Announcements
... After Inflation, the strong nuclear force “freezes out” and the universe enters the Quark Epoch The universe is now a quark-gluon plasma. The quarks were created in the Unified Era and ...
... After Inflation, the strong nuclear force “freezes out” and the universe enters the Quark Epoch The universe is now a quark-gluon plasma. The quarks were created in the Unified Era and ...
Relativistic Quantum Mechanics
... We have found that the Klein-Gordon equation, a candidate for describing the quantum mechanics of spinless particles, admits unacceptable negative energy states when is interpreted as the single particle wave function. There is another way forward (this is the way followed in the textbook of Halze ...
... We have found that the Klein-Gordon equation, a candidate for describing the quantum mechanics of spinless particles, admits unacceptable negative energy states when is interpreted as the single particle wave function. There is another way forward (this is the way followed in the textbook of Halze ...
lecture2.pdf
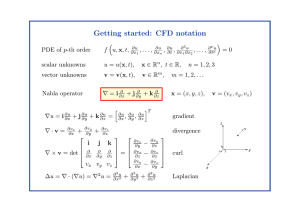
... It is important to understand the meaning and significance of each equation in order to develop a good numerical method and properly interpret the results ...
... It is important to understand the meaning and significance of each equation in order to develop a good numerical method and properly interpret the results ...
Tutorial 1 - NUS Physics
... (d) (x) 2 ( x x ) 2 x 2 x 2 , where x is the position operator. (e) the expectation value of momentum, p (f) (p ) 2 p 2 p 2 , where p is the momentum operator. (g) the expectation value of the potential energy. Is x p ( / 2) [Heisenberg’s uncertainty prin ...
... (d) (x) 2 ( x x ) 2 x 2 x 2 , where x is the position operator. (e) the expectation value of momentum, p (f) (p ) 2 p 2 p 2 , where p is the momentum operator. (g) the expectation value of the potential energy. Is x p ( / 2) [Heisenberg’s uncertainty prin ...
3.3 Why do atoms radiate light?
... • This explains too, why atoms can be stable, although they have a rotational momentum (in the classical description they would always radiate light and thus be destroyed). This classical explanation results from the wrong picture, that the electron is moving through the orbital, leading to a steady ...
... • This explains too, why atoms can be stable, although they have a rotational momentum (in the classical description they would always radiate light and thus be destroyed). This classical explanation results from the wrong picture, that the electron is moving through the orbital, leading to a steady ...
6.1.5. Number Representation: Operators
... where, to avoid ambiguity, we have used subscript to indicate the particle occupying the state. Taking the hermitian conjugate, we obtain the adjoint basis vector ...
... where, to avoid ambiguity, we have used subscript to indicate the particle occupying the state. Taking the hermitian conjugate, we obtain the adjoint basis vector ...
Seminar 7: CENTRAL FORCE PROBLEM Problem 26 A particle of
... and we know that this orbit is an ellipse with one of the foci at the origin of the plane polar coordinates and with the eccentricity ε. Indeed, you know that an ellipse is defined as the curve traced by a particle moving so that the sum of its distances from two fixed points F, F 0 is constant. The ...
... and we know that this orbit is an ellipse with one of the foci at the origin of the plane polar coordinates and with the eccentricity ε. Indeed, you know that an ellipse is defined as the curve traced by a particle moving so that the sum of its distances from two fixed points F, F 0 is constant. The ...
L01_5342_Sp02
... • Compton showed Dp = hkinitial - hkfinal, so an photon (wave) is particle-like • DeBroglie hypothesized a particle could be wave-like, l = h/p • Davisson and Germer demonstrated wave-like interference phenomena for electrons to complete the duality model L1 January 15 ...
... • Compton showed Dp = hkinitial - hkfinal, so an photon (wave) is particle-like • DeBroglie hypothesized a particle could be wave-like, l = h/p • Davisson and Germer demonstrated wave-like interference phenomena for electrons to complete the duality model L1 January 15 ...
Atomic Physics
... !Bohr model fails describing atoms heavier than H !Does it violate the Heisenberg uncertainty principle? A) YES B) No ...
... !Bohr model fails describing atoms heavier than H !Does it violate the Heisenberg uncertainty principle? A) YES B) No ...
QUASICLASSICAL AND QUANTUM SYSTEMS OF ANGULAR FOR QUANTUM-MECHANICAL MODELS WITH SYMMETRIES
... Presented by Jan J. Sławianowski Abstract. We use the mathematical structure of group algebras and H + -algebras for describing certain problems concerning the quantum dynamics of systems of angular momenta, including also the spin systems. The underlying groups are SU(2) and its quotient SO(3, R). ...
... Presented by Jan J. Sławianowski Abstract. We use the mathematical structure of group algebras and H + -algebras for describing certain problems concerning the quantum dynamics of systems of angular momenta, including also the spin systems. The underlying groups are SU(2) and its quotient SO(3, R). ...