Vitamins - Shanyar
... • The haematological feature is megaloblastic anemia • The neurological disease sometimes predominates: B12 (not folate) is needed for the integrity of mylin • In severe deficiency there is demylination manifested as peripheral neuropathy, spinal cord degeneration, dementia and optic atrophy • Treat ...
... • The haematological feature is megaloblastic anemia • The neurological disease sometimes predominates: B12 (not folate) is needed for the integrity of mylin • In severe deficiency there is demylination manifested as peripheral neuropathy, spinal cord degeneration, dementia and optic atrophy • Treat ...
Cellular Respiration
... • If no oxygen is available- the process stops. • If oxygen becomes available, the process moves onto oxidative reduction & the kreb’s cycle. • Possible for 36 ATP to be made. ...
... • If no oxygen is available- the process stops. • If oxygen becomes available, the process moves onto oxidative reduction & the kreb’s cycle. • Possible for 36 ATP to be made. ...
Titration curve of amino acids
... Substances having this dual nature are amphoteric. So, amino acids in aqueous solution are exist predominantly in isoelectric form. The characteristic pH at which the net electric charge is zero is called the isoelectric point (pI). So, an amino acid has a net negative charge at any pH above its pI, ...
... Substances having this dual nature are amphoteric. So, amino acids in aqueous solution are exist predominantly in isoelectric form. The characteristic pH at which the net electric charge is zero is called the isoelectric point (pI). So, an amino acid has a net negative charge at any pH above its pI, ...
Supplementary Text - Overview of nutrition for endurance athletes
... integrity. Therefore, it is relevant to also consider the possible beneficial role of gastrointestinal microbial metabolism in relation to sports nutrition. Not only does gut bacterial metabolism contribute significantly to the body’s energy balance [16], but one of the metabolic products, the short ...
... integrity. Therefore, it is relevant to also consider the possible beneficial role of gastrointestinal microbial metabolism in relation to sports nutrition. Not only does gut bacterial metabolism contribute significantly to the body’s energy balance [16], but one of the metabolic products, the short ...
ppt file/carboxilase
... needs Mg2+ as cofactor to bind ATP K+, VO2+ as activators to bind HCO3Mn2+ to maintain enzyme structure ...
... needs Mg2+ as cofactor to bind ATP K+, VO2+ as activators to bind HCO3Mn2+ to maintain enzyme structure ...
No Slide Title
... The amino acid sequence (also called primary structure) of a protein is the order of the amino acids in the protein chain. The sequence is always read from the N-terminus to the Cterminus of the protein. ...
... The amino acid sequence (also called primary structure) of a protein is the order of the amino acids in the protein chain. The sequence is always read from the N-terminus to the Cterminus of the protein. ...
Anaerobic and Aerobic Glycolysis
... how does aerobic metabolism also help energize our muscles? ~The three main energy sources for our muscles. ...
... how does aerobic metabolism also help energize our muscles? ~The three main energy sources for our muscles. ...
... 50% yield with >98% regioselectivity by reaction of the corresponding free sugar with ethyl L-lactate in the presence of 10% water. Compounds 2a and 2b were further converted to 4a and 4b, respectively, via reaction with pyruvate catalyzed by sialic acid aldolase. Compounds 3a and 3b were deoxygenat ...
Metabolism
... – Takes place in liver & stimulated by insulin – Body can store about 500 grams of glycogen (25% liver, 75% muscle) – Glycogenolysis - catabolism of glycogen • Gluconeogenesis - protein (certain AA’s) or fat (glycerol) glucose – Occurs when starving, eating low carbo meals, or hormonal stimulation ...
... – Takes place in liver & stimulated by insulin – Body can store about 500 grams of glycogen (25% liver, 75% muscle) – Glycogenolysis - catabolism of glycogen • Gluconeogenesis - protein (certain AA’s) or fat (glycerol) glucose – Occurs when starving, eating low carbo meals, or hormonal stimulation ...
Biosynthesis of Plant Secondary metabolites
... The metabolic process of glycoside formation essentially consists of two parts. 1.The first part of biosynthesis is the reactions by means of which various type of aglycones are formed, where as the 2. Other part of biosynthesis process takes into account metabolic pathway involving coupling of agly ...
... The metabolic process of glycoside formation essentially consists of two parts. 1.The first part of biosynthesis is the reactions by means of which various type of aglycones are formed, where as the 2. Other part of biosynthesis process takes into account metabolic pathway involving coupling of agly ...
Lecture Presentation to accompany Principles of Life
... Lipids break down to fatty acids and glycerol. Fatty acids can be converted to acetyl CoA. Proteins are hydrolyzed to amino acids that can feed into glycolysis or the citric acid cycle. ...
... Lipids break down to fatty acids and glycerol. Fatty acids can be converted to acetyl CoA. Proteins are hydrolyzed to amino acids that can feed into glycolysis or the citric acid cycle. ...
Predicted effects of mineral neutralization and bisulfate - CE-CERT
... been shown to increase with removal of hemicellulose (2). Furthermore, the addition of dilute acid accelerates the breakdown of hemicellulose through the generation of greater concentrations of hydrogen ions and also improves recovery of hemicellulose sugars for later fermentation to ethanol and oth ...
... been shown to increase with removal of hemicellulose (2). Furthermore, the addition of dilute acid accelerates the breakdown of hemicellulose through the generation of greater concentrations of hydrogen ions and also improves recovery of hemicellulose sugars for later fermentation to ethanol and oth ...
Ch. 33 Synthesis of Fatty acids, Triacylglycerols, Membrane lipids
... • 16-C Palmitate is typical product • FAS is large enzyme: 2 subunits (one polypeptide each) with 7 catalytic activities and ACP domain • ACP – acyl carrier protein segment (Ser) is joined to a derivative of coenzyme A: • Oriented with phosphopantetheinyl SH group (PSH) of one subunit near Cys SH gr ...
... • 16-C Palmitate is typical product • FAS is large enzyme: 2 subunits (one polypeptide each) with 7 catalytic activities and ACP domain • ACP – acyl carrier protein segment (Ser) is joined to a derivative of coenzyme A: • Oriented with phosphopantetheinyl SH group (PSH) of one subunit near Cys SH gr ...
Biology Name_____________________________________
... information, graphic organizers not only help categorize facts but serve as a memory aid. You will make a graphic organizer that will serve as a study aid for this chapter. Your organizer must include symbols, pictures, diagrams, charts, etc. Do not simply put the words on a piece of paper. This ass ...
... information, graphic organizers not only help categorize facts but serve as a memory aid. You will make a graphic organizer that will serve as a study aid for this chapter. Your organizer must include symbols, pictures, diagrams, charts, etc. Do not simply put the words on a piece of paper. This ass ...
ppt
... Ceramide is central molecule • Serine basis • Fatty acid addition, release CO2 • Reduction • Other fatty acid to NH2 group • Oxidation ...
... Ceramide is central molecule • Serine basis • Fatty acid addition, release CO2 • Reduction • Other fatty acid to NH2 group • Oxidation ...
AP Biology Cell Respiration Quiz Study Guide
... 4. How do FADH2 and NADH function similarly? How are they different? 5. What is the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain? 6. From what macromolecules would you obtain the highest amount of ATP? 7. What is chemiosmosis? 8. Which respiratory process generates the most ATP? 9. Why is ...
... 4. How do FADH2 and NADH function similarly? How are they different? 5. What is the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain? 6. From what macromolecules would you obtain the highest amount of ATP? 7. What is chemiosmosis? 8. Which respiratory process generates the most ATP? 9. Why is ...
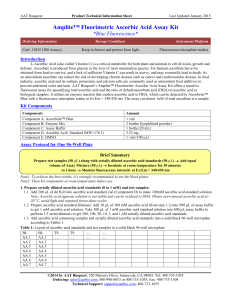
13835_Amplite™ Fluorimetric Ascorbic Acid Assay
... L-Ascorbic Acid (also called Vitamin C) is a critical metabolite for both plant and animals in cell division, growth and defense. Ascorbate is produced from glucose in the liver of most mammalian species. For humans ascorbate has to be obtained from food to survive, and a lack of sufficient Vitamin ...
... L-Ascorbic Acid (also called Vitamin C) is a critical metabolite for both plant and animals in cell division, growth and defense. Ascorbate is produced from glucose in the liver of most mammalian species. For humans ascorbate has to be obtained from food to survive, and a lack of sufficient Vitamin ...
07 Aromatic compounds. Acids of arom.s.,their salts, esters,amides
... of these are anisidine(C-9) and phenetidine (C-10), which are the methyl and ethyl ethers, respectively. However, it becomes apparent that a free amino group in these compounds, although promoting a strong antipyretic action, was also conducive to methemoglobin formation. The only exception to the p ...
... of these are anisidine(C-9) and phenetidine (C-10), which are the methyl and ethyl ethers, respectively. However, it becomes apparent that a free amino group in these compounds, although promoting a strong antipyretic action, was also conducive to methemoglobin formation. The only exception to the p ...
Biosc_48_Chapter_5_lecture
... b. Involved in thermogenesis (heat production), especially in newborns c. Adults also have some brown fat that contributes to calories and heat production d. Sympathetic release of norepinephrine causes brown fat to form an uncoupling protein called UCPI; H+ leaks out of inner mitochondrial membrane ...
... b. Involved in thermogenesis (heat production), especially in newborns c. Adults also have some brown fat that contributes to calories and heat production d. Sympathetic release of norepinephrine causes brown fat to form an uncoupling protein called UCPI; H+ leaks out of inner mitochondrial membrane ...
Lecture 39 - Amino Acid Metabolism 2
... mutations in the tyrosinase gene which is required for pigment biosynthesis ...
... mutations in the tyrosinase gene which is required for pigment biosynthesis ...
physiology – metabolism
... B. Ketone bodies are metabolized in liver normally C. Ketone bodies accumulates as entry of acetic acid into the Kreb cycle is reduced D. In intracellular glucose depletion, fatty liver results E. Carbohydrate is antiketogenic 20. Ketosis occurs during: A. Starvation B. Diabetes mellitus C. High fat ...
... B. Ketone bodies are metabolized in liver normally C. Ketone bodies accumulates as entry of acetic acid into the Kreb cycle is reduced D. In intracellular glucose depletion, fatty liver results E. Carbohydrate is antiketogenic 20. Ketosis occurs during: A. Starvation B. Diabetes mellitus C. High fat ...
Butyric acid
Butyric acid (from Greek βούτῡρον, meaning ""butter""), also known under the systematic name butanoic acid, abbreviated BTA, is a carboxylic acid with the structural formula CH3CH2CH2-COOH. Salts and esters of butyric acid are known as butyrates or butanoates. Butyric acid is found in milk, especially goat, sheep and buffalo milk, butter, parmesan cheese, and as a product of anaerobic fermentation (including in the colon and as body odor). It has an unpleasant smell and acrid taste, with a sweetish aftertaste (similar to ether). It can be detected by mammals with good scent detection abilities (such as dogs) at 10 parts per billion, whereas humans can detect it in concentrations above 10 parts per million.Butyric acid is present in, and is the main distinctive smell of, human vomit.Butyric acid was first observed (in impure form) in 1814 by the French chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul. By 1818, he had purified it sufficiently to characterize it. The name of butyric acid comes from the Latin word for butter, butyrum (or buturum), the substance in which butyric acid was first found.