Chapter 6 Review
... and explain what they mean. c) Graph the relation. d) What would a 4-h house call cost? 7. Determine the x- and y-intercepts of each line. Then, graph the line. a) 4x + 5y = 20 b) 2x − 3y = 6 8. Christopher is at a movie with his younger sister, Cindy. He has $24 to spend on popcorn and pop. Popcorn ...
... and explain what they mean. c) Graph the relation. d) What would a 4-h house call cost? 7. Determine the x- and y-intercepts of each line. Then, graph the line. a) 4x + 5y = 20 b) 2x − 3y = 6 8. Christopher is at a movie with his younger sister, Cindy. He has $24 to spend on popcorn and pop. Popcorn ...
Lecture 4
... Now, we need to include spin in our description. Electrons have spin antisymmetric. ...
... Now, we need to include spin in our description. Electrons have spin antisymmetric. ...
Asymptotic Freedom: From Paradox to Paradigm
... Screening by virtual particles wipes out interactions The demise of quantum field theory was widely proclaimed - and welcomed! ...
... Screening by virtual particles wipes out interactions The demise of quantum field theory was widely proclaimed - and welcomed! ...
You are going to read the chapter at home.
... Ψ(x1 … xN ; t ) must be symmetric with respect to interchange of any two coordinates; i.e., Ψ( … xk … xl … ; t ) = + Ψ( … xl … xk … ; t ) ...
... Ψ(x1 … xN ; t ) must be symmetric with respect to interchange of any two coordinates; i.e., Ψ( … xk … xl … ; t ) = + Ψ( … xl … xk … ; t ) ...
Hydrogen Mastery Answers
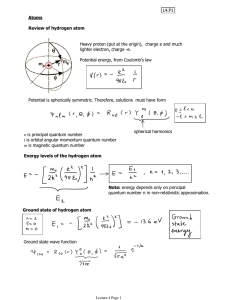
... 1. Given an orbital (such as 2s, 3pz), write down the wavefunction (given the general formula). From this wavefunction, solve for the equations for the nodes. Sketch the orbital and its nodes. First, we determine the quantum numbers n,l,m. We then plug these values into the equation above for wavefu ...
... 1. Given an orbital (such as 2s, 3pz), write down the wavefunction (given the general formula). From this wavefunction, solve for the equations for the nodes. Sketch the orbital and its nodes. First, we determine the quantum numbers n,l,m. We then plug these values into the equation above for wavefu ...
January 2005
... J05M.2 - Planet Moving Through Dust Cloud Problem A planet of mass M and radius R moves through a cloud of interplanetary dust at a constant velocity v0 . The dust particles have negligible mass. Depending on its initial position when the planet is still far away, each dust particle will either hit ...
... J05M.2 - Planet Moving Through Dust Cloud Problem A planet of mass M and radius R moves through a cloud of interplanetary dust at a constant velocity v0 . The dust particles have negligible mass. Depending on its initial position when the planet is still far away, each dust particle will either hit ...
Part II. Statistical mechanics Chapter 9. Classical and quantum
... equilibriums states based on microscopic dynamics. For example, while thermodynamics can manipulate equations of state and fundamental relations, it cannot be used to derive them. Statistical mechanics can derive such equations and relations from first principles. Before we study statistical mechani ...
... equilibriums states based on microscopic dynamics. For example, while thermodynamics can manipulate equations of state and fundamental relations, it cannot be used to derive them. Statistical mechanics can derive such equations and relations from first principles. Before we study statistical mechani ...
PPT
... measuring instruments…the necessity of a final revision of the classical ideal of causality and a radical revision of our attitude towards the problem of physical reality. The criterion of reality proposed contains an essential ambiguity… regarding the expression 'without in any way disturbing the s ...
... measuring instruments…the necessity of a final revision of the classical ideal of causality and a radical revision of our attitude towards the problem of physical reality. The criterion of reality proposed contains an essential ambiguity… regarding the expression 'without in any way disturbing the s ...
PPT
... • First term, (squared momentum), depends on how wiggles in space. Like 1/wavelength squared, p2/2m – Second term, (potential energy), due to various neighbors (whose positions are presumed fixed in our reference frame). – Third term (total energy) is how fast y changes in time: frequency. E=hf. • ...
... • First term, (squared momentum), depends on how wiggles in space. Like 1/wavelength squared, p2/2m – Second term, (potential energy), due to various neighbors (whose positions are presumed fixed in our reference frame). – Third term (total energy) is how fast y changes in time: frequency. E=hf. • ...
量子力學
... for the dipole transition involved in absorption and emission of a photon. 31. A time t=0 s spin 1/2 particle with spin in the x-direction enters a region of space in which there is a uniform magnetic field H in the z-direction. Find the probability that at time t the spin is still in the x-directio ...
... for the dipole transition involved in absorption and emission of a photon. 31. A time t=0 s spin 1/2 particle with spin in the x-direction enters a region of space in which there is a uniform magnetic field H in the z-direction. Find the probability that at time t the spin is still in the x-directio ...