Quantum Mechanics - UCSD Department of Physics
... – Emergent picture is one of probability distributions describing where electrons can be The energy levels of hydrogen match the observed spectra, and fall out of the mathematics of quantum mechanics ...
... – Emergent picture is one of probability distributions describing where electrons can be The energy levels of hydrogen match the observed spectra, and fall out of the mathematics of quantum mechanics ...
QUANTUM TUNNELING AND SPIN by Robert J
... Now if one of THOSE beams is sent into a third SG experiment, along the original orientation, what happens? ...
... Now if one of THOSE beams is sent into a third SG experiment, along the original orientation, what happens? ...
Ek = hf - hfo Ek = hf
... photoelectrons by raising the voltage until the current across the tube stopped flowing. In this way he could measure very accurate values of the kinetic energy of the photoelectrons for different light frequencies. ...
... photoelectrons by raising the voltage until the current across the tube stopped flowing. In this way he could measure very accurate values of the kinetic energy of the photoelectrons for different light frequencies. ...
Chapt7
... Shapes of Atomic Orbitals Atomic orbitals are best viewed as "clouds of electron density" and represented as contour plots of the probability of finding the electron. ...
... Shapes of Atomic Orbitals Atomic orbitals are best viewed as "clouds of electron density" and represented as contour plots of the probability of finding the electron. ...
PPT | 345.5 KB - Joint Quantum Institute
... Physicists supported by the PFC at the Joint Quantum Institute have developed a new source of “entangled” photons – fundamental units of light whose properties are so intertwined that if the condition of one is measured, the condition of the other is instantaneously known, even if the photons are th ...
... Physicists supported by the PFC at the Joint Quantum Institute have developed a new source of “entangled” photons – fundamental units of light whose properties are so intertwined that if the condition of one is measured, the condition of the other is instantaneously known, even if the photons are th ...
Slide 1
... • Atomic spectra: Result from excited atoms emitting light. • Line spectra: Result from electron transitions between specific energy levels. • Blackbody radiation is the visible glow that solid objects emit when heated. ...
... • Atomic spectra: Result from excited atoms emitting light. • Line spectra: Result from electron transitions between specific energy levels. • Blackbody radiation is the visible glow that solid objects emit when heated. ...
Lecture 6
... Note that this is clearly a relativistic equation. We’ll find this comes from the term for the virtual particle in the full calculation of the probability of these interactions. The W+ can be produced at it’s median mass value and the decay of top to W+ and b is the dominant decay. Therefore this de ...
... Note that this is clearly a relativistic equation. We’ll find this comes from the term for the virtual particle in the full calculation of the probability of these interactions. The W+ can be produced at it’s median mass value and the decay of top to W+ and b is the dominant decay. Therefore this de ...
Probing the Orbital Energy of an Electron in an Atom
... position, r0, where its kinetic energy is zero, Bills contradicts accepted quantum mechanical ideas regarding the behavior of electrons in atoms. The wave functions of atomic electrons are not eigenfunctions of the position, momentum, kinetic energy or potential energy operators. Consequently, accor ...
... position, r0, where its kinetic energy is zero, Bills contradicts accepted quantum mechanical ideas regarding the behavior of electrons in atoms. The wave functions of atomic electrons are not eigenfunctions of the position, momentum, kinetic energy or potential energy operators. Consequently, accor ...
Black Hole
... Since (differently from electric charges) one has only one sign of the mass, the lowest moment is the 4-pole. ...
... Since (differently from electric charges) one has only one sign of the mass, the lowest moment is the 4-pole. ...
modern mini test Jan 2011
... a) What is the half-life of the radioisotope? b) How much time is required (from the original 320 g sample) for the mass of the remaining radioisotope to decrease to 5 g? 2. A particle has a de Broglie wavelength of 6.8 1014 m. Calculate the mass of the particle if it is travelling at a speed of ...
... a) What is the half-life of the radioisotope? b) How much time is required (from the original 320 g sample) for the mass of the remaining radioisotope to decrease to 5 g? 2. A particle has a de Broglie wavelength of 6.8 1014 m. Calculate the mass of the particle if it is travelling at a speed of ...
Energy Transformations
... •Thermal: movement of microscopic particles (such as atoms, molecules) EX: heat, movement of helium gas atoms –Kinetic thermal energy can be transferred from one particle to another via conduction and convection (there is a 3rd, but we are skipping it for now) see the next slide ...
... •Thermal: movement of microscopic particles (such as atoms, molecules) EX: heat, movement of helium gas atoms –Kinetic thermal energy can be transferred from one particle to another via conduction and convection (there is a 3rd, but we are skipping it for now) see the next slide ...
Atomic Structure - Winona State University
... Line Spectra and the Bohr Model Limitations of the Bohr Model • Can only explain the line spectrum of hydrogen adequately. • Can only work for (at least) one electron atoms. • Cannot explain multi-lines with each color. • Electrons are not completely described as small particles. • Electrons can ha ...
... Line Spectra and the Bohr Model Limitations of the Bohr Model • Can only explain the line spectrum of hydrogen adequately. • Can only work for (at least) one electron atoms. • Cannot explain multi-lines with each color. • Electrons are not completely described as small particles. • Electrons can ha ...
Hwk Set #14 - Publisher`s solutions
... speed that can excite the n = 2 state in the nucleus, then the proton has K2 = 7.2 MeV at the distance r2 equal to the radius of nucleus (4 fm). Its potential energy at this point is the electrostatic potential energy between the proton of charge +e and the nucleus of charge +Ze, with Z = 13. The co ...
... speed that can excite the n = 2 state in the nucleus, then the proton has K2 = 7.2 MeV at the distance r2 equal to the radius of nucleus (4 fm). Its potential energy at this point is the electrostatic potential energy between the proton of charge +e and the nucleus of charge +Ze, with Z = 13. The co ...
AP Chapter 5
... attracted toward one another; if the bodies are similarly charged, both positive or both negative, the force between them is repulsive. ...
... attracted toward one another; if the bodies are similarly charged, both positive or both negative, the force between them is repulsive. ...
Identical particles
... Elementary particles have spin, which is the name that we give to the intrinsic angular momentum of the particle. It is the angular momentum that the particle has that does not come from its motion via the orbital angular momentum L = r × p . The symbol used for spin is usually s or S. Like orbital ...
... Elementary particles have spin, which is the name that we give to the intrinsic angular momentum of the particle. It is the angular momentum that the particle has that does not come from its motion via the orbital angular momentum L = r × p . The symbol used for spin is usually s or S. Like orbital ...
Matter: a Material World
... However, they do move in different “energy states” – some electrons in a given atom have more energy than others These energy states are “quantized”– there are only certain energies that the electrons are allowed to have. This is quantum physics. ...
... However, they do move in different “energy states” – some electrons in a given atom have more energy than others These energy states are “quantized”– there are only certain energies that the electrons are allowed to have. This is quantum physics. ...
August 15, 1996 Part I
... 1. An asteroid with mass M, radius r and velocity v is heading for a collision with Earth. Suppose that we are able to place an explosive charge on the asteroid which is capable of blowing out a piece of rock with mass m and an initial speed equal to the escape velocity from the asteroid. The charge ...
... 1. An asteroid with mass M, radius r and velocity v is heading for a collision with Earth. Suppose that we are able to place an explosive charge on the asteroid which is capable of blowing out a piece of rock with mass m and an initial speed equal to the escape velocity from the asteroid. The charge ...
The topic that fascinated me the most in my Science lessons this
... germanium, gallium and scandium were found and their physical and chemical ‘behaviour’ were just as Mendeleev predicted! Hence, even though Mendeleev did not physically stumble upon these elements, he could be said to have discovered them. Why is Mendeleev able to predict the properties of undiscove ...
... germanium, gallium and scandium were found and their physical and chemical ‘behaviour’ were just as Mendeleev predicted! Hence, even though Mendeleev did not physically stumble upon these elements, he could be said to have discovered them. Why is Mendeleev able to predict the properties of undiscove ...
Lecture 18_Anal_Tech_Part1
... Because the analyst requires a frequency spectrum (a plot of the intensity at each individual frequency) in order to make an identification, the measured interferogram signal can not be interpreted directly. A means of “decoding” the individual frequencies is required. This can be accomplished via ...
... Because the analyst requires a frequency spectrum (a plot of the intensity at each individual frequency) in order to make an identification, the measured interferogram signal can not be interpreted directly. A means of “decoding” the individual frequencies is required. This can be accomplished via ...
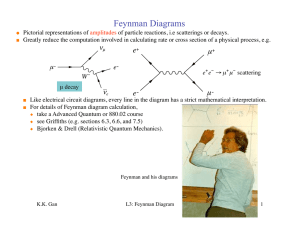
Electron scattering

Electron scattering occurs when electrons are deviated from their original trajectory. This is due to the electrostatic forces within matter interaction or, if an external magnetic field is present, the electron may be deflected by the Lorentz force. This scattering typically happens with solids such as metals, semiconductors and insulators; and is a limiting factor in integrated circuits and transistors.The application of electron scattering is such that it can be used as a high resolution microscope for hadronic systems, that allows the measurement of the distribution of charges for nucleons and nuclear structure. The scattering of electrons has allowed us to understand that protons and neutrons are made up of the smaller elementary subatomic particles called quarks.Electrons may be scattered through a solid in several ways:Not at all: no electron scattering occurs at all and the beam passes straight through.Single scattering: when an electron is scattered just once.Plural scattering: when electron(s) scatter several times.Multiple scattering: when electron(s) scatter very many times over.The likelihood of an electron scattering and the proliferance of the scattering is a probability function of the specimen thickness to the mean free path.