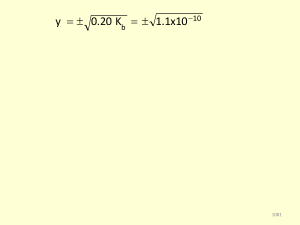LipidCat+AAmetabolism
... LDLs deliver cholesterol to peripheral tissues via cell-surface binding High intracellular [cholesterol] inhibits synthesis of HMGCoA reductase and the receptor People without LDL receptor: cholesterol accumulates in the blood and gets deposited in skin and arteries This risk leads to the descriptio ...
... LDLs deliver cholesterol to peripheral tissues via cell-surface binding High intracellular [cholesterol] inhibits synthesis of HMGCoA reductase and the receptor People without LDL receptor: cholesterol accumulates in the blood and gets deposited in skin and arteries This risk leads to the descriptio ...
supplementary text 1
... Current model of the cytokinin and abscisic acid metabolism mechanisms in ...
... Current model of the cytokinin and abscisic acid metabolism mechanisms in ...
Kofaktörler - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
... groups (fatty acids) are made wmore water soluble w/CoA attached ...
... groups (fatty acids) are made wmore water soluble w/CoA attached ...
The Mechanism of Propionic Acid Formation by
... by the difference in the amounts of acetate converted to CO, due to their different levels of oxidation as indicated by the experiments of Carson (1948). It appears that the large variations reported in the literature for the ratio of propionic acid :acetic acid in fermentations of glucose and lacta ...
... by the difference in the amounts of acetate converted to CO, due to their different levels of oxidation as indicated by the experiments of Carson (1948). It appears that the large variations reported in the literature for the ratio of propionic acid :acetic acid in fermentations of glucose and lacta ...
16N-containing Substances
... -Side chains: different porphyrins vary of the side chain that are attached to pyrrole rings. *Distribution of side chains: different types I, II, III, IV of porphyrins. ...
... -Side chains: different porphyrins vary of the side chain that are attached to pyrrole rings. *Distribution of side chains: different types I, II, III, IV of porphyrins. ...
citric acid cycle - usmle step 1 and 2 for android
... Citrate is freely permeable across the mitochondrial membrane It serves as a good source of cytosolic acetyl CoA which is used for synthesis of fatty acids Citrate inhibits phosphofructokinase and activates acetyl CoA carboxylase 2 & 3. Citrate is isomerized to isocitrate by enzyme aconitase ...
... Citrate is freely permeable across the mitochondrial membrane It serves as a good source of cytosolic acetyl CoA which is used for synthesis of fatty acids Citrate inhibits phosphofructokinase and activates acetyl CoA carboxylase 2 & 3. Citrate is isomerized to isocitrate by enzyme aconitase ...
chemistry 103 - chem.uwec.edu
... Example: Calculate the pH of a buffer system containing 1.0 M CH3CO2H and 1.0 M NaCH3CO2. What is the pH of the buffer after the addition of 0.10 moles of gaseous HCl to 1.00 liter of the buffer solution? The Ka for acetic acid is 1.8 x 10-5. Because acetic acid is a weak acid, we can ignore the sm ...
... Example: Calculate the pH of a buffer system containing 1.0 M CH3CO2H and 1.0 M NaCH3CO2. What is the pH of the buffer after the addition of 0.10 moles of gaseous HCl to 1.00 liter of the buffer solution? The Ka for acetic acid is 1.8 x 10-5. Because acetic acid is a weak acid, we can ignore the sm ...
Multiple Choice Review- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
... 38. How many turns of the Calvin Cycle are needed to create one molecule of glucose? a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 6 39. Which of the following is the reduced form of a molecule used only in photosynthesis and not in cellular respiration? a. NADH b. FADH2 c. NAD+ d. NADPH 40. Which of the following is not a res ...
... 38. How many turns of the Calvin Cycle are needed to create one molecule of glucose? a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 6 39. Which of the following is the reduced form of a molecule used only in photosynthesis and not in cellular respiration? a. NADH b. FADH2 c. NAD+ d. NADPH 40. Which of the following is not a res ...
lec32_F2015
... molecules (60 kJ/mol). The released pyrophosphate is hydrolyzed to inorganic phosphate, making the overall ΔG negative for the reaction (indirect coupling). Note: it is only necessary to utilize ATP once in the activation of the fatty acid. B. Transport into mitochondria: The acyl-CoA is transported ...
... molecules (60 kJ/mol). The released pyrophosphate is hydrolyzed to inorganic phosphate, making the overall ΔG negative for the reaction (indirect coupling). Note: it is only necessary to utilize ATP once in the activation of the fatty acid. B. Transport into mitochondria: The acyl-CoA is transported ...
Cell Respiration PP
... acid(aka citrate) • The carbons from the acetyle group are oxidized into 2CO2 • 3 molecules of NAD+ are reduced into NADH • 1 molecule of FAD is reduced into FADH2 • 1 ATP is produced • The citrate is converted back into oxaloacetate. *this happens 2X per glucose ...
... acid(aka citrate) • The carbons from the acetyle group are oxidized into 2CO2 • 3 molecules of NAD+ are reduced into NADH • 1 molecule of FAD is reduced into FADH2 • 1 ATP is produced • The citrate is converted back into oxaloacetate. *this happens 2X per glucose ...
Questions for Respiration and Photoshyntesis
... 28. Where do they occur? Thylakoid membranes 29. What are the products of the dark reactions? G3P (used to make glucose and other organic molecules), 30. Where do they occur? Stroma 31. Describe the structure of the chloroplast and mitochondria. SEE BOARD 32. What happens when a pigment absorbs a ph ...
... 28. Where do they occur? Thylakoid membranes 29. What are the products of the dark reactions? G3P (used to make glucose and other organic molecules), 30. Where do they occur? Stroma 31. Describe the structure of the chloroplast and mitochondria. SEE BOARD 32. What happens when a pigment absorbs a ph ...
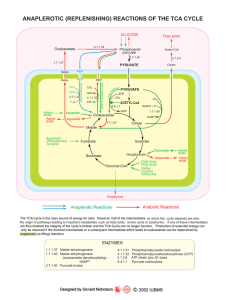
Aerobic Metabolism: The Citric Acid Cycle
... the energy charge of the cell is high. Such enzymes include the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex that synthesizes the acetyl-CoA needed for the first reaction of the TCA cycle. Also the enzymes citrate synthase, isocitrate dehydrogenase and alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, that regulate the firs ...
... the energy charge of the cell is high. Such enzymes include the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex that synthesizes the acetyl-CoA needed for the first reaction of the TCA cycle. Also the enzymes citrate synthase, isocitrate dehydrogenase and alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, that regulate the firs ...
Lipid metabolism
... Use of ketone bodies by the extrahepatal tissues • acetoacetate and 3-hydroxybutyrate are reconverted to acetyl-CoA (→ citric acid cycle) • is located in matrix of mitochondria of the peripheral tissues • is significant in skeletal muscles, heart and also in the brain if lack of Glc occurs ...
... Use of ketone bodies by the extrahepatal tissues • acetoacetate and 3-hydroxybutyrate are reconverted to acetyl-CoA (→ citric acid cycle) • is located in matrix of mitochondria of the peripheral tissues • is significant in skeletal muscles, heart and also in the brain if lack of Glc occurs ...
Definitions of Acids and Bases Electrolytes
... a solution of a weak electrolyte conducts a weak electrical current low concentration of mobile ions present in solution substance dissolves and dissociates less than 100% into ions (some dissociates into ions and the rest dissolves as neutral molecules) weak electrolytes: weak acids and weak bases ...
... a solution of a weak electrolyte conducts a weak electrical current low concentration of mobile ions present in solution substance dissolves and dissociates less than 100% into ions (some dissociates into ions and the rest dissolves as neutral molecules) weak electrolytes: weak acids and weak bases ...
Aerobic Metabolism: The Citric Acid Cycle
... the energy charge of the cell is high. Such enzymes include the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex that synthesizes the acetyl-CoA needed for the first reaction of the TCA cycle. Also the enzymes citrate synthase, isocitrate dehydrogenase and alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, that regulate the firs ...
... the energy charge of the cell is high. Such enzymes include the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex that synthesizes the acetyl-CoA needed for the first reaction of the TCA cycle. Also the enzymes citrate synthase, isocitrate dehydrogenase and alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, that regulate the firs ...
Amino Acid Differences in the Deduced 5
... restriction site at the starting ATG and a HindIII site just behind the stop codon. The NcoI/HindIII restriction fragment was then ligated into the expression vector, and bacteria (HB 101) were transformed with the recombinant plasmid. Then bacteria were cultured at 37°C in 5 mL of LB medium contain ...
... restriction site at the starting ATG and a HindIII site just behind the stop codon. The NcoI/HindIII restriction fragment was then ligated into the expression vector, and bacteria (HB 101) were transformed with the recombinant plasmid. Then bacteria were cultured at 37°C in 5 mL of LB medium contain ...
Role of Water soluble Vitamins in Food Industry
... this oxidation that accelerates the reduction of nitrosomet-myoglobin to nitrosomyoglobin, which imparts to cured meats their characteristic color. Ascorbic acid can prevent nitrosamine formation in cured meats by reducing nitrate to nitrogen oxide, which will not be able to react with the amines to ...
... this oxidation that accelerates the reduction of nitrosomet-myoglobin to nitrosomyoglobin, which imparts to cured meats their characteristic color. Ascorbic acid can prevent nitrosamine formation in cured meats by reducing nitrate to nitrogen oxide, which will not be able to react with the amines to ...
第六章 脂类代谢
... adipocytes are hydrolyzed by lipases, to produce free fatty acids (FFA) and glycerol, which are released to the blood, this process is called fat mobilization. ...
... adipocytes are hydrolyzed by lipases, to produce free fatty acids (FFA) and glycerol, which are released to the blood, this process is called fat mobilization. ...
第六章 脂类代谢
... adipocytes are hydrolyzed by lipases, to produce free fatty acids (FFA) and glycerol, which are released to the blood, this process is called fat mobilization. ...
... adipocytes are hydrolyzed by lipases, to produce free fatty acids (FFA) and glycerol, which are released to the blood, this process is called fat mobilization. ...
Uncommon pathways of metabolism among lactic acid bacteria
... shown to produce unusual amino acid derivatives from ornithine and lysine. Analysis of the intraceUular amino acid pool of Lactococc~.s lactls strain 133 during growth in 'spent' medium, revealed high levels of a neutral compound, tentatively identified as ' valine' [39]. This new amino acid, which ...
... shown to produce unusual amino acid derivatives from ornithine and lysine. Analysis of the intraceUular amino acid pool of Lactococc~.s lactls strain 133 during growth in 'spent' medium, revealed high levels of a neutral compound, tentatively identified as ' valine' [39]. This new amino acid, which ...
Thin-Layer Chromatography: Applying TLC as a
... synthesis of aspirin. For example, when using pure hexane the entire solvent has a nonpolar composition. Therefore acetylsalicylic acid, the more nonpolar compound, will be more attracted to the mobile phase and move with the hexane solvent while salicylic acid, the more polar compound, will be extr ...
... synthesis of aspirin. For example, when using pure hexane the entire solvent has a nonpolar composition. Therefore acetylsalicylic acid, the more nonpolar compound, will be more attracted to the mobile phase and move with the hexane solvent while salicylic acid, the more polar compound, will be extr ...
Quinolizidine Alkaloids
... * They are characterized by the presence of two fused pyrrolidine rings . * There is a common nitrogen between these two rings . * They are based on the presence of two five membered nitrogenous rings , we said before that the five membered heterocyclic ring is derived from the amino acid ornithine ...
... * They are characterized by the presence of two fused pyrrolidine rings . * There is a common nitrogen between these two rings . * They are based on the presence of two five membered nitrogenous rings , we said before that the five membered heterocyclic ring is derived from the amino acid ornithine ...
Butyric acid
Butyric acid (from Greek βούτῡρον, meaning ""butter""), also known under the systematic name butanoic acid, abbreviated BTA, is a carboxylic acid with the structural formula CH3CH2CH2-COOH. Salts and esters of butyric acid are known as butyrates or butanoates. Butyric acid is found in milk, especially goat, sheep and buffalo milk, butter, parmesan cheese, and as a product of anaerobic fermentation (including in the colon and as body odor). It has an unpleasant smell and acrid taste, with a sweetish aftertaste (similar to ether). It can be detected by mammals with good scent detection abilities (such as dogs) at 10 parts per billion, whereas humans can detect it in concentrations above 10 parts per million.Butyric acid is present in, and is the main distinctive smell of, human vomit.Butyric acid was first observed (in impure form) in 1814 by the French chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul. By 1818, he had purified it sufficiently to characterize it. The name of butyric acid comes from the Latin word for butter, butyrum (or buturum), the substance in which butyric acid was first found.