Matter
... – Collection of the combination same type of atom elements and/or – Cannot be compounds or decomposed both. • Compound • USUALLY – 2 or more different heterogeneous atoms chemically bonded together. ...
... – Collection of the combination same type of atom elements and/or – Cannot be compounds or decomposed both. • Compound • USUALLY – 2 or more different heterogeneous atoms chemically bonded together. ...
Study Guide for Composition of Matter Test - seys
... - bar graph: a graph consisting of a series of vertical or horizontal bars representing statistical data - life cycle: all of the stages that a container goes through together are called the life cycle of a product - life-cycle diagram: one way of illustrating each stage in the cycle - raw material: ...
... - bar graph: a graph consisting of a series of vertical or horizontal bars representing statistical data - life cycle: all of the stages that a container goes through together are called the life cycle of a product - life-cycle diagram: one way of illustrating each stage in the cycle - raw material: ...
- Jersey College For Girls
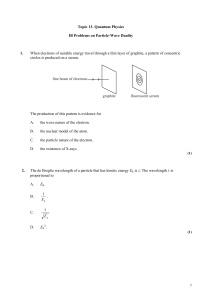
... Q3. Atoms contain three different types of particle. These are electrons, neutrons and protons. (a) Which one of the three particles has a negative charge? ...
... Q3. Atoms contain three different types of particle. These are electrons, neutrons and protons. (a) Which one of the three particles has a negative charge? ...
Important Concepts from Chapter 9 • DRAWING LEWIS ELECTRON
... How to account for three bonds with 120° angle using one spherical s orbital and three p orbitals (that are 90° to each other)? The boron atom in its ground state has only 1 unpaired electron, not the three needed to form three covalent bonds. ...
... How to account for three bonds with 120° angle using one spherical s orbital and three p orbitals (that are 90° to each other)? The boron atom in its ground state has only 1 unpaired electron, not the three needed to form three covalent bonds. ...
Lectuer 15
... - The z component of the angular momentum is determined completely by m through L z = m ħ. - The quantum number m is called the magnetic quantum number because the energy of a hydrogen atom in a magnetic field depends on m. - The (2 Ɩ + 1) – fold degeneracy in the absence of a magnetic field is spli ...
... - The z component of the angular momentum is determined completely by m through L z = m ħ. - The quantum number m is called the magnetic quantum number because the energy of a hydrogen atom in a magnetic field depends on m. - The (2 Ɩ + 1) – fold degeneracy in the absence of a magnetic field is spli ...
Metric conversion chart - Welcome to Chemistry At Central High
... Bonding: estimated ∆H reaction = Bond energy of bonds broken – bonds made Bond order = 1/2 (# bonding electrons – # anti bonding electrons) diamagnetic= all electrons paired; paramagnetic = has unpaired electrons ...
... Bonding: estimated ∆H reaction = Bond energy of bonds broken – bonds made Bond order = 1/2 (# bonding electrons – # anti bonding electrons) diamagnetic= all electrons paired; paramagnetic = has unpaired electrons ...
o Orbital dipole moments. Orbital precession. Spin-orbit interaction.
... o With field on, classically expect random distribution at target. In fact find two bands as beam is split in two. o There is directional quantisation, parallel or antiparallel to B. o Atomic magnetic moment has µz = ±µB. o Find same deflection for all atoms which have an s electron in the outer ...
... o With field on, classically expect random distribution at target. In fact find two bands as beam is split in two. o There is directional quantisation, parallel or antiparallel to B. o Atomic magnetic moment has µz = ±µB. o Find same deflection for all atoms which have an s electron in the outer ...
1.4 Isotopes and Average Atomic Mass
... Atomic mass units are a relative measure used to express the masses of atoms and molecules. All atomic masses relate to the carbon-12 atom Therefore 1u = 1/12 of the mass of a carbon atom Isotopic abundance: the relative amount in which each isotope is present in an element. The average atomic mass ...
... Atomic mass units are a relative measure used to express the masses of atoms and molecules. All atomic masses relate to the carbon-12 atom Therefore 1u = 1/12 of the mass of a carbon atom Isotopic abundance: the relative amount in which each isotope is present in an element. The average atomic mass ...
The atom:
... nucleus. When the electron for H is in the first energy level it is said to be in the ground state. When energy is imparted to the atom, the electron will take that energy and “jump” to a new level, perhaps on n=2 or 3. This is the excited or high energy state. Maintaining the high energy state requ ...
... nucleus. When the electron for H is in the first energy level it is said to be in the ground state. When energy is imparted to the atom, the electron will take that energy and “jump” to a new level, perhaps on n=2 or 3. This is the excited or high energy state. Maintaining the high energy state requ ...
Electronic Structure - Chemistry Teaching Resources
... electrons of an element are located. The Aufbau Principle states that electrons will fill orbitals starting with the orbital of lowest energy. For degenerate orbitals, electrons fill each orbital singly before any orbital gets a second electron (Hund’s Rule of Maximum ...
... electrons of an element are located. The Aufbau Principle states that electrons will fill orbitals starting with the orbital of lowest energy. For degenerate orbitals, electrons fill each orbital singly before any orbital gets a second electron (Hund’s Rule of Maximum ...
vuletic
... Cooling and trapping techniques Stabilizing Ions with Light Ions are a promising qubit for quantum computation. Ions are standardly trapped with time varying (RF) electric fields. These traps are limited in size and by micromotion, residual motion inherent in these RF traps. We are developing a new ...
... Cooling and trapping techniques Stabilizing Ions with Light Ions are a promising qubit for quantum computation. Ions are standardly trapped with time varying (RF) electric fields. These traps are limited in size and by micromotion, residual motion inherent in these RF traps. We are developing a new ...
Science
... computer that works at room temperature. In order to read out the states of the atoms, the researchers had to open up a new bag of tricks. “Atoms are relatively unaffected by the magnetic noise of their surroundings, because they only have a small magnetic moment,” explains Dr Hanson. “This makes th ...
... computer that works at room temperature. In order to read out the states of the atoms, the researchers had to open up a new bag of tricks. “Atoms are relatively unaffected by the magnetic noise of their surroundings, because they only have a small magnetic moment,” explains Dr Hanson. “This makes th ...
atomic physics
... 1. Electrons in atoms orbit the nucleus. 2. The electrons can only orbit stably, without radiating, in certain orbits (called the "stationary orbits”) at a certain discrete set of distances from the nucleus. These orbits are associated with definite energies and are also called energy shells or ener ...
... 1. Electrons in atoms orbit the nucleus. 2. The electrons can only orbit stably, without radiating, in certain orbits (called the "stationary orbits”) at a certain discrete set of distances from the nucleus. These orbits are associated with definite energies and are also called energy shells or ener ...
- Form when atoms SHARE electrons instead of transferring them
... and oxygen) is probably due to the triple bond. A few notes on the triple bond: - For atoms to share three pairs of electrons, they have to move closer to one another than they would if they were sharing one or two pairs of electrons. Triple bonds have the shortest BOND DISTANCE of all covalent bond ...
... and oxygen) is probably due to the triple bond. A few notes on the triple bond: - For atoms to share three pairs of electrons, they have to move closer to one another than they would if they were sharing one or two pairs of electrons. Triple bonds have the shortest BOND DISTANCE of all covalent bond ...
1. Which of the following statements best describes the
... Gas particles are packed closely together in fixed positions. ...
... Gas particles are packed closely together in fixed positions. ...
Electron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6.Electronic configurations describe electrons as each moving independently in an orbital, in an average field created by all other orbitals. Mathematically, configurations are described by Slater determinants or configuration state functions.According to the laws of quantum mechanics, for systems with only one electron, an energy is associated with each electron configuration and, upon certain conditions, electrons are able to move from one configuration to another by the emission or absorption of a quantum of energy, in the form of a photon.Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements. The concept is also useful for describing the chemical bonds that hold atoms together. In bulk materials, this same idea helps explain the peculiar properties of lasers and semiconductors.