1 Problem 1 (10 points): (a) (3 points) An electron bound to a proton
... principal quantum number, ` is the orbital angular momentum quantum number, and m is the magnetic quantum number (we are ignoring spin in this problem). Circle those of the following wave functions that you think are possible: ψ1,2,3 ...
... principal quantum number, ` is the orbital angular momentum quantum number, and m is the magnetic quantum number (we are ignoring spin in this problem). Circle those of the following wave functions that you think are possible: ψ1,2,3 ...
Advanced Quantum Mechanics Syllabus and Introduction
... Course Content: Advanced quantum mechanics (or “QM II” for short) begins where ordinary quantum mechanics leaves off in two very important respects. First there is the issue of relativity. Relativity requires that space and time coordinates be treated in the same way, and this is not possible so lon ...
... Course Content: Advanced quantum mechanics (or “QM II” for short) begins where ordinary quantum mechanics leaves off in two very important respects. First there is the issue of relativity. Relativity requires that space and time coordinates be treated in the same way, and this is not possible so lon ...
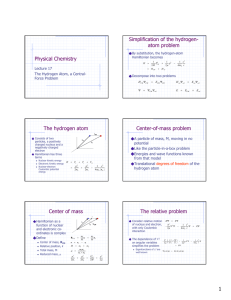
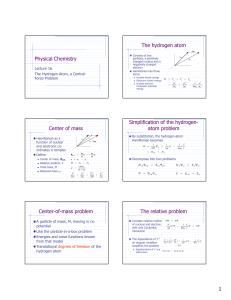
Physical Chemistry The hydrogen atom Center of mass
... The spatial part is incomplete One incorporates spin as a separate coordinate Wave function is a product n ,l ,m , I ,mI (r , , ) ...
... The spatial part is incomplete One incorporates spin as a separate coordinate Wave function is a product n ,l ,m , I ,mI (r , , ) ...
Midterm Exam No. 02 (Fall 2014) PHYS 520A: Electromagnetic Theory I
... Find the effective charge density by calculating −∇ · P. In particular, you should obtain two terms, one containing θ(R − r) that is interpreted as a volume charge density, and another containing δ(R − r) that can be interpreted as a surface charge density. 4. (25 points.) A particle of mass m and c ...
... Find the effective charge density by calculating −∇ · P. In particular, you should obtain two terms, one containing θ(R − r) that is interpreted as a volume charge density, and another containing δ(R − r) that can be interpreted as a surface charge density. 4. (25 points.) A particle of mass m and c ...
Energy_and_Momentum_Units_in_Particle_Physics
... In ordinary Newtonian physics, given the kinetic energy Ek of a particle (4 Joules, say) and its momentum p (4 kg m/s), one can calculate m = p2/2Ek = 2 kg ...
... In ordinary Newtonian physics, given the kinetic energy Ek of a particle (4 Joules, say) and its momentum p (4 kg m/s), one can calculate m = p2/2Ek = 2 kg ...
PHYS 212 - Modern Physics - American University of Beirut
... Theory and Quantum Theory. After finishing this course, the students should be able to: • Understand how the new ideas about spacetime required a radical revision of the Newtonian mechanics. • Realize that one fundament of theory of special relativity is the invariance of the speed of light being in ...
... Theory and Quantum Theory. After finishing this course, the students should be able to: • Understand how the new ideas about spacetime required a radical revision of the Newtonian mechanics. • Realize that one fundament of theory of special relativity is the invariance of the speed of light being in ...
Riemannian method in quantum field theory about curved space-time
... of world lines along which observers may move, we describe an algorithm to obtain the quantum theory of scalar particles of mass m. Let ei denote the 4-velocities of the world lines, and let V~, s real, be a family o f non-intersecting space-like hypersurfaces. We assume that the submanifolds V~ cov ...
... of world lines along which observers may move, we describe an algorithm to obtain the quantum theory of scalar particles of mass m. Let ei denote the 4-velocities of the world lines, and let V~, s real, be a family o f non-intersecting space-like hypersurfaces. We assume that the submanifolds V~ cov ...
Solid State 3, Problem Set 2 Lecturer: Eytan Grosfeld
... 2. Transport on the surface of a topological insulator Electrons confined to the two-dimensional surface of a topological insulator tuned to the Dirac point are described by the continuum limit Hamiltonian H = vσ · p where σa are Pauli matrices (a = x, y) related to the electronic spin and v is a ve ...
... 2. Transport on the surface of a topological insulator Electrons confined to the two-dimensional surface of a topological insulator tuned to the Dirac point are described by the continuum limit Hamiltonian H = vσ · p where σa are Pauli matrices (a = x, y) related to the electronic spin and v is a ve ...
GAMOW VECTORS IN THE BAKAMJIAN-THOMAS CONSTRUCTION SUJEEV WICKRAMASEKARA
... such as the existence of fields that mediate the interactions. In classical relativistic mechanics, Dirac’s problem does not have a non-trivial solution if the particles are subjected to the (unphysical) constraint of having covariant world-lines. Worldline constraints do not certainly hold in the q ...
... such as the existence of fields that mediate the interactions. In classical relativistic mechanics, Dirac’s problem does not have a non-trivial solution if the particles are subjected to the (unphysical) constraint of having covariant world-lines. Worldline constraints do not certainly hold in the q ...