Slides PPT - The University of Sydney
... • They develop liver steatosis (fatty livers) probably because of impaired oxidation of fatty acids • A total PEPCK knock out in all tissues is lethal…mice die within days of birth. ...
... • They develop liver steatosis (fatty livers) probably because of impaired oxidation of fatty acids • A total PEPCK knock out in all tissues is lethal…mice die within days of birth. ...
1 glucose 2 molecules acetyl CoA
... • Acetyl CoA combines with oxaloacetic acid to form citric acid. • Citric acid starts the Krebs cycle. – It is a cycle because citric acid moves through a series of reactions to produce oxaloacetic acid again. ...
... • Acetyl CoA combines with oxaloacetic acid to form citric acid. • Citric acid starts the Krebs cycle. – It is a cycle because citric acid moves through a series of reactions to produce oxaloacetic acid again. ...
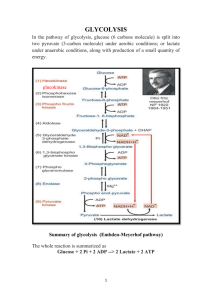
Summary of glycolysis (Embden
... 1. It is the only pathway that is taking place in all the cells (cytoplasm) of the body. 2. Glycolysis is the only source of energy in erythrocytes. 3. In strenuous exercise, when muscle tissue lacks enough oxygen, anaerobic glycolysis forms the major source of energy for muscles. 4. The glycolytic ...
... 1. It is the only pathway that is taking place in all the cells (cytoplasm) of the body. 2. Glycolysis is the only source of energy in erythrocytes. 3. In strenuous exercise, when muscle tissue lacks enough oxygen, anaerobic glycolysis forms the major source of energy for muscles. 4. The glycolytic ...
Digestion Powerpoint - School
... What do proteins provide? As with carbohydrates, proteins are made of chains of chemicals. However, instead of the chain containing identical molecules, in protein these molecules are different. Protein is made up of chains of amino acids. There are over 20 different kinds of amino acid. Protein is ...
... What do proteins provide? As with carbohydrates, proteins are made of chains of chemicals. However, instead of the chain containing identical molecules, in protein these molecules are different. Protein is made up of chains of amino acids. There are over 20 different kinds of amino acid. Protein is ...
Biochemistry of kidney
... In contrast when secretion of ADH is inhibited, it allows dilute urine to be formed. This occures mainly, when plasma sodium concentration falls such as following drinking large quantities of water. This fall is detected by osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus. ...
... In contrast when secretion of ADH is inhibited, it allows dilute urine to be formed. This occures mainly, when plasma sodium concentration falls such as following drinking large quantities of water. This fall is detected by osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus. ...
Seminar compendium 2016/2017
... lungs is more efficient, leading to a better oxygen supply in the cells. How is glucose metabolized in the muscle when the cells get the oxygen they need? Where in the cell do the participating processes take place, and how are substances transported between compartments? How is the aerobic product ...
... lungs is more efficient, leading to a better oxygen supply in the cells. How is glucose metabolized in the muscle when the cells get the oxygen they need? Where in the cell do the participating processes take place, and how are substances transported between compartments? How is the aerobic product ...
Acid - Perkins Science
... mirror images of each other. They are like left- and right-handed gloves: if the palms are facing the same direction, they cannot be superimposed on each other. See D- and L-glyceraldehyde ...
... mirror images of each other. They are like left- and right-handed gloves: if the palms are facing the same direction, they cannot be superimposed on each other. See D- and L-glyceraldehyde ...
Organic Molecules
... liquid at fats. temperature. room The kinks provided by the double bonds prevent the molecules from packing tightly together. ...
... liquid at fats. temperature. room The kinks provided by the double bonds prevent the molecules from packing tightly together. ...
Mitochondrion Pyruvate Oxidation & Kreb`s Cycle
... (biochemist at the Univ. of Sheffield) in 1937. He won the Nobel Prize in 1953 along with Fritz Albert Lipmann who discovered the importance of coenzyme-A. An 8-step process with each step catalyzed by a specific enzyme. It is a cycle because the product of step 8 is the reactant in step 1 (oxaloace ...
... (biochemist at the Univ. of Sheffield) in 1937. He won the Nobel Prize in 1953 along with Fritz Albert Lipmann who discovered the importance of coenzyme-A. An 8-step process with each step catalyzed by a specific enzyme. It is a cycle because the product of step 8 is the reactant in step 1 (oxaloace ...
PATHWAYS THAT HARVEST CHEMICAL ENERGY CHAPTER 9
... • Glycolysis: phosphofructokinase—allosterically inhibited by ATP. • Citric acid cycle: isocitrate dehydrogenase—inhibited by NADH + H+ and ATP. • If ATP levels are high: 1. Accumulation of citrate diverts acetyl CoA to fatty acid synthesis, for storage. 2. Fatty acids may be metabolized later to pr ...
... • Glycolysis: phosphofructokinase—allosterically inhibited by ATP. • Citric acid cycle: isocitrate dehydrogenase—inhibited by NADH + H+ and ATP. • If ATP levels are high: 1. Accumulation of citrate diverts acetyl CoA to fatty acid synthesis, for storage. 2. Fatty acids may be metabolized later to pr ...
Organic Chemistry & Carbohydrates: Structure & Function
... Aldehydes if the carbonyl group is at the end of the carbon skeleton ...
... Aldehydes if the carbonyl group is at the end of the carbon skeleton ...
Figure 5-2
... 10. A molecule that has long chains of hydrocarbons is probably a: a. Carbohydrate c. Lipid b. Protein d. Nucleic acid 11. Glucose and galactose have the same chemical formula (C6H12O6) but different structural arrangements. Glucose and galactose are: a. Isotopes c. Polymers b. Isomers d. Disacchar ...
... 10. A molecule that has long chains of hydrocarbons is probably a: a. Carbohydrate c. Lipid b. Protein d. Nucleic acid 11. Glucose and galactose have the same chemical formula (C6H12O6) but different structural arrangements. Glucose and galactose are: a. Isotopes c. Polymers b. Isomers d. Disacchar ...
Compare and contrast organic molecules and inorganic - bl-whs
... 9. Where do humans get most of their carbohydrates? Diet ...
... 9. Where do humans get most of their carbohydrates? Diet ...
Biochem 462 - public.asu.edu
... Fixation of carbon dioxide during photosynthesis involves which reaction? a) Addition of CO2 to pyruvate to form oxaloacetate and then PEP which undergoes gluconeogenesis to form glucose. b) Addition of CO2 to acetyl Co-enzyme A to form pyruvate which then undergoes gluconeogenesis to form glucose. ...
... Fixation of carbon dioxide during photosynthesis involves which reaction? a) Addition of CO2 to pyruvate to form oxaloacetate and then PEP which undergoes gluconeogenesis to form glucose. b) Addition of CO2 to acetyl Co-enzyme A to form pyruvate which then undergoes gluconeogenesis to form glucose. ...
The_Light_Independent_Reactions
... form an unstable 6 carbon compound. • RuBP is a CO2 acceptor molecule. • This process is catalysed by the enzyme RUBISCO and is a carboxylation reaction • RUBISCO is made in chloroplasts using chloroplast DNA • The 6C compound immediately splits into two molecules of a 3C compound called glycerate-3 ...
... form an unstable 6 carbon compound. • RuBP is a CO2 acceptor molecule. • This process is catalysed by the enzyme RUBISCO and is a carboxylation reaction • RUBISCO is made in chloroplasts using chloroplast DNA • The 6C compound immediately splits into two molecules of a 3C compound called glycerate-3 ...
Theory_2004
... In the early post-absorbtive period, the brain uses about 120g of glucose per day Fatty acids are released once all body glycogen stores have been used up Although we store most of our energy as fat, we cannot convert fatty acids into carbohydrate Net gluconeogenesis is possible from part of triacyl ...
... In the early post-absorbtive period, the brain uses about 120g of glucose per day Fatty acids are released once all body glycogen stores have been used up Although we store most of our energy as fat, we cannot convert fatty acids into carbohydrate Net gluconeogenesis is possible from part of triacyl ...
the science of weight loss - Beyond
... 2. Leptin enhances the body’s ability to access and utilize fat stores as energy. Sahu A. Leptin signaling in the hypothalamus: emphasis on energy homeostasis and leptin resistance. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2003 Dec;24(4):225-253. Wang MY, Orci L, Ravazzola M, Unger RH. Fat storage in adipocytes requi ...
... 2. Leptin enhances the body’s ability to access and utilize fat stores as energy. Sahu A. Leptin signaling in the hypothalamus: emphasis on energy homeostasis and leptin resistance. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2003 Dec;24(4):225-253. Wang MY, Orci L, Ravazzola M, Unger RH. Fat storage in adipocytes requi ...
Nutrition
... cristae of the mitochondria A) Involves membrane proteins acting as H+ pumps that will release energy as an electron is transferred from one to another B) NADH and FADH2 drop off their hydrogen atoms to the chain of electron acceptors C) As the H are dropped off they lose their electrons which trave ...
... cristae of the mitochondria A) Involves membrane proteins acting as H+ pumps that will release energy as an electron is transferred from one to another B) NADH and FADH2 drop off their hydrogen atoms to the chain of electron acceptors C) As the H are dropped off they lose their electrons which trave ...
File
... Liver also manages circulating lipids. Lipids come in many forms: Chylomicrons arrive from intestines and need to be broken down. Very low density lipoproteins (VLDL) are synthesized by hepatocytes which transport the triglycerides synthesized in liver into blood plasma for storage and use. Choles ...
... Liver also manages circulating lipids. Lipids come in many forms: Chylomicrons arrive from intestines and need to be broken down. Very low density lipoproteins (VLDL) are synthesized by hepatocytes which transport the triglycerides synthesized in liver into blood plasma for storage and use. Choles ...
1 - BrainMass
... c. What is/are the molecular reasons for this functional difference? d. How do you suppose a cell can make these two separate molecules without making errors such as glycogen-cellulose hybrid molecules? 2. Diagram the pathway of Glycolysis from glucose to pyruvate, giving structures and names of all ...
... c. What is/are the molecular reasons for this functional difference? d. How do you suppose a cell can make these two separate molecules without making errors such as glycogen-cellulose hybrid molecules? 2. Diagram the pathway of Glycolysis from glucose to pyruvate, giving structures and names of all ...
1. Substrate level phosphorylation A) is part
... The regulation process known as “acceptor control” predicts that in normal mitochondria A) elevated NAD+ increases ATP production B) increased ADP decreases NADH oxidation rate C) decreased ADP slows the respiratory chain D) increased proton gradient increases ATP synthesis ...
... The regulation process known as “acceptor control” predicts that in normal mitochondria A) elevated NAD+ increases ATP production B) increased ADP decreases NADH oxidation rate C) decreased ADP slows the respiratory chain D) increased proton gradient increases ATP synthesis ...
Ketosis

Ketosis /kɨˈtoʊsɨs/ is a metabolic state where most of the body's energy supply comes from ketone bodies in the blood, in contrast to a state of glycolysis where blood glucose provides most of the energy. It is characterised by serum concentrations of ketone bodies over 0.5 millimolar, with low and stable levels of insulin and blood glucose. It is almost always generalized with hyperketonemia, that is, an elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood throughout the body. Ketone bodies are formed by ketogenesis when liver glycogen stores are depleted (or from metabolising medium-chain triglycerides). The main ketone bodies used for energy are acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate, and the levels of ketone bodies are regulated mainly by insulin and glucagon. Most cells in the body can use both glucose and ketone bodies for fuel, and during ketosis, free fatty acids and glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis) fuel the remainder.Longer-term ketosis may result from fasting or staying on a low-carbohydrate diet, and deliberately induced ketosis serves as a medical intervention for intractable epilepsy. In glycolysis, higher levels of insulin promote storage of body fat and block release of fat from adipose tissues, while in ketosis, fat reserves are readily released and consumed. For this reason, ketosis is sometimes referred to as the body's ""fat burning"" mode.