Lecture 3
... •But its validity can be tested by comparing the results obtained from this equations with various experimental situations. •The operator H is the hamiltonian or the total energy operator and is the sum of the kinetic energy operator and the potential energy operator. As explained earlier this can b ...
... •But its validity can be tested by comparing the results obtained from this equations with various experimental situations. •The operator H is the hamiltonian or the total energy operator and is the sum of the kinetic energy operator and the potential energy operator. As explained earlier this can b ...
Homework 4 Answer Key
... eigenfunctions and eigenvalues for this system (use spherical polar coordinates)? Looking! at the Schrödinger equation for the free particle may be helpful, but this case is quantized, while that for the free particle is not—why is there a difference? What are the lowest 3 possible energies? What de ...
... eigenfunctions and eigenvalues for this system (use spherical polar coordinates)? Looking! at the Schrödinger equation for the free particle may be helpful, but this case is quantized, while that for the free particle is not—why is there a difference? What are the lowest 3 possible energies? What de ...
Review Sheet
... Endothermic vs. exothermic Stoichiometry using energy (using enthalpy of reaction and balanced chemical reactions) Calculating H using Hess’s Law, Enthalpy Diagrams, and/or H° of formations Calorimetry calculations to determine H and q Standard States and enthalpy of formation Using Hess’s Law eq ...
... Endothermic vs. exothermic Stoichiometry using energy (using enthalpy of reaction and balanced chemical reactions) Calculating H using Hess’s Law, Enthalpy Diagrams, and/or H° of formations Calorimetry calculations to determine H and q Standard States and enthalpy of formation Using Hess’s Law eq ...
PHYS6520 Quantum Mechanics II Spring 2013 HW #5
... initial state is a plane wave coming from the left, that is φ(x) ≡ �x|i� = eikx / 2π ...
... initial state is a plane wave coming from the left, that is φ(x) ≡ �x|i� = eikx / 2π ...
Quantum Mechanics
... Matter exhibits wave-particle duality; particles may exhibit both particle and wave properties, but not both at the same time (complementarity principle). Measuring devices are classical devices, and as such do not ...
... Matter exhibits wave-particle duality; particles may exhibit both particle and wave properties, but not both at the same time (complementarity principle). Measuring devices are classical devices, and as such do not ...
Monday, September 10 - Long Island University
... following a 50femtosecond laser pulse with a central wavelength of 800 nanometers hitting an aluminum surface. The field is 170 x 170 microns, and there are 12 images (not evenly spaced in time) covering the time from 0 to 9 nanoseconds (the fifth image is at 1 nanosecond). ...
... following a 50femtosecond laser pulse with a central wavelength of 800 nanometers hitting an aluminum surface. The field is 170 x 170 microns, and there are 12 images (not evenly spaced in time) covering the time from 0 to 9 nanoseconds (the fifth image is at 1 nanosecond). ...
File
... a. This double-slit experiment shows that electrons, quantum particles: A) behave like waves and behave like particles. B) behave like waves, but are particles C) behave like particles, but are waves. D) are both waves and particles. b. This shows the electrons have a dual nature, physicists call th ...
... a. This double-slit experiment shows that electrons, quantum particles: A) behave like waves and behave like particles. B) behave like waves, but are particles C) behave like particles, but are waves. D) are both waves and particles. b. This shows the electrons have a dual nature, physicists call th ...
Microsoft PowerPoint
... – Compton’s photon-electron scattering experiment supported Plank-Einstein’s theorem (1923), so photons and phonons are particle like, or “real” waves (with zero static mass, reflecting the interaction between matters) can be particle like – Davison and Germer’s electron-Nickel crystal scattering ex ...
... – Compton’s photon-electron scattering experiment supported Plank-Einstein’s theorem (1923), so photons and phonons are particle like, or “real” waves (with zero static mass, reflecting the interaction between matters) can be particle like – Davison and Germer’s electron-Nickel crystal scattering ex ...
7 - Physics at Oregon State University
... • Operators “embed” the kets and eigenvalues • The projector operator MODELS measurements – it tells us what state (ket) the atom is in after the measurement: • It tells us about the probability of finding a particular eigenvalue from a measurement • P+|ψ> = |+><+| ψ> = ψ+|+> = coefficient of Psi al ...
... • Operators “embed” the kets and eigenvalues • The projector operator MODELS measurements – it tells us what state (ket) the atom is in after the measurement: • It tells us about the probability of finding a particular eigenvalue from a measurement • P+|ψ> = |+><+| ψ> = ψ+|+> = coefficient of Psi al ...
Matthew Jones - Phys 378 Web page:
... Examples using ROOT will be provided on web the page Everyone should have an account with PCN First exercise will be to make sure that this ...
... Examples using ROOT will be provided on web the page Everyone should have an account with PCN First exercise will be to make sure that this ...
A Brief Introduction to Relativistic Quantum Mechanics
... ρ does reduce to ρs = Ψ∗ Ψ in the non-relativistic limit. However, ρ is not positive -definite and hence can not describe a probability density for a single particle. Pauli and Weisskopf in 1934 showed that Klein-Gordon equation describes a spin-0 (scalar) field. ρ and j are interpreted as charge an ...
... ρ does reduce to ρs = Ψ∗ Ψ in the non-relativistic limit. However, ρ is not positive -definite and hence can not describe a probability density for a single particle. Pauli and Weisskopf in 1934 showed that Klein-Gordon equation describes a spin-0 (scalar) field. ρ and j are interpreted as charge an ...
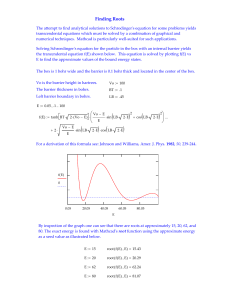
Mathcad - ROOTS.mcd
... For a derivation of this formula see: Johnson and Williams, Amer. J. Phys. 1982, 50, 239‐244. ...
... For a derivation of this formula see: Johnson and Williams, Amer. J. Phys. 1982, 50, 239‐244. ...
Introduction: what is quantum field theory ?
... example, two electrons are identical in every way, regardless of where they came from and what they’ve been through. The same is true of every other fundamental particle. Suppose we capture a proton from a cosmic ray which we identify as coming from a supernova lying 8 billion lightyears away. We co ...
... example, two electrons are identical in every way, regardless of where they came from and what they’ve been through. The same is true of every other fundamental particle. Suppose we capture a proton from a cosmic ray which we identify as coming from a supernova lying 8 billion lightyears away. We co ...