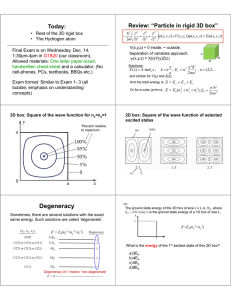
Degeneracy
... Schrodinger’s Solutions for Hydrogen If you understand the 1D quantum well (and how we went from 1D to 3D), then it is easy for you to understand Schrödinger's hydrogen atom! ...
... Schrodinger’s Solutions for Hydrogen If you understand the 1D quantum well (and how we went from 1D to 3D), then it is easy for you to understand Schrödinger's hydrogen atom! ...
Any crystal that scratches glass is a diamond. Rocks must be heavy
... group 9/1998. http://www.amasci.com/miscon/opphys.html) ...
... group 9/1998. http://www.amasci.com/miscon/opphys.html) ...
Element: pure substances that are made up of one kind of atom
... Nucleus: located at the center of the atom. Consists of protons and neutrons. Electrons surround the nucleus. Electron Cloud: the current model of an atom contains an electron cloud that shows electrons traveling in specific energy levels around a nucleus. The farther away from the nucleus an electr ...
... Nucleus: located at the center of the atom. Consists of protons and neutrons. Electrons surround the nucleus. Electron Cloud: the current model of an atom contains an electron cloud that shows electrons traveling in specific energy levels around a nucleus. The farther away from the nucleus an electr ...
J.
... The fact that the relation derived in this note becomes inexact for finite (instead of infinitesimal) field strength deserves some comment; it exhibits the difficulty of associating the effect of the magnetic field with the sign change of half-integer spin particles under rotations through 2m'. The ...
... The fact that the relation derived in this note becomes inexact for finite (instead of infinitesimal) field strength deserves some comment; it exhibits the difficulty of associating the effect of the magnetic field with the sign change of half-integer spin particles under rotations through 2m'. The ...
Lewis Structure Activity
... Name ______________________________________________________________ Pd ____ ...
... Name ______________________________________________________________ Pd ____ ...
College Physics - Gianpietro Cagnoli's Homepage
... traveling with velocity 13.0 m/s toward the east, and the other is traveling north with speed v2i. Neither driver sees the other. The vehicles collide in the intersection and stick together, leaving parallel skid marks at an angle of 55.0° north of east. The speed limit for both roads is 35 mi/h, an ...
... traveling with velocity 13.0 m/s toward the east, and the other is traveling north with speed v2i. Neither driver sees the other. The vehicles collide in the intersection and stick together, leaving parallel skid marks at an angle of 55.0° north of east. The speed limit for both roads is 35 mi/h, an ...
Solution - UD Physics
... plate. The electron enters a uniform field of 10V/m generated by another two parallel plates. (Assuming E becomes zero outside and no edge effect). The separation of two plates is 2.0 cm. Calculate (a) (10pts) the velocity of the electron before it enters E field; (b) (10 pts) the acceleration of th ...
... plate. The electron enters a uniform field of 10V/m generated by another two parallel plates. (Assuming E becomes zero outside and no edge effect). The separation of two plates is 2.0 cm. Calculate (a) (10pts) the velocity of the electron before it enters E field; (b) (10 pts) the acceleration of th ...
Man-Made Accelerators (Earth-Based)
... “WHEN J. J. THOMSON discovered the electron, he did not call the instrument the was using an accelerator, but an accelerator it certainly was. He accelerated particles between two electrodes to which he had applied a difference in electric potential. He manipulated the resulting beam with electric a ...
... “WHEN J. J. THOMSON discovered the electron, he did not call the instrument the was using an accelerator, but an accelerator it certainly was. He accelerated particles between two electrodes to which he had applied a difference in electric potential. He manipulated the resulting beam with electric a ...
v - Purdue Physics
... A negatively charged particle is moving horizontally to the right in a uniform magnetic field that is pointing in the same direction as the velocity. What is the direction of the magnetic force on the charge? ...
... A negatively charged particle is moving horizontally to the right in a uniform magnetic field that is pointing in the same direction as the velocity. What is the direction of the magnetic force on the charge? ...
McGill String Cosmology Workshop April 2005
... enhanced symmetry, it created particles χ with energy density proportional to φ. Therefore the rolling field slows down and stops at the point when ...
... enhanced symmetry, it created particles χ with energy density proportional to φ. Therefore the rolling field slows down and stops at the point when ...
Final Exam Class Review - Mrs. Kittrell`s Science Classes
... A beta particle is a fast moving electron which is emitted from the nucleus of an atom undergoing radioactive decay. ...
... A beta particle is a fast moving electron which is emitted from the nucleus of an atom undergoing radioactive decay. ...
Graphene Graphene is allotrope of carbon
... lattice.It is a basic building block for graphite material of all other dimenisonalities including graphite charcoal,carbon nano-tubes,fullerences etc., This discovery of explaining properties of explaining properties of grapheme leads university of Manchester scientists were awarded 2010 NOBEL PRIZ ...
... lattice.It is a basic building block for graphite material of all other dimenisonalities including graphite charcoal,carbon nano-tubes,fullerences etc., This discovery of explaining properties of explaining properties of grapheme leads university of Manchester scientists were awarded 2010 NOBEL PRIZ ...
pdf file - HST
... taking place in a few billionths of a second. The pictures also have a mysterious beauty. • Elementary physics concepts—such as Newton’s Second Law, momentum and energy conservation, the forces exerted by magnetic fields on electric currents (moving charges), the fact that the origin of electromagne ...
... taking place in a few billionths of a second. The pictures also have a mysterious beauty. • Elementary physics concepts—such as Newton’s Second Law, momentum and energy conservation, the forces exerted by magnetic fields on electric currents (moving charges), the fact that the origin of electromagne ...
Characteristics of Waves
... electrons in the atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers. 3) Hund’s Rule: Electrons occupy equal energy orbitals so that a maximum numbered of unpaired electrons results, and all e- in singly occupied orbitals must have the same spin. ...
... electrons in the atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers. 3) Hund’s Rule: Electrons occupy equal energy orbitals so that a maximum numbered of unpaired electrons results, and all e- in singly occupied orbitals must have the same spin. ...
Essentials of Particle Physics
... also demands existence of a massless vector field: identified as the photon, the carrier particle of electromagnetic interaction. ...
... also demands existence of a massless vector field: identified as the photon, the carrier particle of electromagnetic interaction. ...
File.
... . EXCEEDED EXPERIMENTAL TESTS IN ENERGY RANGES VERY DISTANT FROM THE ONES INCLUDED IN ITS ORIGINAL DESIGN ...
... . EXCEEDED EXPERIMENTAL TESTS IN ENERGY RANGES VERY DISTANT FROM THE ONES INCLUDED IN ITS ORIGINAL DESIGN ...
Chapter Three - GEOCITIES.ws
... The nucleus is made up of protons and neutrons. Protons and neutrons are both relatively the same mass and size but protons have a positive electrical charge and neutrons have no electrical charge. ...
... The nucleus is made up of protons and neutrons. Protons and neutrons are both relatively the same mass and size but protons have a positive electrical charge and neutrons have no electrical charge. ...
1700_QM_2_wavemech
... • Fermions, which have spin ½ (angular momentum of h/4) obey the Pauli exclusion principle (e.g. electrons, neutrinos, protons, neutrons, quarks) ...
... • Fermions, which have spin ½ (angular momentum of h/4) obey the Pauli exclusion principle (e.g. electrons, neutrinos, protons, neutrons, quarks) ...
Electron scattering

Electron scattering occurs when electrons are deviated from their original trajectory. This is due to the electrostatic forces within matter interaction or, if an external magnetic field is present, the electron may be deflected by the Lorentz force. This scattering typically happens with solids such as metals, semiconductors and insulators; and is a limiting factor in integrated circuits and transistors.The application of electron scattering is such that it can be used as a high resolution microscope for hadronic systems, that allows the measurement of the distribution of charges for nucleons and nuclear structure. The scattering of electrons has allowed us to understand that protons and neutrons are made up of the smaller elementary subatomic particles called quarks.Electrons may be scattered through a solid in several ways:Not at all: no electron scattering occurs at all and the beam passes straight through.Single scattering: when an electron is scattered just once.Plural scattering: when electron(s) scatter several times.Multiple scattering: when electron(s) scatter very many times over.The likelihood of an electron scattering and the proliferance of the scattering is a probability function of the specimen thickness to the mean free path.