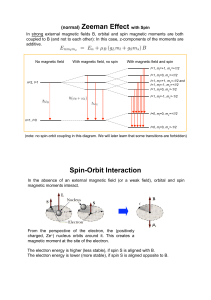
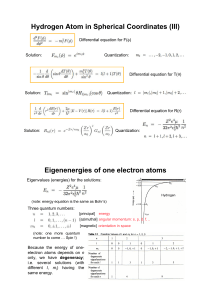
Answer Key
... To establish the Schrödinger equation for the system, we need to figure out the Hamiltonian. In one dimension, the Hamiltonian operator is defined as ...
... To establish the Schrödinger equation for the system, we need to figure out the Hamiltonian. In one dimension, the Hamiltonian operator is defined as ...
Quantum Mechanics
... 4. A particle moves in one dimension and in a potential of the form V (x) = 0, for |x| < a and V (x) = V0 > 0 for |x| > a. The particle has energy 0 < E < V0 . a. Solve the Schrödinger equation in each of the three regions: I: −∞ < x < −a, II: −a < x < +a and III: +a < x < +∞. b. Specify the contin ...
... 4. A particle moves in one dimension and in a potential of the form V (x) = 0, for |x| < a and V (x) = V0 > 0 for |x| > a. The particle has energy 0 < E < V0 . a. Solve the Schrödinger equation in each of the three regions: I: −∞ < x < −a, II: −a < x < +a and III: +a < x < +∞. b. Specify the contin ...
Periodic boundary physics etc
... In physics, specifically quantum mechanics, the Schrödinger equation is an equation that describes how the quantum state of a physical system changes in time. It is as central to quantum mechanics as Newton's laws are to classical mechanics. In the standard interpretation of quantum mechanics, the q ...
... In physics, specifically quantum mechanics, the Schrödinger equation is an equation that describes how the quantum state of a physical system changes in time. It is as central to quantum mechanics as Newton's laws are to classical mechanics. In the standard interpretation of quantum mechanics, the q ...
1.1 What has to be explained by Quantum mechanics?
... • What is: Schrödinger equation, Operator, commutator, probability function, wave function, quantum number, ...... ...
... • What is: Schrödinger equation, Operator, commutator, probability function, wave function, quantum number, ...... ...
CLASSICAL-QUANTUM CORRESPONDENCE AND WAVE PACKET SOLUTIONS OF THE DIRAC
... well-known relation E = ~ω in the specific form H = ~W , where H is the classical Hamiltonian of a particle and W is the dispersion relation of the sought-for wave equation. We derive the expression of H in a curved space-time with an electromagnetic field. Then we derive the Dirac equation from fac ...
... well-known relation E = ~ω in the specific form H = ~W , where H is the classical Hamiltonian of a particle and W is the dispersion relation of the sought-for wave equation. We derive the expression of H in a curved space-time with an electromagnetic field. Then we derive the Dirac equation from fac ...
Problem Set 12
... • Find all the solutions to this equation, and show how the momentum operator and space-translations act on solutions. • Show explicitly how the double-cover of the Euclidean group acts on the space of solutions. • Find a solution of the equation that is a helicity eigenvector (eigenvector of J · P) ...
... • Find all the solutions to this equation, and show how the momentum operator and space-translations act on solutions. • Show explicitly how the double-cover of the Euclidean group acts on the space of solutions. • Find a solution of the equation that is a helicity eigenvector (eigenvector of J · P) ...
Problem set 3
... 1. Recall that the angular momentum raising operator is L+ = ~eiφ (∂θ + i cot θ ∂φ ). Use this to find L− . 2. Use the above formulae for L± to find the coordinate representation of the angular momentum basis states Y11 , Y10 and Y1,−1 up to normalization. 3. Write out the 9 equations summarized in ...
... 1. Recall that the angular momentum raising operator is L+ = ~eiφ (∂θ + i cot θ ∂φ ). Use this to find L− . 2. Use the above formulae for L± to find the coordinate representation of the angular momentum basis states Y11 , Y10 and Y1,−1 up to normalization. 3. Write out the 9 equations summarized in ...
The Nilpotent generalization of Dirac`s famous Equation D(N)
... The Nilpotent generalization of Dirac’s famous Equation D(N) ...
... The Nilpotent generalization of Dirac’s famous Equation D(N) ...