Mod6QM1
... Finite square well: • BC: Ψ is NOT zero at the edges, so wavefunction can spill out of potential • Wide deep well has many, but finite, states • Shallow, narrow well has at least one bound state ...
... Finite square well: • BC: Ψ is NOT zero at the edges, so wavefunction can spill out of potential • Wide deep well has many, but finite, states • Shallow, narrow well has at least one bound state ...
Quantum Mechanics
... (i) If ( x, t ) is a solution , then A ( x, t ) is also a solution. Normalized the wave function to determine the factor A (ii) If the integral is infinite for some wave functions, no factor to make it been normalizable. The non-normalizable wave function cannot represent particles. (iii) the con ...
... (i) If ( x, t ) is a solution , then A ( x, t ) is also a solution. Normalized the wave function to determine the factor A (ii) If the integral is infinite for some wave functions, no factor to make it been normalizable. The non-normalizable wave function cannot represent particles. (iii) the con ...
Homework 8
... where k is a constant and z is vertical. Obtain the Hamiltonian equations of motion. 4) (a) Formulate the canonical equations including friction. A hanger of mass m for a car with a spring-damping system is moving along the x-direction with constant velocity v. It performs sinusoidal oscillations in ...
... where k is a constant and z is vertical. Obtain the Hamiltonian equations of motion. 4) (a) Formulate the canonical equations including friction. A hanger of mass m for a car with a spring-damping system is moving along the x-direction with constant velocity v. It performs sinusoidal oscillations in ...
Sec 4-1 Chapter 4 Notes
... A quantum is the minimum quantity of energy that can be lost or gained by an atom. (Quantum Mechanics is now a branch of physics) ...
... A quantum is the minimum quantity of energy that can be lost or gained by an atom. (Quantum Mechanics is now a branch of physics) ...
Lecture 2
... • This famous equation describes how an electron moves in 6-D phase space. • Consider 2-D (x and kx) and some force Fx • Electron moves a distance vx∆t in time ∆t • Electron changes momentum according to • i.e., transport between position states is taken to be classical • Transport between momentum ...
... • This famous equation describes how an electron moves in 6-D phase space. • Consider 2-D (x and kx) and some force Fx • Electron moves a distance vx∆t in time ∆t • Electron changes momentum according to • i.e., transport between position states is taken to be classical • Transport between momentum ...
Ψ (x,t) = | Ψ (x,t) - University of Notre Dame
... Has the solution E = E0 cos(kx-ωt) verify by differentiating this twice… To find that k2 = ω2/c2 or ω = kc N.B. - Substitute ω=E/ħ and k=p/ħ to give E=pc just as we knew for a massless particle (a photon) For a particle with charge q, mass m – e.g. an electron in the voltage trap, we can write the e ...
... Has the solution E = E0 cos(kx-ωt) verify by differentiating this twice… To find that k2 = ω2/c2 or ω = kc N.B. - Substitute ω=E/ħ and k=p/ħ to give E=pc just as we knew for a massless particle (a photon) For a particle with charge q, mass m – e.g. an electron in the voltage trap, we can write the e ...
Quantum Theory of Atoms and Molecules
... Electrostatics and Wave phenomena. Coulomb’s law, charge, electric field, electrostatic potential, dipole moment, polarisability; simple harmonic motion, forced oscillations, resonance; standing waves, travelling waves, transverse waves, longitudinal waves; the wave equation. ...
... Electrostatics and Wave phenomena. Coulomb’s law, charge, electric field, electrostatic potential, dipole moment, polarisability; simple harmonic motion, forced oscillations, resonance; standing waves, travelling waves, transverse waves, longitudinal waves; the wave equation. ...
Homework Set 1
... any system is the most in need of a quantum description.) c. Taking λ/r ≤ 0.1 as the (arbitrary) cut-off when classical mechanics begins to be valid as Bohr’s quantum number n increases, calculate the lowest (smallest n) classical Bohr orbit. d. Using the Bohr theory, calculate the ionization energi ...
... any system is the most in need of a quantum description.) c. Taking λ/r ≤ 0.1 as the (arbitrary) cut-off when classical mechanics begins to be valid as Bohr’s quantum number n increases, calculate the lowest (smallest n) classical Bohr orbit. d. Using the Bohr theory, calculate the ionization energi ...
$doc.title
... OK irrespective of signs of A or B But if exchange once, for A +ve, B could be +ve or –ve…. Reality: It’s –ve for Fermions and +ve for Bosons! Means that if we try to get fermions 1 and 2 into same state then ψ → 0 !!!! This is the Pauli Exclusion Principle: No two fermions (electrons) can h ...
... OK irrespective of signs of A or B But if exchange once, for A +ve, B could be +ve or –ve…. Reality: It’s –ve for Fermions and +ve for Bosons! Means that if we try to get fermions 1 and 2 into same state then ψ → 0 !!!! This is the Pauli Exclusion Principle: No two fermions (electrons) can h ...
Lecture 4: Charged Particle Motion
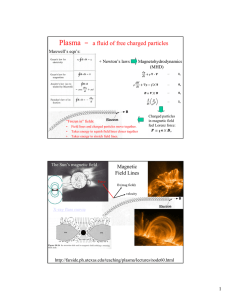
... + so, with current density and velocity, we can determine the charge density of an electron beam. Relativistic motion Let's back up, for non-relativistic particles, if a force acts on a particle, its velocity can change ...
... + so, with current density and velocity, we can determine the charge density of an electron beam. Relativistic motion Let's back up, for non-relativistic particles, if a force acts on a particle, its velocity can change ...
Homework 8 Due at the beginning of class March 26
... that no current can flow anywhere but to the ocean bottom made of rock which is at ground (or 0 Volts) potential. Most of this bottom is covered with thick silt which acts somewhat as an insulator allowing only a small amount of current to flow through it to the rock bottom. The Titanic rests on the ...
... that no current can flow anywhere but to the ocean bottom made of rock which is at ground (or 0 Volts) potential. Most of this bottom is covered with thick silt which acts somewhat as an insulator allowing only a small amount of current to flow through it to the rock bottom. The Titanic rests on the ...
(Quantum Mechanics) 1. State basic concepts (or postulates) of
... wavefunction for this purpose? (d) What are the factors determining the tunneling probability? 9. The Hamiltonian , the ground state wafefunction , and the 1st excited state wavefunction are given below for a one-dimentional harmonic oscillator with mass and natural frequency . ...
... wavefunction for this purpose? (d) What are the factors determining the tunneling probability? 9. The Hamiltonian , the ground state wafefunction , and the 1st excited state wavefunction are given below for a one-dimentional harmonic oscillator with mass and natural frequency . ...