling proteins and to genes) Enzymes that phosphorylate other proteins The idea that DNA makes RNA which makes protein An intermediate in sign ...
CELL SIGNALLING
... Caffeine potentiates the action of cAMP by inhibiting its breakdown by phosphodiesterase ...
... Caffeine potentiates the action of cAMP by inhibiting its breakdown by phosphodiesterase ...
signal molecule
... (e.g. estrogen, vitamin D, thyroid hormone, retinoic acid) and bind to intracellular receptors The hormone-receptor complex has an exposed DNA binding site and can activate transcription directly (or, more typically as a homo- or hetero-dimer) This usually initiates a cascade of transcription events ...
... (e.g. estrogen, vitamin D, thyroid hormone, retinoic acid) and bind to intracellular receptors The hormone-receptor complex has an exposed DNA binding site and can activate transcription directly (or, more typically as a homo- or hetero-dimer) This usually initiates a cascade of transcription events ...
Cell Signaling Mechanisms
... Cells interact with their environment by interpreting extracellular signals via proteins that span their plasma membrane called receptors Receptors are comprised of extracellular and intracellular domains The extracellular domain relays information about the outside world to the intracellular ...
... Cells interact with their environment by interpreting extracellular signals via proteins that span their plasma membrane called receptors Receptors are comprised of extracellular and intracellular domains The extracellular domain relays information about the outside world to the intracellular ...
G-Protein Coupled Receptor
... signals from receptors target molecules Protein kinase: enzyme that phosphorylates and activates proteins at next level Phosphorylation cascade: enhance and amplify signal ...
... signals from receptors target molecules Protein kinase: enzyme that phosphorylates and activates proteins at next level Phosphorylation cascade: enhance and amplify signal ...
Essential Cell Biology
... cells respond with a normal biological response to the appropriate first messenger. In mutated cells, however, no response was evoked, because the cells lacked the G-protein. The function could be restored by G-protein derived from another tissue such as brain. ...
... cells respond with a normal biological response to the appropriate first messenger. In mutated cells, however, no response was evoked, because the cells lacked the G-protein. The function could be restored by G-protein derived from another tissue such as brain. ...
Document
... • Long-chain saturated fatty acids are found predominantly in the 1 position of phospholipids • the polyunsaturated acids (eg, the precursors of prostaglandins) are incorporated more into the 2 ...
... • Long-chain saturated fatty acids are found predominantly in the 1 position of phospholipids • the polyunsaturated acids (eg, the precursors of prostaglandins) are incorporated more into the 2 ...
Cell Communication Problem Set
... In a fight-or-flight response, epinephrine released by the adrenal glands binds to a membrane receptor on muscle cells. Which of the following events result from ligand binding? A. B. C. ...
... In a fight-or-flight response, epinephrine released by the adrenal glands binds to a membrane receptor on muscle cells. Which of the following events result from ligand binding? A. B. C. ...
How specific is ligand
... of the enzyme phospholipase C (amplifier enzyme). • Activated phospholipase C catalyzes the breakdown of a mb phospholipid to diacylglyerol and inositol triphosphate ...
... of the enzyme phospholipase C (amplifier enzyme). • Activated phospholipase C catalyzes the breakdown of a mb phospholipid to diacylglyerol and inositol triphosphate ...
Problem 5: Bacterial Cell Signaling
... A new drug, STI-571 or Gleevec specifically inhibits the Abl tyrosine kinase that is mutated in chronic myeloid leukemia. Treating patients with the drug dramatically improves survival, but people with a "blast crisis" form of the cancer begin to develop resistance. Which of the following statements ...
... A new drug, STI-571 or Gleevec specifically inhibits the Abl tyrosine kinase that is mutated in chronic myeloid leukemia. Treating patients with the drug dramatically improves survival, but people with a "blast crisis" form of the cancer begin to develop resistance. Which of the following statements ...
Slide 1
... • Sphingosine can be phosphorylated by sphingosine kinases, ubiquitous enzymes in the cytosol, ER and nucleus to make sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P). • Sphingosine-1-phosphate, a lysophospholipid, acts as a potent messenger molecule that operates both intra- and inter-cellularly. • Within the cell, i ...
... • Sphingosine can be phosphorylated by sphingosine kinases, ubiquitous enzymes in the cytosol, ER and nucleus to make sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P). • Sphingosine-1-phosphate, a lysophospholipid, acts as a potent messenger molecule that operates both intra- and inter-cellularly. • Within the cell, i ...
Lipid signaling

Lipid signaling, broadly defined, refers to any biological signaling event involving a lipid messenger that binds a protein target, such as a receptor, kinase or phosphatase, which in turn mediate the effects of these lipids on specific cellular responses. Lipid signaling is thought to be qualitatively different from other classical signaling paradigms (such as monoamine neurotransmission) because lipids can freely diffuse through membranes (see osmosis.) One consequence of this is that lipid messengers cannot be stored in vesicles prior to release and so are often biosynthesized ""on demand"" at their intended site of action. As such, many lipid signaling molecules cannot circulate freely in solution but, rather, exist bound to special carrier proteins in serum.