Quantum Statistics Applications
... Phonon Gas and Heat Capacity • Heat capacity of a solid depends on vibrational modes of atoms • electron’s energy levels forced high by Pauli Ex. And so do not contribute ...
... Phonon Gas and Heat Capacity • Heat capacity of a solid depends on vibrational modes of atoms • electron’s energy levels forced high by Pauli Ex. And so do not contribute ...
Quantum mechanics and electron structure
... The missing link in Bohr’s model was the quantum nature of the electron Quantum mechanics yields a viable model for electronic structure in all elements Quantum mechanics replaced the particle by the wave The extent to which it is physical reality or an abstract mathematical model remains a fascinat ...
... The missing link in Bohr’s model was the quantum nature of the electron Quantum mechanics yields a viable model for electronic structure in all elements Quantum mechanics replaced the particle by the wave The extent to which it is physical reality or an abstract mathematical model remains a fascinat ...
De Broglie waves
... Wave function • Each particle is represented by a wave function, and the square of its absolute magnitude |ψ|2 evaluated at a particular place at a particular time is proportional to the probability of finding the body there at that time. Probability density. • The probability density |ψ|2 is given ...
... Wave function • Each particle is represented by a wave function, and the square of its absolute magnitude |ψ|2 evaluated at a particular place at a particular time is proportional to the probability of finding the body there at that time. Probability density. • The probability density |ψ|2 is given ...
MiniQuiz 3
... DeBroglie proposed that the electron had wave properties, as well as particle properties. He proposed that the wavelength of a particle was related to the mass through the equation λ = h/mυ, where υ is the velocity. His original proposal was based on: a•) b) c) d) e) ...
... DeBroglie proposed that the electron had wave properties, as well as particle properties. He proposed that the wavelength of a particle was related to the mass through the equation λ = h/mυ, where υ is the velocity. His original proposal was based on: a•) b) c) d) e) ...
From quantum to quantum computer
... Nobel Prizes: 1932: W. Heisenberg "for the creation of QM…" 1933: E. Schrodinger and P. Dirac "for the discovery of new productive forms of atomic theory" Prizes conferred in the same year 1933 (no prize given in 1931 and 1932) ...
... Nobel Prizes: 1932: W. Heisenberg "for the creation of QM…" 1933: E. Schrodinger and P. Dirac "for the discovery of new productive forms of atomic theory" Prizes conferred in the same year 1933 (no prize given in 1931 and 1932) ...
The Addition Property of Equality if a = b, then a + c = b + c
... •We can add a positive number to both sides of the equation and it will not change the equality. •We can add a negative number to both sides of the equation and it will not change the equality. (adding a negative number is the same as subtracting a positive) ...
... •We can add a positive number to both sides of the equation and it will not change the equality. •We can add a negative number to both sides of the equation and it will not change the equality. (adding a negative number is the same as subtracting a positive) ...
Dynamics
... kinematic properties of object. We indirectly control position, velocity, and acceleration by exerting forces and torques Current position f ...
... kinematic properties of object. We indirectly control position, velocity, and acceleration by exerting forces and torques Current position f ...
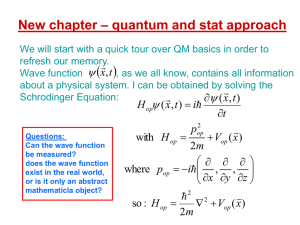
quantum and stat approach
... Average values (a.k.a. “expectation values”) Suppose that you perform measurements of a quantity associated with a Ωop operator, on a quantum system that at the time of each measurement is in the same state ψ . Each measurement yields an eigenvalue, but each time it may be a different one from the ...
... Average values (a.k.a. “expectation values”) Suppose that you perform measurements of a quantity associated with a Ωop operator, on a quantum system that at the time of each measurement is in the same state ψ . Each measurement yields an eigenvalue, but each time it may be a different one from the ...
Problem set 9
... work in the momentum basis. So you need to know how x̂ acts in k -space. This was worked ...
... work in the momentum basis. So you need to know how x̂ acts in k -space. This was worked ...
Chapter 10 • We want to complete our discussion of quantum Schr
... wave function that encoded the probability of finding the particle in a particular location. We have seen that as a particle moves through a potential, V(x), that is changing with position, as long as the particle is in a classically allowed region, the wave function still had the general shape of a ...
... wave function that encoded the probability of finding the particle in a particular location. We have seen that as a particle moves through a potential, V(x), that is changing with position, as long as the particle is in a classically allowed region, the wave function still had the general shape of a ...
Spin-Orbit Interaction - diss.fu
... not affect the band structure, except for certain points of the Brillouin zone (BZ), where the influence of spin-orbit interaction can be very important. As an example, we consider the center of a BZ (Γ point) that has cubic symmetry. In a tight binding model, we can build up the p bands from atomic ...
... not affect the band structure, except for certain points of the Brillouin zone (BZ), where the influence of spin-orbit interaction can be very important. As an example, we consider the center of a BZ (Γ point) that has cubic symmetry. In a tight binding model, we can build up the p bands from atomic ...
Quantum Numbers
... Number of orbitals in an energy level= n 2 How many orbitals are contained in the 3 rd energy level? 3 rd energy level and below? ...
... Number of orbitals in an energy level= n 2 How many orbitals are contained in the 3 rd energy level? 3 rd energy level and below? ...
F34TPP Particle Physics 1 Lecture one
... • how many possible combinations of qi and q̄i are there for three quark flavours? • of these possible combinations, which is the SU(3) singet, i.e. invariant under u → d, or u → s etc.? • with this singlet removed, arrange the remaining states into an octet, where the top row of the hexagon has S=1 ...
... • how many possible combinations of qi and q̄i are there for three quark flavours? • of these possible combinations, which is the SU(3) singet, i.e. invariant under u → d, or u → s etc.? • with this singlet removed, arrange the remaining states into an octet, where the top row of the hexagon has S=1 ...
Spinning Spins - Journal Club for Condensed Matter Physics
... also transfer angular momentum between the spins and the lattice. This is the mechanism behind the Einstein-deHaas effect in which a freely suspended magnetic material begins to mechanically rotate when it is cooled below the Curie temperature. The sign of the spontaneous magnetic order determines t ...
... also transfer angular momentum between the spins and the lattice. This is the mechanism behind the Einstein-deHaas effect in which a freely suspended magnetic material begins to mechanically rotate when it is cooled below the Curie temperature. The sign of the spontaneous magnetic order determines t ...
AS Physics
... “Number of protons in the nucleus (also equal to number of electrons)” Nucleon number or Mass number “Number of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus” Isotope “A form of an element with the same proton number but different neutron number” ...
... “Number of protons in the nucleus (also equal to number of electrons)” Nucleon number or Mass number “Number of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus” Isotope “A form of an element with the same proton number but different neutron number” ...