Chapter 3 Atoms: The Building Blocks
... chemical reactions or physical changes. The Law of Definite Proportions A chemical compound contains the same elements in exactly the same proportions by mass An atom is the smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of that element All matter is made up of atoms ...
... chemical reactions or physical changes. The Law of Definite Proportions A chemical compound contains the same elements in exactly the same proportions by mass An atom is the smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of that element All matter is made up of atoms ...
doc
... vi. You have one other option: you could reconstruct the invariant mass of the second jet and the W boson reconstructed from jets three and four, where the second jet has an energy of E2=70GeV,and an angle of 30 degrees with the direction of the W boson. What is the invariant mass? Assuming we are t ...
... vi. You have one other option: you could reconstruct the invariant mass of the second jet and the W boson reconstructed from jets three and four, where the second jet has an energy of E2=70GeV,and an angle of 30 degrees with the direction of the W boson. What is the invariant mass? Assuming we are t ...
The Structure of Matter: The Basic Particle Model - ag
... Consequence: A point like object cannot oscillate because this would mean a permanent violation of the momentum law The electron has a mass Consequence: No motion with the speed of light c is possible. This would be a violation of special relativity ...
... Consequence: A point like object cannot oscillate because this would mean a permanent violation of the momentum law The electron has a mass Consequence: No motion with the speed of light c is possible. This would be a violation of special relativity ...
pacing guide - Tallapoosa County Schools
... the Doppler effect. Explaining reasons for differences in speed, frequency, and wavelength of a propagating wave in varying materials Describing uses of different components of the electromagnetic spectrum, including radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiati ...
... the Doppler effect. Explaining reasons for differences in speed, frequency, and wavelength of a propagating wave in varying materials Describing uses of different components of the electromagnetic spectrum, including radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiati ...
Photoelectric Effect 1 Introduction 2 Experiment
... is proportional to the intensity of the light. In fact, the original investigators found the maximum kinetic energy to be independent of the light intensity and instead proportional to the frequency of the light. Thus, blue light created more energetic electrons than did red light (which is of a low ...
... is proportional to the intensity of the light. In fact, the original investigators found the maximum kinetic energy to be independent of the light intensity and instead proportional to the frequency of the light. Thus, blue light created more energetic electrons than did red light (which is of a low ...
Special Issue on Neutrino Research
... by the standards of subatomic particles. Their mass has never been measured accurately. Neutrinos do not carry electric charge, which means that they are not affected by the electromagnetic forces that act on charged particles such as electrons and protons. Neutrinos are affected only by the weak su ...
... by the standards of subatomic particles. Their mass has never been measured accurately. Neutrinos do not carry electric charge, which means that they are not affected by the electromagnetic forces that act on charged particles such as electrons and protons. Neutrinos are affected only by the weak su ...
chem_intro
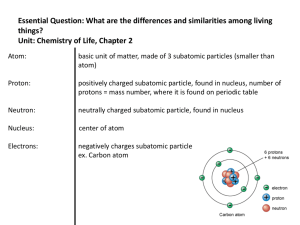
... atoms of same element with different numbers of neutrons ex. Carbon 12= 6 protons, 6 neutrons, 6 electrons Carbon 13= 6 protons, 7 neutrons, 6 electrons Carbon 14= 6 protons, 8 neutrons, 6 electrons ...
... atoms of same element with different numbers of neutrons ex. Carbon 12= 6 protons, 6 neutrons, 6 electrons Carbon 13= 6 protons, 7 neutrons, 6 electrons Carbon 14= 6 protons, 8 neutrons, 6 electrons ...
Basic Ideas for Particle Properties
... What are the practical wave functions? 1,2 A 1 2 B 2 1 symmetric 1,2 A 1 2 B 2 1 anti - symmetric ...
... What are the practical wave functions? 1,2 A 1 2 B 2 1 symmetric 1,2 A 1 2 B 2 1 anti - symmetric ...
Chapter 8 - Clayton State University
... Planck showed that there is a minimum amount of energy, in the form of a quantum. If the energy of an electron in an atom is related to its distance from the nucleus, then there is a certain minimum distance for the first electron. Each additional electron must be a certain distance farther away. Th ...
... Planck showed that there is a minimum amount of energy, in the form of a quantum. If the energy of an electron in an atom is related to its distance from the nucleus, then there is a certain minimum distance for the first electron. Each additional electron must be a certain distance farther away. Th ...
nuclear physics ppt
... A beta positive particle b+ is essentially an electron with positive charge. The mass and speeds are similar. A gamma ray g has very high electromagnetic radiation carrying energy away from the nucleus. ...
... A beta positive particle b+ is essentially an electron with positive charge. The mass and speeds are similar. A gamma ray g has very high electromagnetic radiation carrying energy away from the nucleus. ...
history of double
... light is an electromagnetic wave using his doubleslit experiment. In 1887 Heinrich Hertz observed the photoelectric effect. Electrons are emitted from metal when irradiated by an electromagnetic wave. In 1905 Albert Einstein came with his explanation of the photoelectric effect by describing light b ...
... light is an electromagnetic wave using his doubleslit experiment. In 1887 Heinrich Hertz observed the photoelectric effect. Electrons are emitted from metal when irradiated by an electromagnetic wave. In 1905 Albert Einstein came with his explanation of the photoelectric effect by describing light b ...
lecture31
... There are four different quantum numbers needed to specify the state of an electron in an atom: 1) Principal quantum number n gives the total energy: ...
... There are four different quantum numbers needed to specify the state of an electron in an atom: 1) Principal quantum number n gives the total energy: ...
Slide 1
... (a), (b) = (c), (d). The magnitude of the force depends on the value of sin θ. The maximum force occurs when the wire is perpendicular to the field (a), and there is zero force when the wire is parallel (d). Choices (2) and (3) represent the same force because Case 1 tells us that a straight wire b ...
... (a), (b) = (c), (d). The magnitude of the force depends on the value of sin θ. The maximum force occurs when the wire is perpendicular to the field (a), and there is zero force when the wire is parallel (d). Choices (2) and (3) represent the same force because Case 1 tells us that a straight wire b ...
Document
... • All matter is made of indivisible particles called atoms. • All atoms of a given element are identical in mass & properties. • Atoms are not created or destroyed - just rearranged in reactions. • Different atoms can combine in simple ratios to make compounds. Atoms, according to Dalton: ...
... • All matter is made of indivisible particles called atoms. • All atoms of a given element are identical in mass & properties. • Atoms are not created or destroyed - just rearranged in reactions. • Different atoms can combine in simple ratios to make compounds. Atoms, according to Dalton: ...
Chapters 5.1 and 5.2: A Review – Be sure to Explain your answers
... 7. In class we performed chemical flame tests to observe the effects of thermal or heat energy on the electrons of different metal salts. If all you had was two different metal salts and a source of flame, how could you tell the two different metals apart? A sample of each metal salt could be added ...
... 7. In class we performed chemical flame tests to observe the effects of thermal or heat energy on the electrons of different metal salts. If all you had was two different metal salts and a source of flame, how could you tell the two different metals apart? A sample of each metal salt could be added ...
國立屏東教育大學95學年度研究所碩士班入學考試
... 1. If matter is uniform throughout, cannot be separated into other substances by physical processes, but can be decomposed into other substances by chemical processes, it is called a (an) __________. (A) heterogeneous mixture (B) element (C) homogeneous mixture (D) compound (E) mixture of elements 2 ...
... 1. If matter is uniform throughout, cannot be separated into other substances by physical processes, but can be decomposed into other substances by chemical processes, it is called a (an) __________. (A) heterogeneous mixture (B) element (C) homogeneous mixture (D) compound (E) mixture of elements 2 ...
Document
... numbers also result in small energy differences • Pauli exclusion principle: no two electrons in the same atom can be in the same quantum state • Electrons are grouped into shells and subshells • Periodic table reflects shell structure •Atoms with the same number of electrons in their outer shells h ...
... numbers also result in small energy differences • Pauli exclusion principle: no two electrons in the same atom can be in the same quantum state • Electrons are grouped into shells and subshells • Periodic table reflects shell structure •Atoms with the same number of electrons in their outer shells h ...
lecture31
... numbers also result in small energy differences • Pauli exclusion principle: no two electrons in the same atom can be in the same quantum state • Electrons are grouped into shells and subshells • Periodic table reflects shell structure •Atoms with the same number of electrons in their outer shells h ...
... numbers also result in small energy differences • Pauli exclusion principle: no two electrons in the same atom can be in the same quantum state • Electrons are grouped into shells and subshells • Periodic table reflects shell structure •Atoms with the same number of electrons in their outer shells h ...
Electron scattering

Electron scattering occurs when electrons are deviated from their original trajectory. This is due to the electrostatic forces within matter interaction or, if an external magnetic field is present, the electron may be deflected by the Lorentz force. This scattering typically happens with solids such as metals, semiconductors and insulators; and is a limiting factor in integrated circuits and transistors.The application of electron scattering is such that it can be used as a high resolution microscope for hadronic systems, that allows the measurement of the distribution of charges for nucleons and nuclear structure. The scattering of electrons has allowed us to understand that protons and neutrons are made up of the smaller elementary subatomic particles called quarks.Electrons may be scattered through a solid in several ways:Not at all: no electron scattering occurs at all and the beam passes straight through.Single scattering: when an electron is scattered just once.Plural scattering: when electron(s) scatter several times.Multiple scattering: when electron(s) scatter very many times over.The likelihood of an electron scattering and the proliferance of the scattering is a probability function of the specimen thickness to the mean free path.