
Brief introduction to quantum mechanics
... „There was a time when newspapers said that only twelve men understood the theory of relativity. I do not believe that there ever was such a time... On the other hand, I think it is safe to say that no one understands quantum mechanics“ R.P. Feynman The Character of Physical Law (1967) ...
... „There was a time when newspapers said that only twelve men understood the theory of relativity. I do not believe that there ever was such a time... On the other hand, I think it is safe to say that no one understands quantum mechanics“ R.P. Feynman The Character of Physical Law (1967) ...
Student Presentation
... have been previously regarded as particles also show wave-like characteristics with wavelengths given by the equation: λ = h/p = h/mv – h (Planck’s constant) = 6.626 x 10-34 J·s ...
... have been previously regarded as particles also show wave-like characteristics with wavelengths given by the equation: λ = h/p = h/mv – h (Planck’s constant) = 6.626 x 10-34 J·s ...
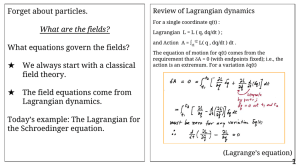
Forget about particles. What equations govern the fields? What are the fields?
... Exercise: Figure out the Lagrangian that would include a 2-body potential. Hint: The Lagrangian must include a term quartic in the field. Exercise: Verify that H is the generator of translation in time, in the quantum theory. ...
... Exercise: Figure out the Lagrangian that would include a 2-body potential. Hint: The Lagrangian must include a term quartic in the field. Exercise: Verify that H is the generator of translation in time, in the quantum theory. ...
Section 9
... Sum of rest energies of parts, which does not include kinetic energy or interactions ...
... Sum of rest energies of parts, which does not include kinetic energy or interactions ...
Document
... de Broglie’s intriguing idea of “matter wave” (1924) Extend notation of “wave-particle duality” from light to matter For photons, P E hf h ...
... de Broglie’s intriguing idea of “matter wave” (1924) Extend notation of “wave-particle duality” from light to matter For photons, P E hf h ...
[2012 question paper]
... [4.1] Using the Taylor expansion for a function f (x), one can define functions f (A) of a square matrix A. Thus consider the exponential of a matrix A through the Taylor expansion for ex . Evaluate Exp[iασ 1 ] and reduce it to a simple expression, where α is a constant, i2 = −1, and σ 1 = (01 10 ) ...
... [4.1] Using the Taylor expansion for a function f (x), one can define functions f (A) of a square matrix A. Thus consider the exponential of a matrix A through the Taylor expansion for ex . Evaluate Exp[iασ 1 ] and reduce it to a simple expression, where α is a constant, i2 = −1, and σ 1 = (01 10 ) ...
Transparancies for Revision Lecture - University of Manchester
... For multi-electron atoms Energy splitting depends on l even in absence of magnetic field. ...
... For multi-electron atoms Energy splitting depends on l even in absence of magnetic field. ...
Problem set 2
... is real, so that we are justified in calling it a phase angle. Here ψn (t) are orthonormal eigenstates of the hamiltonians H(t) for each t with eigenvalues En (t). 2. With the same notation as above, show that Ėn = hψn |Ḣ|ψn i. ...
... is real, so that we are justified in calling it a phase angle. Here ψn (t) are orthonormal eigenstates of the hamiltonians H(t) for each t with eigenvalues En (t). 2. With the same notation as above, show that Ėn = hψn |Ḣ|ψn i. ...
The Impact of Special Relativity in Nuclear Physics: It`s not just E=Mc 2
... give different coordinates. ...
... give different coordinates. ...
Modern Physics
... Klein-Gordon describes a free, relativistic spinless particle. It requires two initial conditions [Ψ(t=0) and ∂Ψ/∂t(t=0)] because of 2nd derivative wrt time. Therefore specifying a wavefunction Ψ at t=0 is insufficient to uniquely specify the system’s behavior. ...
... Klein-Gordon describes a free, relativistic spinless particle. It requires two initial conditions [Ψ(t=0) and ∂Ψ/∂t(t=0)] because of 2nd derivative wrt time. Therefore specifying a wavefunction Ψ at t=0 is insufficient to uniquely specify the system’s behavior. ...
MIT Physics Graduate General Exams
... Part I Concepts Students studying for the Fall 2003 Part I exam found it useful to first categorize each problem by the concept they thought was being tested. Such an approach simplified their subsequent attempt at solving the problem. The following is a list of all the concepts they thought could b ...
... Part I Concepts Students studying for the Fall 2003 Part I exam found it useful to first categorize each problem by the concept they thought was being tested. Such an approach simplified their subsequent attempt at solving the problem. The following is a list of all the concepts they thought could b ...
SCHRÖDINGER EQUATION FOR A PARTICLE ON A CURVED SPACE AND SUPERINTEGRABILITY
... of the linear momentum operator. Plane waves are therefore simultaneous eigenfunctions of energy and linear momentum. As soon as the problem is thought of in a space with curvature, the analysis becomes much more complicated [11, 14, 15]. First of all, the canonical momenta do not in general coincid ...
... of the linear momentum operator. Plane waves are therefore simultaneous eigenfunctions of energy and linear momentum. As soon as the problem is thought of in a space with curvature, the analysis becomes much more complicated [11, 14, 15]. First of all, the canonical momenta do not in general coincid ...
Document
... Using spherical symmetry property can be reduced to two coupled differential equations ...
... Using spherical symmetry property can be reduced to two coupled differential equations ...
Group and phase velocity
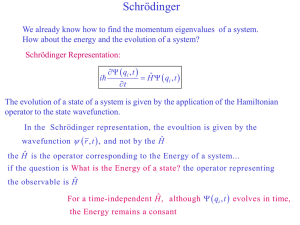
... The evolution of a state of a system is given by the application of the Hamiltonian operator to the state wavefunction. In the Schrodinger representation, the evoultion is given by the wavefunction r , t , and not by the Hˆ ...
... The evolution of a state of a system is given by the application of the Hamiltonian operator to the state wavefunction. In the Schrodinger representation, the evoultion is given by the wavefunction r , t , and not by the Hˆ ...
File
... Physical state of a quantum system is described by a column vector (t ) whose components are probability amplitudes of states in which system can be found. No. of states are equal to the dimension of Hilbert space, which can be finite/infinite. ...
... Physical state of a quantum system is described by a column vector (t ) whose components are probability amplitudes of states in which system can be found. No. of states are equal to the dimension of Hilbert space, which can be finite/infinite. ...
[2011 question paper]
... ∆x = hx2 i − hxi2 in the above initial gaussian wave packet state. (d) Write down the free particle Schrödinger equation for the time-evolution of the above particle and find its stationary states and their energies. (e) Suppose a particle in the above initial state ψ(x, t = 0) evolves in time acco ...
... ∆x = hx2 i − hxi2 in the above initial gaussian wave packet state. (d) Write down the free particle Schrödinger equation for the time-evolution of the above particle and find its stationary states and their energies. (e) Suppose a particle in the above initial state ψ(x, t = 0) evolves in time acco ...





![[2012 question paper]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008881815_1-f519c09d51fa08989c44092ef48b677c-300x300.png)














![[2011 question paper]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008881811_1-8ef23f7493d56bc511a2c01dcc81fc96-300x300.png)