CHAPTER 4: Structure of the Atom
... The number of scattering nuclei per unit area The fraction of incident particles scattered is ...
... The number of scattering nuclei per unit area The fraction of incident particles scattered is ...
CLASSICAL-QUANTUM CORRESPONDENCE AND WAVE PACKET SOLUTIONS OF THE DIRAC
... The idea of wave mechanics leads naturally to assume the well-known relation E = ~ω in the specific form H = ~W , where H is the classical Hamiltonian of a particle and W is the dispersion relation of the sought-for wave equation. We derive the expression of H in a curved space-time with an electrom ...
... The idea of wave mechanics leads naturally to assume the well-known relation E = ~ω in the specific form H = ~W , where H is the classical Hamiltonian of a particle and W is the dispersion relation of the sought-for wave equation. We derive the expression of H in a curved space-time with an electrom ...
Academic Chemistry Atomic History Study Guide 1. Identify and
... in World War I, contributed greatly to science prior to his death by discovering the atomic number. 11. According to the laws of classical physics, a charged particle traveling on a curved path will lose energy. This would cause an electron to drop into the nucleus, which would destroy the atom. ___ ...
... in World War I, contributed greatly to science prior to his death by discovering the atomic number. 11. According to the laws of classical physics, a charged particle traveling on a curved path will lose energy. This would cause an electron to drop into the nucleus, which would destroy the atom. ___ ...
Hydrogen (/ˈhaɪdrɵdʒən/ HY-drə-jən)[7] is a chemical element
... key role in the development of quantum mechanics. Deuterium (symbol D or 2H, also known as heavy hydrogen) is one of two stable isotopes of hydrogen. It has a natural abundance in Earth's oceans of about one atom in 6,420 of hydrogen (~156.25 ppm on an atom basis). Deuterium accounts for approximate ...
... key role in the development of quantum mechanics. Deuterium (symbol D or 2H, also known as heavy hydrogen) is one of two stable isotopes of hydrogen. It has a natural abundance in Earth's oceans of about one atom in 6,420 of hydrogen (~156.25 ppm on an atom basis). Deuterium accounts for approximate ...
Word
... A. Review of Basic Ideas: The evolving model of the atom The word “atom” comes from Greek, and means indivisible (a- not, tom- divisible). In about 450 BC Democritus postulated that matter was made up of tiny individual atoms, and that the shape of the atoms determined the properties of the material ...
... A. Review of Basic Ideas: The evolving model of the atom The word “atom” comes from Greek, and means indivisible (a- not, tom- divisible). In about 450 BC Democritus postulated that matter was made up of tiny individual atoms, and that the shape of the atoms determined the properties of the material ...
Quantum Model of the Atom Power point
... •The Heisenberg Uncertainty principle states that is it impossible to determine simultaneously both the position and velocity of an electron or any other particle. •Show video clip. ...
... •The Heisenberg Uncertainty principle states that is it impossible to determine simultaneously both the position and velocity of an electron or any other particle. •Show video clip. ...
Document
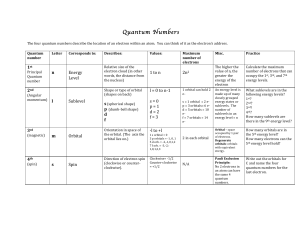
... • n, the principal quantum number, can have any integer value, and gives the energy of the level • l, the orbital quantum number, can have values from 0 to n – 1 • ml, the magnetic quantum number, can have values from –1 to +1 •ms, the spin quantum number, can be +½ or -½ • Energy levels depend on n ...
... • n, the principal quantum number, can have any integer value, and gives the energy of the level • l, the orbital quantum number, can have values from 0 to n – 1 • ml, the magnetic quantum number, can have values from –1 to +1 •ms, the spin quantum number, can be +½ or -½ • Energy levels depend on n ...
lecture31
... • n, the principal quantum number, can have any integer value, and gives the energy of the level • l, the orbital quantum number, can have values from 0 to n – 1 • ml, the magnetic quantum number, can have values from –1 to +1 •ms, the spin quantum number, can be +½ or -½ • Energy levels depend on n ...
... • n, the principal quantum number, can have any integer value, and gives the energy of the level • l, the orbital quantum number, can have values from 0 to n – 1 • ml, the magnetic quantum number, can have values from –1 to +1 •ms, the spin quantum number, can be +½ or -½ • Energy levels depend on n ...
vocab chap 6
... There is also a list of important people who contributed to the Modern Atomic Theory. You will need to know what each one did. ...
... There is also a list of important people who contributed to the Modern Atomic Theory. You will need to know what each one did. ...
Atomic Structure Zumdahl Chemistry Chapter 7
... In which n is an integer Z is the nuclear charge We must emphasize two important points about the Bohr model: 1. The model correctly fits the quantized energy levels of the hydrogen atom and postulates only certain allowed circular orbits for the electron. 2. As the electron becomes more tightly bou ...
... In which n is an integer Z is the nuclear charge We must emphasize two important points about the Bohr model: 1. The model correctly fits the quantized energy levels of the hydrogen atom and postulates only certain allowed circular orbits for the electron. 2. As the electron becomes more tightly bou ...
Vocabulary Terms Defined
... quantum (93) the minimum quantity of energy that can be lost or gained by an atom (plural: quanta) A quantum is the minimum amount of any physical entity involved in an interaction. continuous spectrum (94) the emission of a continuous range of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation excited state ...
... quantum (93) the minimum quantity of energy that can be lost or gained by an atom (plural: quanta) A quantum is the minimum amount of any physical entity involved in an interaction. continuous spectrum (94) the emission of a continuous range of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation excited state ...
PowerPoint - OrgSites.com
... The Puzzle of the Atom Protons and electrons are attracted to each other because of opposite charges Electrically charged particles moving in a curved path give off energy ...
... The Puzzle of the Atom Protons and electrons are attracted to each other because of opposite charges Electrically charged particles moving in a curved path give off energy ...
Hydrogen atom
A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen. The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively charged proton and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the Coulomb force. Atomic hydrogen constitutes about 75% of the elemental (baryonic) mass of the universe.In everyday life on Earth, isolated hydrogen atoms (usually called ""atomic hydrogen"" or, more precisely, ""monatomic hydrogen"") are extremely rare. Instead, hydrogen tends to combine with other atoms in compounds, or with itself to form ordinary (diatomic) hydrogen gas, H2. ""Atomic hydrogen"" and ""hydrogen atom"" in ordinary English use have overlapping, yet distinct, meanings. For example, a water molecule contains two hydrogen atoms, but does not contain atomic hydrogen (which would refer to isolated hydrogen atoms).









![Hydrogen (/ˈhaɪdrɵdʒən/ HY-drə-jən)[7] is a chemical element](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001197267_1-624cb7c7c4dbdb26b0769567aa77b6ad-300x300.png)