Schrödinger equation (Text 5.3)
... Dispersion relation for i(kx -ωt) ∴ Ae is a solution if = hω “free particle” 2m ih ...
... Dispersion relation for i(kx -ωt) ∴ Ae is a solution if = hω “free particle” 2m ih ...
ppt - HEP Educational Outreach
... happens, the counter tube discharges andthrough a relay releases a hammer which shatters a small flask of hydrocyanic acid. If one has left thisentire system to itself for an hour, one would say that the cat still lives if meanwhile no atom hasdecayed. The psi-function of the entire system would exp ...
... happens, the counter tube discharges andthrough a relay releases a hammer which shatters a small flask of hydrocyanic acid. If one has left thisentire system to itself for an hour, one would say that the cat still lives if meanwhile no atom hasdecayed. The psi-function of the entire system would exp ...
Quantum Mechanics in a Nutshell
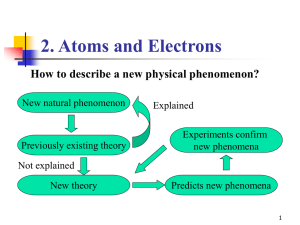
... • Wave-particle duality of light (“wave”) and electrons (“particle”) • Many quantities are “quantized” (e.g., energy, momentum, conductivity, magnetic moment, etc.) • For “matter waves”: Using only three pieces of information (electronic charge, electronic mass, Planck’s constant), the properties of ...
... • Wave-particle duality of light (“wave”) and electrons (“particle”) • Many quantities are “quantized” (e.g., energy, momentum, conductivity, magnetic moment, etc.) • For “matter waves”: Using only three pieces of information (electronic charge, electronic mass, Planck’s constant), the properties of ...
Generalized Momentum Operators
... If the particle is constrained to move on a ring they we expect ψ(x) ∈ H and all of its derivatives to be periodic—a condition that serves even less problematically to kill all all boundary terms. Problems arise, however, if the particle is constrained to move on a finite interval (confined to the i ...
... If the particle is constrained to move on a ring they we expect ψ(x) ∈ H and all of its derivatives to be periodic—a condition that serves even less problematically to kill all all boundary terms. Problems arise, however, if the particle is constrained to move on a finite interval (confined to the i ...
Problem set 6
... Show that we can always define a new real function of time h(t) and a new hermitian operator H such that H(t) = h(t)H . Express h(t) and H in terms of c(t) and K and any other appropriate quantities. 2. Consider the functional equation for a complex-valued function of one real variable f (t + s) = f ...
... Show that we can always define a new real function of time h(t) and a new hermitian operator H such that H(t) = h(t)H . Express h(t) and H in terms of c(t) and K and any other appropriate quantities. 2. Consider the functional equation for a complex-valued function of one real variable f (t + s) = f ...
Physics 202 Final Exam .doc
... 19. Particles that do not engage in strong interactions but are Fermions are called? a. ~ leptons b. hadrons c. bosons d. mesons 20. The prediction of antimatter was due to a. ~ Dirac b. Pauli c. Einstein d. Fermi 21. The exclusion principle was due to a. Dirac b. ~ Pauli c. Einstein d. Fermi 22. Nu ...
... 19. Particles that do not engage in strong interactions but are Fermions are called? a. ~ leptons b. hadrons c. bosons d. mesons 20. The prediction of antimatter was due to a. ~ Dirac b. Pauli c. Einstein d. Fermi 21. The exclusion principle was due to a. Dirac b. ~ Pauli c. Einstein d. Fermi 22. Nu ...
Quantum Mechanics: PHL555 Tutorial 2
... part of the Hamiltonian represents the interaction with the magnetic field. We have neglected the effects due to spin angular momentum of the electron . Treat H 1 as a perturbation and show s(l 0) states are not split , where as p(l 1) states are split into three states separated by the energy i ...
... part of the Hamiltonian represents the interaction with the magnetic field. We have neglected the effects due to spin angular momentum of the electron . Treat H 1 as a perturbation and show s(l 0) states are not split , where as p(l 1) states are split into three states separated by the energy i ...
1 Chemical kinetics 2 Quantum mechanics 3 Tunneling process
... 3.2 Draw the representation of the first four eigenfunctions of the one dimensional timeindependent Schrödinger equation, describing the torsional motion of the molecule. 3.3 Write the general expression of the solution of the time-dependent Schrödinger equation considering the two lowest energy l ...
... 3.2 Draw the representation of the first four eigenfunctions of the one dimensional timeindependent Schrödinger equation, describing the torsional motion of the molecule. 3.3 Write the general expression of the solution of the time-dependent Schrödinger equation considering the two lowest energy l ...
Fall 2012 PHY 335 MODERN PHYSICS / 3 credits. Topics in Modern
... (c) Ability to formulate complex arguments based upon physical foundations and which are testable by experimentation. (d) Ability to produce technologically enabled students with an understanding of the basis for experimental design. ...
... (c) Ability to formulate complex arguments based upon physical foundations and which are testable by experimentation. (d) Ability to produce technologically enabled students with an understanding of the basis for experimental design. ...
10.5.1. Density Operator
... When dealing with a large quantum system, we need to take 2 averages, one over the inherent quantum uncertainties and one over the uninteresting microscopic details. Consider then an isolated system described, in the Schrodinger picture, by a complete set of orthonormal eigenstates n t ...
... When dealing with a large quantum system, we need to take 2 averages, one over the inherent quantum uncertainties and one over the uninteresting microscopic details. Consider then an isolated system described, in the Schrodinger picture, by a complete set of orthonormal eigenstates n t ...
A1979HZ36600001
... states of an atom of definite energy under rotations, the state obtained from one of the ψ ι , under a rotation R, called O Rψ i, can be written as a linear-combination of the original states. The coefficients are denoted by D(R)ki so that ORψi = Σk D(R)kiψk. The D(R) kj satisfy some mathematical re ...
... states of an atom of definite energy under rotations, the state obtained from one of the ψ ι , under a rotation R, called O Rψ i, can be written as a linear-combination of the original states. The coefficients are denoted by D(R)ki so that ORψi = Σk D(R)kiψk. The D(R) kj satisfy some mathematical re ...