particlephysics
... 1 photon producing electron-positron pair It also works the other way around – knowing the mass of the particle-antiparticle pair that annihilate you calculate the energy of the photons produced. ...
... 1 photon producing electron-positron pair It also works the other way around – knowing the mass of the particle-antiparticle pair that annihilate you calculate the energy of the photons produced. ...
Annalen der Physik
... Lord Kelvin reflecting on the status of physics. “I am lucky to have seen all the major accomplishments in Physics! ...
... Lord Kelvin reflecting on the status of physics. “I am lucky to have seen all the major accomplishments in Physics! ...
1 ψ ω ω ω ψ ψ ψ
... for 0 ≤ x ≤ L and zero otherwise. (a) Determine the expectation value of x. (b) Determine the probability of finding the particle near L/2, by calculating the probability that the particle lies in the range 0.490L ≤ x ≤ 0.510L. (c) What If? Determine the probability of finding the particle near L/4, ...
... for 0 ≤ x ≤ L and zero otherwise. (a) Determine the expectation value of x. (b) Determine the probability of finding the particle near L/2, by calculating the probability that the particle lies in the range 0.490L ≤ x ≤ 0.510L. (c) What If? Determine the probability of finding the particle near L/4, ...
(8%) Write (a) the mass-balance expression and (b) the charge-balance equation
... (i) X-ray photoelectrons, and (ii) Auger electrons. (9%) Define the following terms: a. (3%) buffer capacity b. (3%) guard column (HPLC) c. (3%) electrophoretic mobility (CE) (4%) Determine the following thermodynamic quantities extensive or intensive variables: (i) pressure (ii) entropy (iii) chemi ...
... (i) X-ray photoelectrons, and (ii) Auger electrons. (9%) Define the following terms: a. (3%) buffer capacity b. (3%) guard column (HPLC) c. (3%) electrophoretic mobility (CE) (4%) Determine the following thermodynamic quantities extensive or intensive variables: (i) pressure (ii) entropy (iii) chemi ...
The Wave Nature of Matter - Waterford Public Schools
... • The square of a wave function (2) gives the probability of finding an electron in a particular infinitesimally small volume of space in an atom • Because we are treating electrons as waves (not particles), we cannot pinpoint the specific location of an electron! • Instead, mathematical solutions ...
... • The square of a wave function (2) gives the probability of finding an electron in a particular infinitesimally small volume of space in an atom • Because we are treating electrons as waves (not particles), we cannot pinpoint the specific location of an electron! • Instead, mathematical solutions ...
1 B
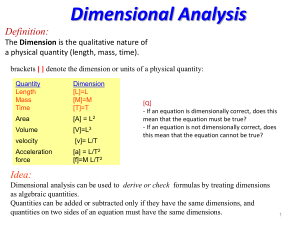
... Dimensional analysis can be used to derive or check formulas by treating dimensions as algebraic quantities. Quantities can be added or subtracted only if they have the same dimensions, and quantities on two sides of an equation must have the same dimensions. ...
... Dimensional analysis can be used to derive or check formulas by treating dimensions as algebraic quantities. Quantities can be added or subtracted only if they have the same dimensions, and quantities on two sides of an equation must have the same dimensions. ...
ChemChapter_4[1]Light
... the exact position and the momentum (velocity) of a small particle at the same time. Schrodinger’s Wave Equation – describes the probability of finding an electron at some distance from the nucleus in terms of the wave function Y ...
... the exact position and the momentum (velocity) of a small particle at the same time. Schrodinger’s Wave Equation – describes the probability of finding an electron at some distance from the nucleus in terms of the wave function Y ...
Chemistry 330 Chapter 11
... Energy of the H atom is quantized Electron is promoted from a low to high energy level by the absorption of a photon The amount of energy absorbed and emitted by the atom is quantized Only orbits of certain angular momenta are allowed ...
... Energy of the H atom is quantized Electron is promoted from a low to high energy level by the absorption of a photon The amount of energy absorbed and emitted by the atom is quantized Only orbits of certain angular momenta are allowed ...
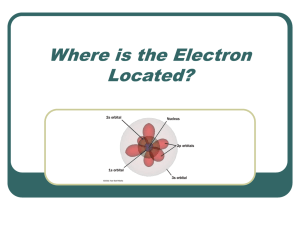
Where is the Electron Located?
... energy level occupied by an electron. Angular Momentum (l): Indicates the shape of the orbital (s,p,d,f,g) ...
... energy level occupied by an electron. Angular Momentum (l): Indicates the shape of the orbital (s,p,d,f,g) ...
Semiclassical calculation of electron spectra in atoms through two
... Coulomb potential leads to the lift of the degeneracy in the orbital momentum l . It has been shown in [1], that the corresponding splitting E nl E nl E n 0 quadratically depends on the orbital momentum l 1/ 2 (here n is a principal quantum number). In addition an analysis of the energy l ...
... Coulomb potential leads to the lift of the degeneracy in the orbital momentum l . It has been shown in [1], that the corresponding splitting E nl E nl E n 0 quadratically depends on the orbital momentum l 1/ 2 (here n is a principal quantum number). In addition an analysis of the energy l ...












![ChemChapter_4[1]Light](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001894151_1-323884b777914f52c04d2bb917d4088a-300x300.png)