Natural Carbon Isotope Abundance of Plasma
... isotopic enrichment of mammals is not solely dictated by diet (between C3-C4 or between marine and terrestrial diets), and studies looking at changes due to dietary differences in isotopic composition find that different tissues and animals incorporate the isotopic shift at various rates [12]. Isoto ...
... isotopic enrichment of mammals is not solely dictated by diet (between C3-C4 or between marine and terrestrial diets), and studies looking at changes due to dietary differences in isotopic composition find that different tissues and animals incorporate the isotopic shift at various rates [12]. Isoto ...
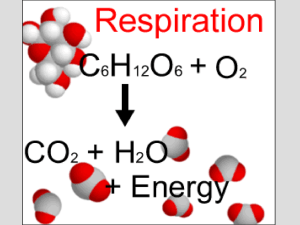
CELLULAR RESPIRATION: AEROBIC HARVESTING OF ENERGY
... – the cells are packed full of mitochondria, – the inner mitochondrial membrane contains an uncoupling protein, which allows H+ to flow back down its concentration gradient without generating ATP, and – ongoing oxidation of stored fats generates additional ...
... – the cells are packed full of mitochondria, – the inner mitochondrial membrane contains an uncoupling protein, which allows H+ to flow back down its concentration gradient without generating ATP, and – ongoing oxidation of stored fats generates additional ...
Slide 1
... 6.1 Photosynthesis and cellular respiration provide energy for life Energy in sunlight is used in photosynthesis to make glucose from CO2 and H2O with release of O2 Other organisms use the O2 and energy in sugar and release CO2 and H2O Together, these two processes are responsible for the maj ...
... 6.1 Photosynthesis and cellular respiration provide energy for life Energy in sunlight is used in photosynthesis to make glucose from CO2 and H2O with release of O2 Other organisms use the O2 and energy in sugar and release CO2 and H2O Together, these two processes are responsible for the maj ...
ch 6 notes
... 6.1 Photosynthesis and cellular respiration provide energy for life Energy in sunlight is used in photosynthesis to make glucose from CO2 and H2O with release of O2 Other organisms use the O2 and energy in sugar and release CO2 and H2O Together, these two processes are responsible for the maj ...
... 6.1 Photosynthesis and cellular respiration provide energy for life Energy in sunlight is used in photosynthesis to make glucose from CO2 and H2O with release of O2 Other organisms use the O2 and energy in sugar and release CO2 and H2O Together, these two processes are responsible for the maj ...
Cellular respiration
... • The conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA is the junction between glycolysis (step 1) and the Krebs cycle (step 2). • If oxygen is present, Pyruvate (3 C each) from glycolysis enters the mitochondrion. • Using Coenzyme A, each pyruvate is converted into a molecule of Acetyl CoA (2 C ...
... • The conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA is the junction between glycolysis (step 1) and the Krebs cycle (step 2). • If oxygen is present, Pyruvate (3 C each) from glycolysis enters the mitochondrion. • Using Coenzyme A, each pyruvate is converted into a molecule of Acetyl CoA (2 C ...
2-Phospho
... product, with no release of CO2 • Lactic acid fermentation by some fungi and bacteria is used to make cheese and yogurt • Human muscle cells use lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP when O2 is scarce ...
... product, with no release of CO2 • Lactic acid fermentation by some fungi and bacteria is used to make cheese and yogurt • Human muscle cells use lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP when O2 is scarce ...
14C2H4 : Distribution of 14G-labeled tissue metabolites
... the neutral fraction revealed two regions of radioactivity (Rf-=0.38) and 0.63 which did not cochromatograph with twenty-two known sugars or neutral metabolites. Chromatogramj of the basic fraction contained 3 regions of radioactivity. Similar distribution patterns were noted when 14CjH< exposure wa ...
... the neutral fraction revealed two regions of radioactivity (Rf-=0.38) and 0.63 which did not cochromatograph with twenty-two known sugars or neutral metabolites. Chromatogramj of the basic fraction contained 3 regions of radioactivity. Similar distribution patterns were noted when 14CjH< exposure wa ...
Flavanoid-Biosynthesis
... forming flavonols from dihydroflavonols by direct abstraction of the two vicinal hydrogen atoms in positions C2 and C3 of the C-ring, introducing a double bond. Cofactors are oxoglutarate, Fe(II) and ...
... forming flavonols from dihydroflavonols by direct abstraction of the two vicinal hydrogen atoms in positions C2 and C3 of the C-ring, introducing a double bond. Cofactors are oxoglutarate, Fe(II) and ...
Chapt 6
... The citric acid cycle completes the oxidation of organic molecules, generating many NADH and FADH2 molecules • During the citric acid cycle • the two-carbon group of acetyl CoA is joined to a four-carbon compound, forming citrate, • citrate is degraded back to the four-carbon compound, • two CO2 ar ...
... The citric acid cycle completes the oxidation of organic molecules, generating many NADH and FADH2 molecules • During the citric acid cycle • the two-carbon group of acetyl CoA is joined to a four-carbon compound, forming citrate, • citrate is degraded back to the four-carbon compound, • two CO2 ar ...
Biochemistry review-ppt
... 14. Which one catalyzes the formation of NADH in both B aerobic and anaerobic glycolysis 15. In the cell, which one catalyzes the formation of NADH C only under aerobic (not anaerobic) conditions 16. Pi, a low energy metabolite in the body, can stimulate the A activity of which one in an allosteric ...
... 14. Which one catalyzes the formation of NADH in both B aerobic and anaerobic glycolysis 15. In the cell, which one catalyzes the formation of NADH C only under aerobic (not anaerobic) conditions 16. Pi, a low energy metabolite in the body, can stimulate the A activity of which one in an allosteric ...
Rapid, Accurate, Sensitive and Reproducible Analysis of
... FLD between peaks #21 and #22. When monitoring at 262 nm (Fig. 3B), a small baseline hump elutes between 7 and 10 minutes due to derivatization byproducts. Since only the primary AAs are monitored (338 nm) during this time, the hump has no impact on their detection or resolution. It is best to ...
... FLD between peaks #21 and #22. When monitoring at 262 nm (Fig. 3B), a small baseline hump elutes between 7 and 10 minutes due to derivatization byproducts. Since only the primary AAs are monitored (338 nm) during this time, the hump has no impact on their detection or resolution. It is best to ...
Application of stable isotopes and mass isotopomer distribution
... appearance of [U-13Cn] isotopomers can only derive from the administered tracer (e.g., dietary [U-13C6]dextrin, n = 6). Therefore, when [U-13Cn] compounds ([M+n]) are administered, appearance of the [M+n] isotopomer in, for example, plasma glucose when [U-13C6]glucose is administered (Figure 1), rep ...
... appearance of [U-13Cn] isotopomers can only derive from the administered tracer (e.g., dietary [U-13C6]dextrin, n = 6). Therefore, when [U-13Cn] compounds ([M+n]) are administered, appearance of the [M+n] isotopomer in, for example, plasma glucose when [U-13C6]glucose is administered (Figure 1), rep ...
substrate specificities of octopine dehydrogenases
... Electrophoresis confirmed that the enzyme activities seen with alternative substrates were, in fact, catalyzed by O D H . For each species examined in the present study the zone staining on starch gels with octopine plus N A D was identical with the zone staining with N A D H + pyruvate + alternativ ...
... Electrophoresis confirmed that the enzyme activities seen with alternative substrates were, in fact, catalyzed by O D H . For each species examined in the present study the zone staining on starch gels with octopine plus N A D was identical with the zone staining with N A D H + pyruvate + alternativ ...
Long-Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Fish: Recent
... In fish, like virtually all living organisms, fatty acid synthase (FAS), a cytosolic multifunctional enzymatic complex, is responsible for de novo biosynthesis of saturated fatty acids up to C16 (palmitic acid, 16:0). The fatty acids synthesised by FAS, as well as dietary FA, can be further converte ...
... In fish, like virtually all living organisms, fatty acid synthase (FAS), a cytosolic multifunctional enzymatic complex, is responsible for de novo biosynthesis of saturated fatty acids up to C16 (palmitic acid, 16:0). The fatty acids synthesised by FAS, as well as dietary FA, can be further converte ...
Vitamin - definition
... Vitamin B1 (thiamine) • Thiamin has a central role in energy-yielding metabolism. • Composed of a substituted pyridine and thiazole ring. • Active form is thiamine diphosphate (thiamin pyrophosphate, TPP), a coenzyme for three multi-enzyme complex → • This complex catalyses oxidative decarboxylatio ...
... Vitamin B1 (thiamine) • Thiamin has a central role in energy-yielding metabolism. • Composed of a substituted pyridine and thiazole ring. • Active form is thiamine diphosphate (thiamin pyrophosphate, TPP), a coenzyme for three multi-enzyme complex → • This complex catalyses oxidative decarboxylatio ...
Fritz Lipmann - Nobel Lecture
... The most important event during this whole period, I now feel, was the accidental observation that in the L. delbrueckii system, pyruvic acid oxidation was completely dependent on the presence of inorganic phosphate. This observation was made in the course of attempts to replace oxygen by methylene ...
... The most important event during this whole period, I now feel, was the accidental observation that in the L. delbrueckii system, pyruvic acid oxidation was completely dependent on the presence of inorganic phosphate. This observation was made in the course of attempts to replace oxygen by methylene ...
Diapositive 1
... Competitive probiotics could be selected to target specifically one or more of the metabolic or stress pathways promoting EHEC survival in cattle ...
... Competitive probiotics could be selected to target specifically one or more of the metabolic or stress pathways promoting EHEC survival in cattle ...
Glycolic acid production in the engineered yeasts Saccharomyces
... routes in acidic biomining [6]. Since these pathways are either dependent on the availability of ethylene glycol or glycolonitrile or specific environmental conditions, a pathway allowing flexible use of different or more abundant carbon sources under normal bioprocessing conditions would be desirab ...
... routes in acidic biomining [6]. Since these pathways are either dependent on the availability of ethylene glycol or glycolonitrile or specific environmental conditions, a pathway allowing flexible use of different or more abundant carbon sources under normal bioprocessing conditions would be desirab ...
SELECTIVE INHIBITORS OF DIHYDROFOLATE REDUCTASE
... homology. Hitchings and Roth found 16 identities between the enzymes from Escherichia coli and those from the mouse tumor L1210 (12). They predicted correctly that study of a wider range of enzymes would reduce the number of identities. If one takes into account enzymes not in the mainstream, e.g. t ...
... homology. Hitchings and Roth found 16 identities between the enzymes from Escherichia coli and those from the mouse tumor L1210 (12). They predicted correctly that study of a wider range of enzymes would reduce the number of identities. If one takes into account enzymes not in the mainstream, e.g. t ...
The Effect of Antibiotics on Synthesis of Mucopeptide
... of unlabelled pool amins acids since Holden (1962) showed generally high levels of endogenous glutamate and low levels of lysine in a number of bacterial species. Aspartic acid was incorporated in substantial quantities, even though it was not required to produce a turbidity increment (Wilkinson & W ...
... of unlabelled pool amins acids since Holden (1962) showed generally high levels of endogenous glutamate and low levels of lysine in a number of bacterial species. Aspartic acid was incorporated in substantial quantities, even though it was not required to produce a turbidity increment (Wilkinson & W ...
Energy coupling in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
... Product pathways with a positive net ATP yield provide microorganisms with free energy for growth and maintenance processes. However, during industrial production of chemicals, excess microbial biomass constitutes an undesirable byproduct, whose formation goes at the expense of the product yield. Op ...
... Product pathways with a positive net ATP yield provide microorganisms with free energy for growth and maintenance processes. However, during industrial production of chemicals, excess microbial biomass constitutes an undesirable byproduct, whose formation goes at the expense of the product yield. Op ...
TCA (Krebs) Cycle
... Catalytic amounts of OAA: replenished by TCA cycle: thus, can oxidize large [acetyl CoA]. Citrate synthase: aldol condensation yields 6-C product, citric acid (citrate). Stereo specific, asymmetric center (chiral). _____________________________________ * When blood [glucose] low, PC increases [OAA] ...
... Catalytic amounts of OAA: replenished by TCA cycle: thus, can oxidize large [acetyl CoA]. Citrate synthase: aldol condensation yields 6-C product, citric acid (citrate). Stereo specific, asymmetric center (chiral). _____________________________________ * When blood [glucose] low, PC increases [OAA] ...
Amino Acid Sequences Containing Cysteine or Cystine Residues in
... to give plakalbumin, is not formed in similar experiments with turkey ovalbumin. The S-peptide, which is released in acidic 6 M urea-Hel, contains two of the four cysteine residues of hen ovalbumin, and provides, in some species, a convenient way of studying the location and homology of amino acid s ...
... to give plakalbumin, is not formed in similar experiments with turkey ovalbumin. The S-peptide, which is released in acidic 6 M urea-Hel, contains two of the four cysteine residues of hen ovalbumin, and provides, in some species, a convenient way of studying the location and homology of amino acid s ...
universidade estadual de maringá metabolic alterations caused by
... Usnic acid is a naturally occurring dibenzofuran derivative found in several lichen species. The compound has been marketed as an ingredient of food supplements for weight reduction. There is evidence that the compound acts as an uncoupler of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation and it is also cl ...
... Usnic acid is a naturally occurring dibenzofuran derivative found in several lichen species. The compound has been marketed as an ingredient of food supplements for weight reduction. There is evidence that the compound acts as an uncoupler of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation and it is also cl ...
Butyric acid
Butyric acid (from Greek βούτῡρον, meaning ""butter""), also known under the systematic name butanoic acid, abbreviated BTA, is a carboxylic acid with the structural formula CH3CH2CH2-COOH. Salts and esters of butyric acid are known as butyrates or butanoates. Butyric acid is found in milk, especially goat, sheep and buffalo milk, butter, parmesan cheese, and as a product of anaerobic fermentation (including in the colon and as body odor). It has an unpleasant smell and acrid taste, with a sweetish aftertaste (similar to ether). It can be detected by mammals with good scent detection abilities (such as dogs) at 10 parts per billion, whereas humans can detect it in concentrations above 10 parts per million.Butyric acid is present in, and is the main distinctive smell of, human vomit.Butyric acid was first observed (in impure form) in 1814 by the French chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul. By 1818, he had purified it sufficiently to characterize it. The name of butyric acid comes from the Latin word for butter, butyrum (or buturum), the substance in which butyric acid was first found.