Request reprint ©
... are used to synthesize egg lipids, while others are used to build energy reserves of the female. But, more than 60% of the amino acids are oxidized to CO2 to provide the energy needed for egg production (Briegel, 1985; Zhou et al., 2004). An important by-product of amino acid oxidation is ammonia, w ...
... are used to synthesize egg lipids, while others are used to build energy reserves of the female. But, more than 60% of the amino acids are oxidized to CO2 to provide the energy needed for egg production (Briegel, 1985; Zhou et al., 2004). An important by-product of amino acid oxidation is ammonia, w ...
Lecture 7- 24 October 2013 Vitamins in metabolism and regulation
... -do not yield energy when broken downthey assist in energy yielding pathways of carbohydrate, lipid and protein metabolism ...
... -do not yield energy when broken downthey assist in energy yielding pathways of carbohydrate, lipid and protein metabolism ...
177 Chapter 26: Biomolecules: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
... R. Bruce Merrifield, Rockefeller University, 1984 Nobel Prize in Chemistry: “for his development of methodology for chemical synthesis on a solid matrix.” ...
... R. Bruce Merrifield, Rockefeller University, 1984 Nobel Prize in Chemistry: “for his development of methodology for chemical synthesis on a solid matrix.” ...
Peptostreptococcus vaginalis sp.
... groups 4 and 5 were differentiated by the DNA homology test, we had only one strain of each group, and the phenotypic characteristics of these organisms were not sufficient to differentiate them from previously described species. Thus, we will not propose them as new species until we acquire more st ...
... groups 4 and 5 were differentiated by the DNA homology test, we had only one strain of each group, and the phenotypic characteristics of these organisms were not sufficient to differentiate them from previously described species. Thus, we will not propose them as new species until we acquire more st ...
Protein digestion and amino acid absorption along
... ileum of cod. If the protein content in minced saithe fillet is assumed to be 60 % (86 % of the diet), the extent of hydrolysis can be estimated approximately. In rainbow trout fed a casein diet, the peptide fraction of the pyloric caeca region contains a maximum of 89 % of total amino acids (Dabrow ...
... ileum of cod. If the protein content in minced saithe fillet is assumed to be 60 % (86 % of the diet), the extent of hydrolysis can be estimated approximately. In rainbow trout fed a casein diet, the peptide fraction of the pyloric caeca region contains a maximum of 89 % of total amino acids (Dabrow ...
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications
... or four domains, such as C–A–T, C–A–T–E, C–A–T, C– A–T–E, C–A–T–E, and C–A–T–TE (Fig. 2A). The A domains were analyzed according to the method of Ansari et al. [12], and the active site residues for amino acid recognition are shown in Fig. 2B. The first, fourth, and sixth amino acids are well conserv ...
... or four domains, such as C–A–T, C–A–T–E, C–A–T, C– A–T–E, C–A–T–E, and C–A–T–TE (Fig. 2A). The A domains were analyzed according to the method of Ansari et al. [12], and the active site residues for amino acid recognition are shown in Fig. 2B. The first, fourth, and sixth amino acids are well conserv ...
Isolated from Humans: Peptostreptococcus vaginalis sp. nov
... groups 4 and 5 were differentiated by the DNA homology test, we had only one strain of each group, and the phenotypic characteristics of these organisms were not sufficient to differentiate them from previously described species. Thus, we will not propose them as new species until we acquire more st ...
... groups 4 and 5 were differentiated by the DNA homology test, we had only one strain of each group, and the phenotypic characteristics of these organisms were not sufficient to differentiate them from previously described species. Thus, we will not propose them as new species until we acquire more st ...
Biosketch - NC State University
... Deborah M. Muoio, and Gary D. Lopaschuk. Insulin-stimulated cardiac glucose oxidation is increased in high fat diet-induced obese mice lacking malonyl CoA decarboxylase. In revision. 37. Timothy R. Koves, Terry E. Jones, Dorothy Slentz, James Way, Ann Louise Olson, G. Lynis Dohm, and Deborah M. Muoi ...
... Deborah M. Muoio, and Gary D. Lopaschuk. Insulin-stimulated cardiac glucose oxidation is increased in high fat diet-induced obese mice lacking malonyl CoA decarboxylase. In revision. 37. Timothy R. Koves, Terry E. Jones, Dorothy Slentz, James Way, Ann Louise Olson, G. Lynis Dohm, and Deborah M. Muoi ...
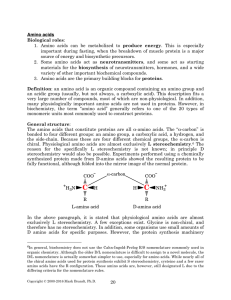
Amino Acids - Rose
... 1. Amino acids can be metabolized to produce energy. This is especially important during fasting, when the breakdown of muscle protein is a major source of energy and biosynthetic precursors. 2. Some amino acids act as neurotransmitters, and some act as starting materials for the biosynthesis of neu ...
... 1. Amino acids can be metabolized to produce energy. This is especially important during fasting, when the breakdown of muscle protein is a major source of energy and biosynthetic precursors. 2. Some amino acids act as neurotransmitters, and some act as starting materials for the biosynthesis of neu ...
The Effects of Exogenous Amino Acids on Growth
... Urea elicited the same response as NH,+ (Figs l b and lc), with an extended period of nitrogenase suppression, confirming the opinion of Neilson & Larsson (1980) that both atoms of N are utilized. Whilst statistical analysis showed the growth rate of NH,Cl-supplemented cultures to be significantly ( ...
... Urea elicited the same response as NH,+ (Figs l b and lc), with an extended period of nitrogenase suppression, confirming the opinion of Neilson & Larsson (1980) that both atoms of N are utilized. Whilst statistical analysis showed the growth rate of NH,Cl-supplemented cultures to be significantly ( ...
PowerPoint
... Rule 4: Degree of Compensation For metabolic acidosis, Expected PCO = 1.5(HCO3) + 8 ± 2 ...
... Rule 4: Degree of Compensation For metabolic acidosis, Expected PCO = 1.5(HCO3) + 8 ± 2 ...
Ch. 9
... In vertebrates, a second pathway anaerobic pathway occurs when oxygen levels drop. Pyruvate is converted to lactic acid where NADH serves as the reducing agent. Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... In vertebrates, a second pathway anaerobic pathway occurs when oxygen levels drop. Pyruvate is converted to lactic acid where NADH serves as the reducing agent. Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Guide Kjeldahl
... and protein determinations, which also can be carried out by non academic lab personnel, has been put into practice by Büchi’s Kjeldahl systems since 1961. The Büchi Kjeldahl Guide you have in your hands is addressed to laboratory personnel, laboratory supervisors, students and teachers. It is our i ...
... and protein determinations, which also can be carried out by non academic lab personnel, has been put into practice by Büchi’s Kjeldahl systems since 1961. The Büchi Kjeldahl Guide you have in your hands is addressed to laboratory personnel, laboratory supervisors, students and teachers. It is our i ...
REAL-TIME PCR KITS FOR DIAGNOSIS
... RTA HCV Real-Time PCR Kit is perfectly designed to amplify and detect a highly conserved region within the HCV genome by Real Time PCR. It is possible to monitor the nucleic acid amount on-line, during the reaction utilizing hydrolysis probe method in which fluorescence emission increases proportion ...
... RTA HCV Real-Time PCR Kit is perfectly designed to amplify and detect a highly conserved region within the HCV genome by Real Time PCR. It is possible to monitor the nucleic acid amount on-line, during the reaction utilizing hydrolysis probe method in which fluorescence emission increases proportion ...
Cellular Respiration
... Begins by the addition of a two-carbon acetyl group to a four-carbon molecule (oxaloacetate), forming a six-carbon molecule (citric acid) NADH, FADH2 capture energy rich electrons ATP formed by substrate-level phosphorylation Turns twice for one glucose molecule. Produces 4 CO2, 2 ATP, 6 NADH and 2 ...
... Begins by the addition of a two-carbon acetyl group to a four-carbon molecule (oxaloacetate), forming a six-carbon molecule (citric acid) NADH, FADH2 capture energy rich electrons ATP formed by substrate-level phosphorylation Turns twice for one glucose molecule. Produces 4 CO2, 2 ATP, 6 NADH and 2 ...
Document
... • Maple syrup urine disease (branched-chain ketonuria) – α-keto acid decarboxylase complex – Plasma and urinary levels of leucine, isoleucine, valine, α-keto acids, and α-hydroxy acids (reduced α-keto acids) are elevated ...
... • Maple syrup urine disease (branched-chain ketonuria) – α-keto acid decarboxylase complex – Plasma and urinary levels of leucine, isoleucine, valine, α-keto acids, and α-hydroxy acids (reduced α-keto acids) are elevated ...
carbohydrate metabolism
... aldohexose. It is oxidized by hot alkaline copper solution, potassium ferricyanide solution. These methods give 10-20 mg higher values because in the blood there are other reducing substances (gluthathion, ascorbic acid). Colorimetric methods are rapid and based on the reaction between the glucose a ...
... aldohexose. It is oxidized by hot alkaline copper solution, potassium ferricyanide solution. These methods give 10-20 mg higher values because in the blood there are other reducing substances (gluthathion, ascorbic acid). Colorimetric methods are rapid and based on the reaction between the glucose a ...
Chapter 19: Acids and Bases
... You now know that HCl and HF are acids because they can donate a hydrogen ion in an acid-base reaction. From their chemical formulas, you can see that each acid can donate only one hydrogen ion per molecule. An acid that can donate only one hydrogen ion is called a monoprotic acid. Other monoprotic ...
... You now know that HCl and HF are acids because they can donate a hydrogen ion in an acid-base reaction. From their chemical formulas, you can see that each acid can donate only one hydrogen ion per molecule. An acid that can donate only one hydrogen ion is called a monoprotic acid. Other monoprotic ...
SPC - HPRA
... Ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) Ascorbic acid is a water soluble vitamin and a powerful antioxidant. It is a cofactor in numerous biological processes, such as the metabolism of folic acid, amino acid oxidation and the absorption and transport of iron. It is also required for the formation, maintenance an ...
... Ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) Ascorbic acid is a water soluble vitamin and a powerful antioxidant. It is a cofactor in numerous biological processes, such as the metabolism of folic acid, amino acid oxidation and the absorption and transport of iron. It is also required for the formation, maintenance an ...
Chapter 9 Powerpoint
... 24. What are the two mechanisms cells can use to generate ATP when oxygen is not present? • In the absence of O2, glycolysis couples with fermentation or anaerobic respiration to produce ATP • The distinction between these two is based on whether an ETC is present. • Anaerobic respiration uses an e ...
... 24. What are the two mechanisms cells can use to generate ATP when oxygen is not present? • In the absence of O2, glycolysis couples with fermentation or anaerobic respiration to produce ATP • The distinction between these two is based on whether an ETC is present. • Anaerobic respiration uses an e ...
Plant and Soil
... some evidence supporting the repression hypothesis. Cells grown on any substrate had glucosedependent 02 consumption, which support the previous observation indicating the presence of a constitutive glucose transport system in R. meliloti (Theodoropoulos et al., 1985), however as compared to the glu ...
... some evidence supporting the repression hypothesis. Cells grown on any substrate had glucosedependent 02 consumption, which support the previous observation indicating the presence of a constitutive glucose transport system in R. meliloti (Theodoropoulos et al., 1985), however as compared to the glu ...
Butyric acid
Butyric acid (from Greek βούτῡρον, meaning ""butter""), also known under the systematic name butanoic acid, abbreviated BTA, is a carboxylic acid with the structural formula CH3CH2CH2-COOH. Salts and esters of butyric acid are known as butyrates or butanoates. Butyric acid is found in milk, especially goat, sheep and buffalo milk, butter, parmesan cheese, and as a product of anaerobic fermentation (including in the colon and as body odor). It has an unpleasant smell and acrid taste, with a sweetish aftertaste (similar to ether). It can be detected by mammals with good scent detection abilities (such as dogs) at 10 parts per billion, whereas humans can detect it in concentrations above 10 parts per million.Butyric acid is present in, and is the main distinctive smell of, human vomit.Butyric acid was first observed (in impure form) in 1814 by the French chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul. By 1818, he had purified it sufficiently to characterize it. The name of butyric acid comes from the Latin word for butter, butyrum (or buturum), the substance in which butyric acid was first found.