Unit 3: Electrons
... Light (Einstein) and electrons (de Broglie) have a dual nature: particle and wave. The nature of light/electrons depends on the technique one uses to study them. Complex mathematical models are the basis for the quantum mechanical model of the atom. Schrödinger’s wavefunctions produc atomic orbi ...
... Light (Einstein) and electrons (de Broglie) have a dual nature: particle and wave. The nature of light/electrons depends on the technique one uses to study them. Complex mathematical models are the basis for the quantum mechanical model of the atom. Schrödinger’s wavefunctions produc atomic orbi ...
1 slide per page() - Wayne State University Physics and Astronomy
... In 1913 Bohr provided an explanation of atomic spectra that includes some features of the currently accepted theory His model includes both classical and non-classical ideas His model included an attempt to explain why the atom was stable ...
... In 1913 Bohr provided an explanation of atomic spectra that includes some features of the currently accepted theory His model includes both classical and non-classical ideas His model included an attempt to explain why the atom was stable ...
Physics 322 Final Exam Study Guide (2015) [Pages 4 Only]
... spectroscopic notation to indicate the various ℓ states (NOTE: The order is s, p, d, f, g, h,...) 7. Radial Probability a. Understand what is represented by the radial probability in equation 7-38 (a probability per unit radial distance). b. Know the difference between most likely location, most lik ...
... spectroscopic notation to indicate the various ℓ states (NOTE: The order is s, p, d, f, g, h,...) 7. Radial Probability a. Understand what is represented by the radial probability in equation 7-38 (a probability per unit radial distance). b. Know the difference between most likely location, most lik ...
Lecture 18: Intro. to Quantum Mechanics
... • The idea behind wave mechanics was that the existence of the electron in fixed energy levels could be though of as a “standing wave”. ...
... • The idea behind wave mechanics was that the existence of the electron in fixed energy levels could be though of as a “standing wave”. ...
FIZICA
... S10. The Pauli principle states that: Into an atom (molecule) there are no two electrons (in general fermions) characterized by identical quantum numbers. Name these four quantum numbers and calculate the maximum number of orbitals for a hidrogenoid atom with two electrons characterized by i) n1 = 2 ...
... S10. The Pauli principle states that: Into an atom (molecule) there are no two electrons (in general fermions) characterized by identical quantum numbers. Name these four quantum numbers and calculate the maximum number of orbitals for a hidrogenoid atom with two electrons characterized by i) n1 = 2 ...
Lecture 6 - physics.udel.edu
... Is ground state of helium triplet, singlet, or can be either one and can not be determined from the given information? The helium excited states have form one electron in the ground state and one electron in the excited state. Do these states have to be singlet, triplet states, or can be both? ...
... Is ground state of helium triplet, singlet, or can be either one and can not be determined from the given information? The helium excited states have form one electron in the ground state and one electron in the excited state. Do these states have to be singlet, triplet states, or can be both? ...
Exam 2 Review - Iowa State University
... 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 515-294-6624 [email protected] http://www.si.iastate.edu ...
... 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 515-294-6624 [email protected] http://www.si.iastate.edu ...
ch-7 [Basic Chemistry]
... orbit (2-3). Once in a high energy orbit, the electron immediately jumps back to its initial orbit and emits light (photon) The photon represents a certain frequency f (color) , and carries energy given by ...
... orbit (2-3). Once in a high energy orbit, the electron immediately jumps back to its initial orbit and emits light (photon) The photon represents a certain frequency f (color) , and carries energy given by ...
Constructive Interference
... exist in stable configurations around nuclei Wavefunctions and energies for these configurations determine most properties of matter ...
... exist in stable configurations around nuclei Wavefunctions and energies for these configurations determine most properties of matter ...
atom
... • Law of definite proportions: a chemical compound contains the same elements in exactly the same proportions by mass regardless of the size of the sample or source of the compound • Law of multiple proportions: if two or more different compounds are composed of the same two elements, then the ratio ...
... • Law of definite proportions: a chemical compound contains the same elements in exactly the same proportions by mass regardless of the size of the sample or source of the compound • Law of multiple proportions: if two or more different compounds are composed of the same two elements, then the ratio ...
Chap 7.
... earlier by Planck and Einstein. The Bohr Atom The nuclear model proposed by Rutherford in 1911 pictures the atom as a heavy, positively-charged nucleus, around which much lighter, negativelycharged electrons circulate, much like planets in the Solar system. This model is however completely untenable ...
... earlier by Planck and Einstein. The Bohr Atom The nuclear model proposed by Rutherford in 1911 pictures the atom as a heavy, positively-charged nucleus, around which much lighter, negativelycharged electrons circulate, much like planets in the Solar system. This model is however completely untenable ...
The Quantum Model of the Atom
... • Idea involved the detection of electrons, which are detected by their interactions with photons • Because photons have about the same energy as electrons, any attempt to locate a specific electron with a photon knocks the electron off its course • Results in uncertainty in trying to locate an el ...
... • Idea involved the detection of electrons, which are detected by their interactions with photons • Because photons have about the same energy as electrons, any attempt to locate a specific electron with a photon knocks the electron off its course • Results in uncertainty in trying to locate an el ...
Definitions are in Book
... change in enthalpy for whole process is the same, regardless of whether you use Hess’s law or heats of formation. In this way enthalpy is a state function. 3) What is meant by “Energy is quantized”? Energy can only be certain values. For example, the 1s orbital has a certain energy and the 2s orbita ...
... change in enthalpy for whole process is the same, regardless of whether you use Hess’s law or heats of formation. In this way enthalpy is a state function. 3) What is meant by “Energy is quantized”? Energy can only be certain values. For example, the 1s orbital has a certain energy and the 2s orbita ...
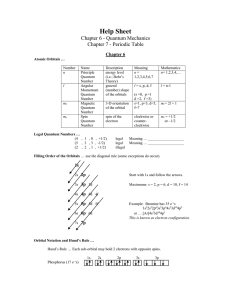
Help Sheet
... General rule: Any element with an odd-electron number must be paramagnetic. Shielding … describes why some orbitals are at higher or lower energy levels than others. Example: A 2s electron spends more of its time (on average) around the nucleus than a 2p electron due to the size of the orbitals. The ...
... General rule: Any element with an odd-electron number must be paramagnetic. Shielding … describes why some orbitals are at higher or lower energy levels than others. Example: A 2s electron spends more of its time (on average) around the nucleus than a 2p electron due to the size of the orbitals. The ...
Chapter 7: Quantum Mechanical Model of Atom
... • Werner Heisenberg - showed that it is impossible to know (or measure) precisely both the position and velocity (or the momentum) at the same time. • The simple act of “seeing” an electron would change ...
... • Werner Heisenberg - showed that it is impossible to know (or measure) precisely both the position and velocity (or the momentum) at the same time. • The simple act of “seeing” an electron would change ...
Chapter 1
... A contemporaneous achievement was the demonstration by J. J. Thomson that cathode rays were composed of particles whose ratio of charge to mass was very much greater than that previously measured for ions. From his identification of electrons as a universal constituent of matter, Thomson developed h ...
... A contemporaneous achievement was the demonstration by J. J. Thomson that cathode rays were composed of particles whose ratio of charge to mass was very much greater than that previously measured for ions. From his identification of electrons as a universal constituent of matter, Thomson developed h ...
Review
... Why is it better? • Schrodinger model: – Gives correct energies. – Gives correct angular momentum. – Describes electron as 3D wave of probability. – Quantized energy levels result from boundary conditions. – Schrodinger equation can generalize to multi-electron atoms. – Doesn’t explain why Sc ...
... Why is it better? • Schrodinger model: – Gives correct energies. – Gives correct angular momentum. – Describes electron as 3D wave of probability. – Quantized energy levels result from boundary conditions. – Schrodinger equation can generalize to multi-electron atoms. – Doesn’t explain why Sc ...
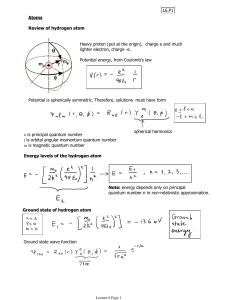
Hydrogen atom
A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen. The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively charged proton and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the Coulomb force. Atomic hydrogen constitutes about 75% of the elemental (baryonic) mass of the universe.In everyday life on Earth, isolated hydrogen atoms (usually called ""atomic hydrogen"" or, more precisely, ""monatomic hydrogen"") are extremely rare. Instead, hydrogen tends to combine with other atoms in compounds, or with itself to form ordinary (diatomic) hydrogen gas, H2. ""Atomic hydrogen"" and ""hydrogen atom"" in ordinary English use have overlapping, yet distinct, meanings. For example, a water molecule contains two hydrogen atoms, but does not contain atomic hydrogen (which would refer to isolated hydrogen atoms).

![Physics 322 Final Exam Study Guide (2015) [Pages 4 Only]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007969504_1-e89a1630d6e27466a3e33b80f7e23b58-300x300.png)






![ch-7 [Basic Chemistry]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002135636_1-6e0da68ae8ae81ce33d9eac4143328a5-300x300.png)