PowerPoint
... Bohr’s theory correctly explained the hydrogen emission spectrum The theory failed for all other elements with more than 1 electron Bohr’s theory attempted to use classical mechanics to solve a problem that could not be solved by classical mechanics ...
... Bohr’s theory correctly explained the hydrogen emission spectrum The theory failed for all other elements with more than 1 electron Bohr’s theory attempted to use classical mechanics to solve a problem that could not be solved by classical mechanics ...
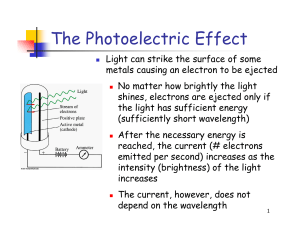
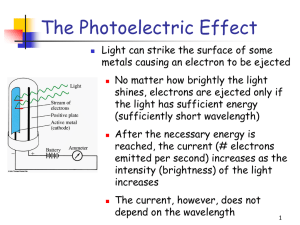
The Photoelectric Effect
... Bohr’s theory correctly explained the hydrogen emission spectrum The theory failed for all other elements with more than 1 electron Bohr’s theory attempted to use classical mechanics to solve a problem that could not be solved by classical mechanics ...
... Bohr’s theory correctly explained the hydrogen emission spectrum The theory failed for all other elements with more than 1 electron Bohr’s theory attempted to use classical mechanics to solve a problem that could not be solved by classical mechanics ...
The Department of Applied Physics (http://physics
... gravity and superfluid 3He. The project combines theoretical and experimental efforts. We expect to hire one researcher with theoretical background and experience in a team work with experimentalists and one with experimental skills, preferably in superfluid 3He. For more information please contact ...
... gravity and superfluid 3He. The project combines theoretical and experimental efforts. We expect to hire one researcher with theoretical background and experience in a team work with experimentalists and one with experimental skills, preferably in superfluid 3He. For more information please contact ...
Greek Alphabet Fundamental constants: Useful conversions:
... binding (zero net charge between protons). Metallic Bond: Many electrons (one or more per atom) shared between a large number N of atoms -> positively charged “rest atoms” in “Fermi gas” of electrons. Electron energy eigenstates are clustered in “bands”; highest (partially or totally unoccupied) ban ...
... binding (zero net charge between protons). Metallic Bond: Many electrons (one or more per atom) shared between a large number N of atoms -> positively charged “rest atoms” in “Fermi gas” of electrons. Electron energy eigenstates are clustered in “bands”; highest (partially or totally unoccupied) ban ...
9. Charges in motion in a magnetic field
... magnetic and electric fields whose magnitude are 0.10 T and 1000 N/C, respectively. Suddenly, the electric field is turned off and the ion is moving on a circular path of radius 1.2 cm, due to the action of the magnetic field, only. Find the mass of the ion. This is a spectrometer device able to ide ...
... magnetic and electric fields whose magnitude are 0.10 T and 1000 N/C, respectively. Suddenly, the electric field is turned off and the ion is moving on a circular path of radius 1.2 cm, due to the action of the magnetic field, only. Find the mass of the ion. This is a spectrometer device able to ide ...
Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms
... velocity of an electron (or any other particle) x – represents position p – represents momentum (velocity multiplied by mass) - represents a constant Δ – in this case, delta represents the uncertainty. ...
... velocity of an electron (or any other particle) x – represents position p – represents momentum (velocity multiplied by mass) - represents a constant Δ – in this case, delta represents the uncertainty. ...
Chapter 29 - Wayne State University Physics and Astronomy
... Small or light weight particles Are point like particles – no internal structure (yet) 6 leptons Electron e, muon m, tau t and their associated neutrinos: ne, nm, nt Also, their antiparticles Neutrinos have tiny mass, ~3 eV/c2 ...
... Small or light weight particles Are point like particles – no internal structure (yet) 6 leptons Electron e, muon m, tau t and their associated neutrinos: ne, nm, nt Also, their antiparticles Neutrinos have tiny mass, ~3 eV/c2 ...
Quantum Mechanical Model - Elmwood Park Memorial Middle School
... • These slides are on the webpage if you would like them. ...
... • These slides are on the webpage if you would like them. ...
Activity 2 - The Bohr Atom
... So we have a new model for the energy levels of the atom. But how does this help get around the original problem: that the electrons should radiate energy as they are accelerated? It is because they can only exist in one of the levels. Therefore if the electron was in the level, there is no lower le ...
... So we have a new model for the energy levels of the atom. But how does this help get around the original problem: that the electrons should radiate energy as they are accelerated? It is because they can only exist in one of the levels. Therefore if the electron was in the level, there is no lower le ...
CLASSICAL MECHANICS II - Makerere University Courses
... Generalized coordinates; Lagrangian formulation and applications; Hamiltonian and application to simple problems including central orbits and small oscillations; canonical coordinates and applications. ...
... Generalized coordinates; Lagrangian formulation and applications; Hamiltonian and application to simple problems including central orbits and small oscillations; canonical coordinates and applications. ...
LAMB SHIFT & VACUUM POLARIZATION CORRECTIONS TO THE
... tion, Dirac devised a relativistic wave equation that is linear in both ∂/∂t and ∇, although he succeeded in avoiding the negative probability density, negative-energy solutions still occurred. That means that an atomic electron can have both negative and positive energies. But according to the qua ...
... tion, Dirac devised a relativistic wave equation that is linear in both ∂/∂t and ∇, although he succeeded in avoiding the negative probability density, negative-energy solutions still occurred. That means that an atomic electron can have both negative and positive energies. But according to the qua ...