What do you know about Cellular Respiration?
... Fatty acids are broken down by beta oxidation and yield acetyl CoA An oxidized gram of fat produces more than twice as much ATP as an oxidized gram of carbohydrate ...
... Fatty acids are broken down by beta oxidation and yield acetyl CoA An oxidized gram of fat produces more than twice as much ATP as an oxidized gram of carbohydrate ...
Oxidation and biosynthesis of fatty acids
... Sources of NADPH for Fatty Acid Synthesis 1. One molecule of NADPH is generated for each molecule of acetyl CoA that is transferred from mitochondria to the cytosol (malic enzyme). ...
... Sources of NADPH for Fatty Acid Synthesis 1. One molecule of NADPH is generated for each molecule of acetyl CoA that is transferred from mitochondria to the cytosol (malic enzyme). ...
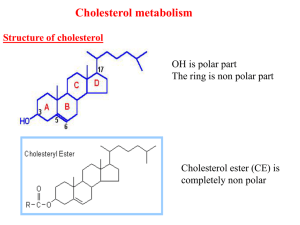
Lec4 Cholesterol met..
... competitively inhibit HMG-CoA reductase. They are used to decrease cholesterol levels in patients with hypercholesterolemia. 3- Diet: its activity activated by high CHO and fat diet and inhibited in starvation. 4- Hormonal regulation: insulin stimulate protein phosphatase enzyme which phosphorylates ...
... competitively inhibit HMG-CoA reductase. They are used to decrease cholesterol levels in patients with hypercholesterolemia. 3- Diet: its activity activated by high CHO and fat diet and inhibited in starvation. 4- Hormonal regulation: insulin stimulate protein phosphatase enzyme which phosphorylates ...
Novel regulatory roles of omega-3 fatty acids in metabolic pathways
... spots with 2 μL each. Calibration was done first externally to obtain 10–20 ppm accuracy with known peptide standards. Internal calibration was performed with known matrix cluster signals and tryptic autolysis peptide signals to achieve a mass accuracy of less than 100 ppm. Single MS with m/z range ...
... spots with 2 μL each. Calibration was done first externally to obtain 10–20 ppm accuracy with known peptide standards. Internal calibration was performed with known matrix cluster signals and tryptic autolysis peptide signals to achieve a mass accuracy of less than 100 ppm. Single MS with m/z range ...
The model was provided with glucose and FFA inputs to
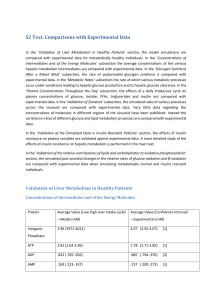
... glucose metabolism, oxidative glucose metabolism and β-oxidation with experimental data from Mandarino et al. for the processes in muscle [14] (presented normalised to basal). Since the experimental results in Tables 3 and 4 are expressed per kg of liver, absolute comparisons of the rates are not po ...
... glucose metabolism, oxidative glucose metabolism and β-oxidation with experimental data from Mandarino et al. for the processes in muscle [14] (presented normalised to basal). Since the experimental results in Tables 3 and 4 are expressed per kg of liver, absolute comparisons of the rates are not po ...
PloS one
... understand the organization of relational ties between metabolites, reflecting not only substrate-product relationships but also regulatory effects, one may apply various similarity measures to (normalized) metabolic profiles. The resulting similarity matrices can, in turn, be effectively used to ge ...
... understand the organization of relational ties between metabolites, reflecting not only substrate-product relationships but also regulatory effects, one may apply various similarity measures to (normalized) metabolic profiles. The resulting similarity matrices can, in turn, be effectively used to ge ...
Insulin hormone: Mechanism and effects on the body and
... reduce the blood glucose levels. In other words, it have regulator role on blood sugar level; insulin secretion is known to be associated with an increase in the amount of energy. Insulin secretion is related with increasing glucose level. It has been shown that it is closely related with intracellu ...
... reduce the blood glucose levels. In other words, it have regulator role on blood sugar level; insulin secretion is known to be associated with an increase in the amount of energy. Insulin secretion is related with increasing glucose level. It has been shown that it is closely related with intracellu ...
Chapter 25
... gluconeogenesis, the pentose phosphate pathway, and the Calvin cycle. Pyruvate, oxaloacetate and -ketoglutarate are keto acids. Pyruvate derives from a number of sources including glycolysis and amino acids and is the port of entry into the citric acid cycle for glucose-derived carbons. Oxaloacetat ...
... gluconeogenesis, the pentose phosphate pathway, and the Calvin cycle. Pyruvate, oxaloacetate and -ketoglutarate are keto acids. Pyruvate derives from a number of sources including glycolysis and amino acids and is the port of entry into the citric acid cycle for glucose-derived carbons. Oxaloacetat ...
Metabolic Responses to Cardiac Hypoxia
... when these precursors were present. The aminotransferase inhibitor, aminooxyacetate, reduced succinate production by hypoxic papillary muscles. This finding demonstrated a close relationship between transamination of amino acids and succinate production. In addition, it is suggested that anaerobic m ...
... when these precursors were present. The aminotransferase inhibitor, aminooxyacetate, reduced succinate production by hypoxic papillary muscles. This finding demonstrated a close relationship between transamination of amino acids and succinate production. In addition, it is suggested that anaerobic m ...
glucose
... removal of ATPase byproducts, ADP, Pi and H+, to sustain efficient energy utilization. Shuttles comprise near equilibrium enzymes capable of facilitating ligand transfer between cellular compartments by rapidly relaying the displacement of equilibrium. ATP delivery is facilitated through creatine ki ...
... removal of ATPase byproducts, ADP, Pi and H+, to sustain efficient energy utilization. Shuttles comprise near equilibrium enzymes capable of facilitating ligand transfer between cellular compartments by rapidly relaying the displacement of equilibrium. ATP delivery is facilitated through creatine ki ...
Multi-Organ Contribution to the Metabolic Plasma Profile Using
... is advantageous to divide the variables into conceptually meaningful blocks and apply hierarchical modelling. The division into blocks results in two model levels. One level (the upper level) explains the relationship between each block whereas the other level (the lower level) contains detailed inf ...
... is advantageous to divide the variables into conceptually meaningful blocks and apply hierarchical modelling. The division into blocks results in two model levels. One level (the upper level) explains the relationship between each block whereas the other level (the lower level) contains detailed inf ...
Chapter 9
... The Pathway of Electron Transport • The electron transport chain is in the inner membrane (cristae) of the mitochondrion • Most of the chain’s components are proteins, which exist in multiprotein complexes • The carriers alternate reduced and oxidized states as they accept and donate electrons • El ...
... The Pathway of Electron Transport • The electron transport chain is in the inner membrane (cristae) of the mitochondrion • Most of the chain’s components are proteins, which exist in multiprotein complexes • The carriers alternate reduced and oxidized states as they accept and donate electrons • El ...
Short-Term Overexpression of a Constitutively Active Form of AMP
... Injection of recombinant Ads and fasting/refeeding experiments. Mice were anesthetized with isoflurane, and Ad -gal or Ad AMPK␣2-CA (1 ⫻ 109 plaque-forming units) was injected into the penis vein. After Ad injection, C57BL/6j mice were divided into two groups: fasted and refed. The fasted group was ...
... Injection of recombinant Ads and fasting/refeeding experiments. Mice were anesthetized with isoflurane, and Ad -gal or Ad AMPK␣2-CA (1 ⫻ 109 plaque-forming units) was injected into the penis vein. After Ad injection, C57BL/6j mice were divided into two groups: fasted and refed. The fasted group was ...
Interaction of Fish Oil and Conjugated Linoleic Acid in
... RNA analysis. RNA in the liver and epididymal adipose tissue was extracted (18), and mRNA levels in these tissues were analyzed by quantitative real-time PCR, using a Prism 7000 sequence detection system (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA). Total RNA was treated with RNase-free DNase I (Roche Diag ...
... RNA analysis. RNA in the liver and epididymal adipose tissue was extracted (18), and mRNA levels in these tissues were analyzed by quantitative real-time PCR, using a Prism 7000 sequence detection system (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA). Total RNA was treated with RNase-free DNase I (Roche Diag ...
CH - IS MU
... 1 Amino acids that are converted to pyruvate: Alanine - by transamination. Serine - by deamination catalyzed of dehydratase (hydrolyase). Glycine - by accepting one-carbon group gives serine. Threonine - by splitting gives glycine that may give serine. Cysteine also gives pyruvate by deamination an ...
... 1 Amino acids that are converted to pyruvate: Alanine - by transamination. Serine - by deamination catalyzed of dehydratase (hydrolyase). Glycine - by accepting one-carbon group gives serine. Threonine - by splitting gives glycine that may give serine. Cysteine also gives pyruvate by deamination an ...
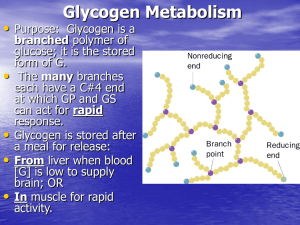
Glycogen Metabolism - http://www.utm.edu
... catalyzed by phosphoprotein phosphatase 1 (PP1). In muscle, phosphorylation of a regulatory glycogen binding protein, GM in response to insulin (which causes dephosphorylation of other Es) at site 1 activates PP1. This results in the opposite activities to the above (GS active to store the plentiful ...
... catalyzed by phosphoprotein phosphatase 1 (PP1). In muscle, phosphorylation of a regulatory glycogen binding protein, GM in response to insulin (which causes dephosphorylation of other Es) at site 1 activates PP1. This results in the opposite activities to the above (GS active to store the plentiful ...
Chapter 32 - How Animals Harvest Energy Stored in Nutrients
... Animals require a constant supply of energy to perform biological work. The energy-rich molecule ATP usually provides this energy. All animals can generate ATP by breaking down organic nutrients (carbohydrates, fats, and proteins). The energy released is used to join ADP and phosphate (Pi) to form A ...
... Animals require a constant supply of energy to perform biological work. The energy-rich molecule ATP usually provides this energy. All animals can generate ATP by breaking down organic nutrients (carbohydrates, fats, and proteins). The energy released is used to join ADP and phosphate (Pi) to form A ...
Propionate stimulates pyruvate oxidation in the - AJP
... based on the appearance of hyperpolarized (HP) [13C]bicarbonate derived from HP [1-13C]pyruvate has been proposed as a method for identifying viable myocardium. The efficacy of propionate for increasing PDH flux in the setting of PDH inhibition by an alternative substrate was studied using isotopome ...
... based on the appearance of hyperpolarized (HP) [13C]bicarbonate derived from HP [1-13C]pyruvate has been proposed as a method for identifying viable myocardium. The efficacy of propionate for increasing PDH flux in the setting of PDH inhibition by an alternative substrate was studied using isotopome ...
PLUMBAGO ZEYLANICA TOXICITY IN RATS Research Article
... damage caused by paracetamol. The above changes can be considered as an expression of the functional improvement of hepatocytes, which may be caused by an accelerated regeneration of parenchymal cells. Effective control of alkaline phosphatase, lactate dehydrogenase, γ‐glutamyl ...
... damage caused by paracetamol. The above changes can be considered as an expression of the functional improvement of hepatocytes, which may be caused by an accelerated regeneration of parenchymal cells. Effective control of alkaline phosphatase, lactate dehydrogenase, γ‐glutamyl ...
Chapter 8: Energy generation:glycolysis
... incremental steps, transferring it to ATP molecules, can be described as a two-stage process (Fig. 8.2). The first stage is called glycolysis. Each six-carbon glucose molecule is broken down to two molecules of the three-carbon sugar called pyruvate. Glycolysis does not require oxygen and so can occ ...
... incremental steps, transferring it to ATP molecules, can be described as a two-stage process (Fig. 8.2). The first stage is called glycolysis. Each six-carbon glucose molecule is broken down to two molecules of the three-carbon sugar called pyruvate. Glycolysis does not require oxygen and so can occ ...
Once this was accomplished we were able to study
... from 29 to 42 per cent of those reported in Table IV; however, the distribution and ratio of LDH activity in the individual units of the nephron remained the same. The over-all decrease in LDH activity was found to coincide with the use of a new batch of DPNH (Sigma). An investigation planned to fin ...
... from 29 to 42 per cent of those reported in Table IV; however, the distribution and ratio of LDH activity in the individual units of the nephron remained the same. The over-all decrease in LDH activity was found to coincide with the use of a new batch of DPNH (Sigma). An investigation planned to fin ...
Mechanistic insights into pancreatic beta
... IRS-2 KO mice display reduced DNA synthesis in response to glucose stimulation in vitro. These results suggest that IRS2 is essential for beta-cell compensation for increased insulin demand due to peripheral insulin resistance. In contrast, increased IRS-2 expression promotes beta-cell replication a ...
... IRS-2 KO mice display reduced DNA synthesis in response to glucose stimulation in vitro. These results suggest that IRS2 is essential for beta-cell compensation for increased insulin demand due to peripheral insulin resistance. In contrast, increased IRS-2 expression promotes beta-cell replication a ...
Pyruvic Acid and Formic Acid Metabolism in Sarcina
... was 6.5 to 6.8. Growth at constant pH. Yeast extract (30 g.) and peptone (30 g.) in 2.8 litres of distilled water were autoclaved in a 5-litre aspirator fitted with a rubber stopper holding a glass pH electrode and ports for alkali addition and gas exit. A tap fitted near the base allowed samples to ...
... was 6.5 to 6.8. Growth at constant pH. Yeast extract (30 g.) and peptone (30 g.) in 2.8 litres of distilled water were autoclaved in a 5-litre aspirator fitted with a rubber stopper holding a glass pH electrode and ports for alkali addition and gas exit. A tap fitted near the base allowed samples to ...
Engineering primary metabolic pathways of industrial
... been substantially superseded by analysis of transcriptomic arrays to detect up- or down-regulation of genes, if genome data were available. This is an interesting alternative to the classic approach for detection of ratelimiting steps, where it is necessary to have extensive knowledge about the pat ...
... been substantially superseded by analysis of transcriptomic arrays to detect up- or down-regulation of genes, if genome data were available. This is an interesting alternative to the classic approach for detection of ratelimiting steps, where it is necessary to have extensive knowledge about the pat ...
Glyceroneogenesis

Glyceroneogenesis is a metabolic pathway which synthesizes glycerol 3-phosphate or triglyceride from precursors other than glucose. Usually glycerol 3-phosphate is generated from glucose by glycolysis, but when glucose concentration drops in the cytosol, it is generated by another pathway called glyceroneogenesis. Glyceroneogenesis uses pyruvate, alanine, glutamine or any substances from the TCA cycle as precursors for glycerol 3-phophate. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPC-K), which is an enzyme that catalyses the decarboxylation of oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate is the main regulator for this pathway. Glyceroneogenesis can be observed in adipose tissue and also liver. It is a significant biochemical pathway which regulates cytosolic lipid levels. Intense suppression of glyceroneogenesis may lead to metabolic disorder such as type 2 diabetes.