
Physical Chemistry (4): Theoretical Chemistry
... The atomic theory allowed the development of modern chemistry, but lots of questions remained unanswered, and in particular the WHY is not being explained: • What is the binding force between atoms? – It is not the charge since atoms are neutral. Why can even two atoms of the same kind (like H-H) fo ...
... The atomic theory allowed the development of modern chemistry, but lots of questions remained unanswered, and in particular the WHY is not being explained: • What is the binding force between atoms? – It is not the charge since atoms are neutral. Why can even two atoms of the same kind (like H-H) fo ...
Nuclear - Orangefield ISD
... ◦ Electrons are held within atom by attraction to positively charged nucleus ◦ Number of protons equals number of electrons ...
... ◦ Electrons are held within atom by attraction to positively charged nucleus ◦ Number of protons equals number of electrons ...
Atomic structure - Theory of Condensed Matter (Cambridge)
... To discuss the predicted energy shifts for particular states, it is helpful to introduce some nomenclature from atomic physics. For a state with principle quantum number n, total spin s, orbital angular momentum ', and total angular momentum j, one may use spectroscopic notation n2s+1 Lj to define t ...
... To discuss the predicted energy shifts for particular states, it is helpful to introduce some nomenclature from atomic physics. For a state with principle quantum number n, total spin s, orbital angular momentum ', and total angular momentum j, one may use spectroscopic notation n2s+1 Lj to define t ...
Matt`s talk about our observation of quantum
... or period of kicks are large enough that atoms (rotor) travel more than one lattice spacing (2 between kicks.→Force on atom is a random variable Scaled Planck's constant is a measure of how 'quantum' the system is. The smaller , the greater the quantum classical correspondence ~ ratio of quantized ...
... or period of kicks are large enough that atoms (rotor) travel more than one lattice spacing (2 between kicks.→Force on atom is a random variable Scaled Planck's constant is a measure of how 'quantum' the system is. The smaller , the greater the quantum classical correspondence ~ ratio of quantized ...
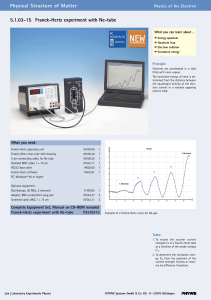
5.1.03-15 Franck-Hertz experiment with Ne
... 1913: An isolated atom consists of a positively charged nucleus about which electrons are distributed in successive orbits. He also postulated that only those orbits occur for which the angular momentum of the electron is an integral multiple of h/2p, i.e. n*h/2p, where n is an integer and h is Plan ...
... 1913: An isolated atom consists of a positively charged nucleus about which electrons are distributed in successive orbits. He also postulated that only those orbits occur for which the angular momentum of the electron is an integral multiple of h/2p, i.e. n*h/2p, where n is an integer and h is Plan ...
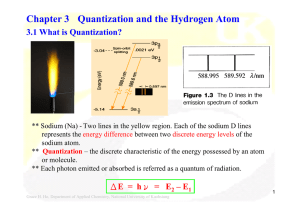
Chapter 3 Quantization and the Hydrogen Atom
... hν = Eionization + ½ mev2 -- In 1900, Plank introduced the quantization of energy and the Planck constant, h. -- In 1905, Einstein described light as composed of discrete quanta (photons), E = hν. ** Dual particle – wave nature of waves proposed by de Broglie in 1924: p = h /λ vs p = mev ** Uncertai ...
... hν = Eionization + ½ mev2 -- In 1900, Plank introduced the quantization of energy and the Planck constant, h. -- In 1905, Einstein described light as composed of discrete quanta (photons), E = hν. ** Dual particle – wave nature of waves proposed by de Broglie in 1924: p = h /λ vs p = mev ** Uncertai ...
o Orbital dipole moments. Orbital precession. Spin-orbit interaction.
... We know that the orientation potential energy of magnetic dipole moment is "E = #µˆ s $ Bˆ ...
... We know that the orientation potential energy of magnetic dipole moment is "E = #µˆ s $ Bˆ ...
Quantum states
... wave packet (= wave function). • A quantum state is characterized by a set of quantum numbers, such as the energy E. • Quantum numbers can be measured exactly. For example, the uncertainty E is zero for a stable state, where one can take an infinite time t for measuring the energy. ...
... wave packet (= wave function). • A quantum state is characterized by a set of quantum numbers, such as the energy E. • Quantum numbers can be measured exactly. For example, the uncertainty E is zero for a stable state, where one can take an infinite time t for measuring the energy. ...
L 33 Modern Physics [1] Modern Physics
... The failure of the “old” physics • We will now discuss an example of an effect that could not be explained by the pre- 20th century laws of physics. • The discovery of the correct explanation led to a revolution in the way we think about light and matter, particles and waves • The new concepts also ...
... The failure of the “old” physics • We will now discuss an example of an effect that could not be explained by the pre- 20th century laws of physics. • The discovery of the correct explanation led to a revolution in the way we think about light and matter, particles and waves • The new concepts also ...
21-SimilarityBetween.. - Saptarishis Astrology
... which pulls the other much smaller matter like stone following Newton’s laws of motion. Scottish physicist James Clark proposed another field called electromagnetic field laying down the laws of electric and magnetic fields. Electricity and magnetism are not two separate fields but different aspects ...
... which pulls the other much smaller matter like stone following Newton’s laws of motion. Scottish physicist James Clark proposed another field called electromagnetic field laying down the laws of electric and magnetic fields. Electricity and magnetism are not two separate fields but different aspects ...
The Harmonic Oscilla..
... Note that these functions (and their magnitudes squared) are very similar to the corresponding functions for the particle-in-the-box problem, being respectively even or odd with respect to reflection about y = 0. There is one important difference, however, and this is that the HO functions do not go ...
... Note that these functions (and their magnitudes squared) are very similar to the corresponding functions for the particle-in-the-box problem, being respectively even or odd with respect to reflection about y = 0. There is one important difference, however, and this is that the HO functions do not go ...
wave
... Where λvac is the wavelength of the light emitted in vacuum, RH is the Rydberg constant for hydrogen, n1 and n2 are integers such that n1 < n2 ...
... Where λvac is the wavelength of the light emitted in vacuum, RH is the Rydberg constant for hydrogen, n1 and n2 are integers such that n1 < n2 ...
Condensed Plasmoids – The Intermediate State of LENR
... A quantum-mechanical model of this strange state of matter is provided by the author [3], which will in the following be called “condensed plasmoids (CP)”. In contrast to the quantum-mechanical model of the atom, which is based on the spherically symmetric electrostatic potential of the nucleus, the ...
... A quantum-mechanical model of this strange state of matter is provided by the author [3], which will in the following be called “condensed plasmoids (CP)”. In contrast to the quantum-mechanical model of the atom, which is based on the spherically symmetric electrostatic potential of the nucleus, the ...
Department of Physical Sciences (Physics)
... (i) Describe the Rutherford model of the atom giving the formula for the balance of forces on the orbiting electron and discuss the experimental evidence that led to this model replacing the earlier JJ Thomson ‘plum pudding’ model. [6 marks] (ii) Explain the deficiencies of the Rutherford model whic ...
... (i) Describe the Rutherford model of the atom giving the formula for the balance of forces on the orbiting electron and discuss the experimental evidence that led to this model replacing the earlier JJ Thomson ‘plum pudding’ model. [6 marks] (ii) Explain the deficiencies of the Rutherford model whic ...
ON THE SHAPES OF ATOMS
... is, in fact, always possible to transform a set of non-orthogonal orbitals into an orthogonal set without altering the wavefunction 'V, so that expression 1 holds when using the new orbitals. These are of the same type as the original ones, i. e. 1 s', 2s', 2p', á , ... and so the conclusion of sphe ...
... is, in fact, always possible to transform a set of non-orthogonal orbitals into an orthogonal set without altering the wavefunction 'V, so that expression 1 holds when using the new orbitals. These are of the same type as the original ones, i. e. 1 s', 2s', 2p', á , ... and so the conclusion of sphe ...
Document
... Planck’s assumption suggests that the energy of any molecular vibration could be only some whole number multiple of hf: ...
... Planck’s assumption suggests that the energy of any molecular vibration could be only some whole number multiple of hf: ...
Quantum Chemistry II: Lecture Notes
... just by replacing L with S and repeating the procedure of Section 5.4 of the textbook. The result is: the eigenvalues of Ŝ2 are ...
... just by replacing L with S and repeating the procedure of Section 5.4 of the textbook. The result is: the eigenvalues of Ŝ2 are ...
Hydrogen atom
A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen. The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively charged proton and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the Coulomb force. Atomic hydrogen constitutes about 75% of the elemental (baryonic) mass of the universe.In everyday life on Earth, isolated hydrogen atoms (usually called ""atomic hydrogen"" or, more precisely, ""monatomic hydrogen"") are extremely rare. Instead, hydrogen tends to combine with other atoms in compounds, or with itself to form ordinary (diatomic) hydrogen gas, H2. ""Atomic hydrogen"" and ""hydrogen atom"" in ordinary English use have overlapping, yet distinct, meanings. For example, a water molecule contains two hydrogen atoms, but does not contain atomic hydrogen (which would refer to isolated hydrogen atoms).






![L 33 Modern Physics [1] Modern Physics](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003217156_1-265c5a519e2bca3f33717b4abd842898-300x300.png)



![L 34 Modern Physics [1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008622077_1-047a8df5b8f51427a7d951942e25e95f-300x300.png)









