Plant and Soil
... some evidence supporting the repression hypothesis. Cells grown on any substrate had glucosedependent 02 consumption, which support the previous observation indicating the presence of a constitutive glucose transport system in R. meliloti (Theodoropoulos et al., 1985), however as compared to the glu ...
... some evidence supporting the repression hypothesis. Cells grown on any substrate had glucosedependent 02 consumption, which support the previous observation indicating the presence of a constitutive glucose transport system in R. meliloti (Theodoropoulos et al., 1985), however as compared to the glu ...
The Terminal Enzymes of Sialic Acid Metabolism: Acylneuraminate
... is thought to represent an important step in catalysis (see below). The presence of a free carboxyl and a glycosidic hydroxyl group is absolutely indispensible. Already in the 1970s experiments were performed with amino acid-modifying reagents to elucidate the role of special amino acids for catalys ...
... is thought to represent an important step in catalysis (see below). The presence of a free carboxyl and a glycosidic hydroxyl group is absolutely indispensible. Already in the 1970s experiments were performed with amino acid-modifying reagents to elucidate the role of special amino acids for catalys ...
Practice Problems on Amino Acids and Peptides
... Biological molecules often have phosphate or pyrophosphate monoester groups. Which one of the following statements regarding this is least correct? A) The phosphate or pyrophosphate provides a handle for electrostatic binding of the molecule by an enzyme B) Phosphates or pyrophosphates will accept h ...
... Biological molecules often have phosphate or pyrophosphate monoester groups. Which one of the following statements regarding this is least correct? A) The phosphate or pyrophosphate provides a handle for electrostatic binding of the molecule by an enzyme B) Phosphates or pyrophosphates will accept h ...
effect of arsenic stress on amino acid profile
... study by Mishra and Dubey (2006) on rice showed enhanced free proline content on increasing concentrations of arsenite which has also been observed in this study. On the other hand free to bound ratio of proline was more enhanced in HARG corresponding to As accumulation suggesting release from prote ...
... study by Mishra and Dubey (2006) on rice showed enhanced free proline content on increasing concentrations of arsenite which has also been observed in this study. On the other hand free to bound ratio of proline was more enhanced in HARG corresponding to As accumulation suggesting release from prote ...
PDF - Poultry Science Journal
... virginiamycin, probiotic Protexin® and Plantago major L. (plantain) on performance, serum metabolites, immune response, and the ileal microbial population of broilers. The experiment was carried out with a total of 200 day-old male Ross 308 broiler chickens in a completely randomized design. Chicken ...
... virginiamycin, probiotic Protexin® and Plantago major L. (plantain) on performance, serum metabolites, immune response, and the ileal microbial population of broilers. The experiment was carried out with a total of 200 day-old male Ross 308 broiler chickens in a completely randomized design. Chicken ...
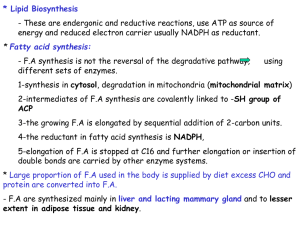
13synthesis
... - Sphingolipids are degraded by sphingomyelinase which remove phosphorylcholine leaving Ceramide. - Ceramide is cleaved by ceramidase into sphingosine and free fatty acid. ...
... - Sphingolipids are degraded by sphingomyelinase which remove phosphorylcholine leaving Ceramide. - Ceramide is cleaved by ceramidase into sphingosine and free fatty acid. ...
video slide
... Concept 9.5: Fermentation enables some cells to produce ATP without the use of oxygen A. Cellular respiration requires O2 to produce ATP B. Glycolysis can produce ATP with or without O2 (in aerobic or anaerobic conditions) C. In the absence of O2, glycolysis couples with fermentation to produce ATP ...
... Concept 9.5: Fermentation enables some cells to produce ATP without the use of oxygen A. Cellular respiration requires O2 to produce ATP B. Glycolysis can produce ATP with or without O2 (in aerobic or anaerobic conditions) C. In the absence of O2, glycolysis couples with fermentation to produce ATP ...
Human Physiology - Orange Coast College
... Lactic acid produced by anaerobic respiration delivered to the liver. LDH converts lactic acid to pyruvic acid. Pyruvic acid converted to glucose-6phosphate: Intermediate for glycogen. Converted to free glucose. Gluconeogenesis: conversion to noncarbohydrate molecules through pyruvic acid to glu ...
... Lactic acid produced by anaerobic respiration delivered to the liver. LDH converts lactic acid to pyruvic acid. Pyruvic acid converted to glucose-6phosphate: Intermediate for glycogen. Converted to free glucose. Gluconeogenesis: conversion to noncarbohydrate molecules through pyruvic acid to glu ...
Document
... anaerobes, meaning that they can survive using either fermentation or cellular respiration • In a facultative anaerobe, pyruvate is a fork in the metabolic road that leads to two alternative ...
... anaerobes, meaning that they can survive using either fermentation or cellular respiration • In a facultative anaerobe, pyruvate is a fork in the metabolic road that leads to two alternative ...
Slide 1
... AMP (citrate leaks out of the mitochondria when you make lots of it!). This ensures that rates of glycolysis will more or less match rates of oxidative phosphorylation at all rates of ATP demand, at least until rates of glycolysis speed up due to increasing muscle contraction. We must remember that ...
... AMP (citrate leaks out of the mitochondria when you make lots of it!). This ensures that rates of glycolysis will more or less match rates of oxidative phosphorylation at all rates of ATP demand, at least until rates of glycolysis speed up due to increasing muscle contraction. We must remember that ...
Sodium Hypochlorite Inactivates Lipoteichoic Acid of Enterococcus
... bacteria including E. faecalis contain polyglycerolphosphate-type LTA, whereas a few gram-positive bacteria such as Streptococcus pneumoniae express polyribitolphosphate-type LTA (12, 13). LTA exclusively activates Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2), which leads to the production of various proinflammatory ...
... bacteria including E. faecalis contain polyglycerolphosphate-type LTA, whereas a few gram-positive bacteria such as Streptococcus pneumoniae express polyribitolphosphate-type LTA (12, 13). LTA exclusively activates Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2), which leads to the production of various proinflammatory ...
Pyruvate Kinase
... Skeletal muscles ferment glucose to lactate during exercise. Lactate released to the blood may be taken up by other tissues, or by skeletal muscle after exercise, and converted via Lactate Dehydrogenase back to pyruvate, which may be oxidized in Krebs Cycle or (in liver) converted to back to glucose ...
... Skeletal muscles ferment glucose to lactate during exercise. Lactate released to the blood may be taken up by other tissues, or by skeletal muscle after exercise, and converted via Lactate Dehydrogenase back to pyruvate, which may be oxidized in Krebs Cycle or (in liver) converted to back to glucose ...
this PDF file - Periodica Polytechnica
... The non-essential amino acid content in winter wheat grains is shown in Table 7. Fertilizing produced significant positive or negative changes in all amino acids except proline (PRO), depending on the treatment. Compared to unfertilized treatment, N increased the contents in arginine (ARG), histidin ...
... The non-essential amino acid content in winter wheat grains is shown in Table 7. Fertilizing produced significant positive or negative changes in all amino acids except proline (PRO), depending on the treatment. Compared to unfertilized treatment, N increased the contents in arginine (ARG), histidin ...
Metabolism
... To operate, machines need energy. Cars use gasoline for fuel, factory machinery uses electricity, and windmills rely on wind power. So what about you? All cells require energy to sustain life. Even during sleep, your body uses energy for breathing, pumping blood, maintaining body temperature, delive ...
... To operate, machines need energy. Cars use gasoline for fuel, factory machinery uses electricity, and windmills rely on wind power. So what about you? All cells require energy to sustain life. Even during sleep, your body uses energy for breathing, pumping blood, maintaining body temperature, delive ...
pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
... complex producing acetyl CoA, which is the major fuel for TCA cycle • This enz complex requires five coenzymes: thiamine pyrophosphate, lipoic acid, FAD, NAD+, and coenzyme-A (which contains the vitamin pantothenic acid) • The reaction is activated by NAD+, coenzyme-A, and pyruvate, and inhibited by ...
... complex producing acetyl CoA, which is the major fuel for TCA cycle • This enz complex requires five coenzymes: thiamine pyrophosphate, lipoic acid, FAD, NAD+, and coenzyme-A (which contains the vitamin pantothenic acid) • The reaction is activated by NAD+, coenzyme-A, and pyruvate, and inhibited by ...
Chap. 3A Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins Topics Amino acids
... The a-carboxyl and a-amino groups of all amino acids, along with the ionizable R groups of 7 amino acids, function as weak acids and bases in aqueous solutions (Table 3-1). The pKas of these functional groups depend on the chemical properties of the groups themselves and range between 1.8-2.4 for th ...
... The a-carboxyl and a-amino groups of all amino acids, along with the ionizable R groups of 7 amino acids, function as weak acids and bases in aqueous solutions (Table 3-1). The pKas of these functional groups depend on the chemical properties of the groups themselves and range between 1.8-2.4 for th ...
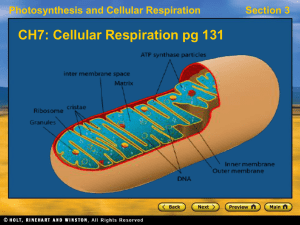
Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
... In cellular respiration, glucose and other organic molecules are broken down in a series of steps Electrons from organic compounds are usually first transferred to NAD+, a coenzyme As an electron acceptor, NAD+ functions as an oxidizing agent during cellular respiration Each NADH (the reduce ...
... In cellular respiration, glucose and other organic molecules are broken down in a series of steps Electrons from organic compounds are usually first transferred to NAD+, a coenzyme As an electron acceptor, NAD+ functions as an oxidizing agent during cellular respiration Each NADH (the reduce ...
Cellular Respiration
... • The process in which carbohydrates are broken down in the absence of oxygen is called fermentation. – Beneficial because it allows glycolysis to continue supplying a cell with ATP in anaerobic conditions. ...
... • The process in which carbohydrates are broken down in the absence of oxygen is called fermentation. – Beneficial because it allows glycolysis to continue supplying a cell with ATP in anaerobic conditions. ...
Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
... The citric acid cycle has eight steps, each catalyzed by a specific enzyme The acetyl group of acetyl CoA joins the cycle by combining with oxaloacetate, forming citrate (i.e., citric acid) The next seven steps decompose the citrate back to oxaloacetate, making the process a cycle The NADH a ...
... The citric acid cycle has eight steps, each catalyzed by a specific enzyme The acetyl group of acetyl CoA joins the cycle by combining with oxaloacetate, forming citrate (i.e., citric acid) The next seven steps decompose the citrate back to oxaloacetate, making the process a cycle The NADH a ...
Unit 9 - Central New Mexico Community College
... such as starch and cellulose, which are synthesized by plants, and glycogen, which is produced in animals are composed of repeating glucose subunits. Bacteria have a variety of pathways to utilize the energy in carbohydrates. Many bacteria produce specific membrane transport proteins to transport a ...
... such as starch and cellulose, which are synthesized by plants, and glycogen, which is produced in animals are composed of repeating glucose subunits. Bacteria have a variety of pathways to utilize the energy in carbohydrates. Many bacteria produce specific membrane transport proteins to transport a ...
Sample pages 1 PDF
... on which carboxylation takes place in presence of an enzyme ribulose-1,5bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase, commonly known as rubisco/Rubisco [3], the most abundant protein in plant, and for that matter on earth. With its 16 subunits, it is one of the largest enzymes in nature. It is a lazy enzyme a ...
... on which carboxylation takes place in presence of an enzyme ribulose-1,5bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase, commonly known as rubisco/Rubisco [3], the most abundant protein in plant, and for that matter on earth. With its 16 subunits, it is one of the largest enzymes in nature. It is a lazy enzyme a ...
File
... by combining with oxaloacetate, forming citrate • The next seven steps decompose the citrate back to oxaloacetate, making the process a ...
... by combining with oxaloacetate, forming citrate • The next seven steps decompose the citrate back to oxaloacetate, making the process a ...
III. 4. Test Respiració cel·lular
... 3) Which of the following statements concerning the metabolic degradation of glucose (C6H12O6) to carbon dioxide (CO2) and water is (are) true? A) The breakdown of glucose to carbon dioxide and water is exergonic. B) The breakdown of glucose to carbon dioxide and water has a free energy change of -6 ...
... 3) Which of the following statements concerning the metabolic degradation of glucose (C6H12O6) to carbon dioxide (CO2) and water is (are) true? A) The breakdown of glucose to carbon dioxide and water is exergonic. B) The breakdown of glucose to carbon dioxide and water has a free energy change of -6 ...
Pyruvate dehydrogenase
... pathway occurring in plants and several bacteria, but not animals. . The glyoxylate cycle allows these organisms to use fats for the synthesis of carbohydrates, a task which vertebrates, including humans, cannot perform. Isocitrate --> succinate + glyoxylate (O=CH-COO-)+acetyl-CoA--> malate-->> gluc ...
... pathway occurring in plants and several bacteria, but not animals. . The glyoxylate cycle allows these organisms to use fats for the synthesis of carbohydrates, a task which vertebrates, including humans, cannot perform. Isocitrate --> succinate + glyoxylate (O=CH-COO-)+acetyl-CoA--> malate-->> gluc ...
Proficiency Test Lyon 2008
... Mol Genet 2004;13:2803; Rzem et al, Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004;101:16849) but the role of this metabolic pathway remained unknown for a long time. It had been showed that urinary excretion of L2-hydroxyglutaric acid (L2OHGA) was independent of feeding, but relied exclusively on endogenous productio ...
... Mol Genet 2004;13:2803; Rzem et al, Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004;101:16849) but the role of this metabolic pathway remained unknown for a long time. It had been showed that urinary excretion of L2-hydroxyglutaric acid (L2OHGA) was independent of feeding, but relied exclusively on endogenous productio ...
Butyric acid
Butyric acid (from Greek βούτῡρον, meaning ""butter""), also known under the systematic name butanoic acid, abbreviated BTA, is a carboxylic acid with the structural formula CH3CH2CH2-COOH. Salts and esters of butyric acid are known as butyrates or butanoates. Butyric acid is found in milk, especially goat, sheep and buffalo milk, butter, parmesan cheese, and as a product of anaerobic fermentation (including in the colon and as body odor). It has an unpleasant smell and acrid taste, with a sweetish aftertaste (similar to ether). It can be detected by mammals with good scent detection abilities (such as dogs) at 10 parts per billion, whereas humans can detect it in concentrations above 10 parts per million.Butyric acid is present in, and is the main distinctive smell of, human vomit.Butyric acid was first observed (in impure form) in 1814 by the French chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul. By 1818, he had purified it sufficiently to characterize it. The name of butyric acid comes from the Latin word for butter, butyrum (or buturum), the substance in which butyric acid was first found.