Universal turning point behavior for Gaussian
... The dependence of Eq. 共5兲 on suggests an inverse relationship between energy uncertainty and the time before the first complete delocalization of the state in phase space 共considerations of Eq. 共11兲 to come will further support this兲. Unfortunately, the autocorrelation function generally provides ...
... The dependence of Eq. 共5兲 on suggests an inverse relationship between energy uncertainty and the time before the first complete delocalization of the state in phase space 共considerations of Eq. 共11兲 to come will further support this兲. Unfortunately, the autocorrelation function generally provides ...
topic 03 outline YT 2010 test
... its state, it must absorb or emit the exact amount of energy that will bring it from the initial state to the final state. (The ground state is the lowest energy state available to the electron. The excuted state is any level higher than the ground state. ) The formula for a change in energy (∆E ...
... its state, it must absorb or emit the exact amount of energy that will bring it from the initial state to the final state. (The ground state is the lowest energy state available to the electron. The excuted state is any level higher than the ground state. ) The formula for a change in energy (∆E ...
Electric Potential Questions
... 9. A proton is moved 10 cm on a path parallel to the field lines of a uniform electric field of 105 V/m. a) What is the change in the proton's potential? Consider both cases of moving with and against the field? b) What is the change in energy in electron volts? c) How much work would be done if the ...
... 9. A proton is moved 10 cm on a path parallel to the field lines of a uniform electric field of 105 V/m. a) What is the change in the proton's potential? Consider both cases of moving with and against the field? b) What is the change in energy in electron volts? c) How much work would be done if the ...
REVIEW OF WAVE MECHANICS
... given position. This restriction to probability rather than certainty extends to all physical measurements, not just position. The only exceptions are when the wave function representing the state of a system happens to be an eigenfunction of the operator representing the physical quantity, and in t ...
... given position. This restriction to probability rather than certainty extends to all physical measurements, not just position. The only exceptions are when the wave function representing the state of a system happens to be an eigenfunction of the operator representing the physical quantity, and in t ...
The Parable of the Three Umpires
... ability to capture or “enframe” in language. An electron, for example, can exhibit both “wave” or “particle” behaviour depending on how we interact with it. ...
... ability to capture or “enframe” in language. An electron, for example, can exhibit both “wave” or “particle” behaviour depending on how we interact with it. ...
Facilitator`s Guide PDF
... participants the visualization of atomic orbitals for hydrogen at http://www.falstad.com/qmatom/. Use the “real orbitals” and start at n=1, moving to n=2 and n=3. Then change the value of l. (Optional: The changing color represents the phase of the wave—this is what’s “waving.” The probability densi ...
... participants the visualization of atomic orbitals for hydrogen at http://www.falstad.com/qmatom/. Use the “real orbitals” and start at n=1, moving to n=2 and n=3. Then change the value of l. (Optional: The changing color represents the phase of the wave—this is what’s “waving.” The probability densi ...
The exotic world of quantum matter
... Band structure of the energy spectrum of electrons in crystals Interaction with lattice vibrations ...
... Band structure of the energy spectrum of electrons in crystals Interaction with lattice vibrations ...
Lectures 6-7
... For four of the d orbitals, both of these nodes are planes, giving a ‘petal-shaped’ orbital. For the fifth d orbital (_____),the nodes look more like a pair of inverted cones. This gives an orbital that looks a bit like a p orbital with a doughnut around it. (Note the phases, though; they are differ ...
... For four of the d orbitals, both of these nodes are planes, giving a ‘petal-shaped’ orbital. For the fifth d orbital (_____),the nodes look more like a pair of inverted cones. This gives an orbital that looks a bit like a p orbital with a doughnut around it. (Note the phases, though; they are differ ...
Lectures 10-11
... For four of the d orbitals, both of these nodes are planes, giving a ‘petal-shaped’ orbital. For the fifth d orbital (_____),the nodes look more like a pair of inverted cones. This gives an orbital that looks a bit like a p orbital with a doughnut around it. (Note the phases, though; they are differ ...
... For four of the d orbitals, both of these nodes are planes, giving a ‘petal-shaped’ orbital. For the fifth d orbital (_____),the nodes look more like a pair of inverted cones. This gives an orbital that looks a bit like a p orbital with a doughnut around it. (Note the phases, though; they are differ ...
Lectures 10-11
... For four of the d orbitals, both of these nodes are planes, giving a ‘petal-shaped’ orbital. For the fifth d orbital (_____),the nodes look more like a pair of inverted cones. This gives an orbital that looks a bit like a p orbital with a doughnut around it. (Note the phases, though; they are differ ...
... For four of the d orbitals, both of these nodes are planes, giving a ‘petal-shaped’ orbital. For the fifth d orbital (_____),the nodes look more like a pair of inverted cones. This gives an orbital that looks a bit like a p orbital with a doughnut around it. (Note the phases, though; they are differ ...
Chemistry (Coughlin) Test V Review
... light ejects more electrons but does not change energy. Light on photons hit metal and collide with electrons and let them fly off. Higher energy harder collision. Brighter light more electron collisions. When solids are heated, they emit electromagnetic radiation over a wide range of waveleng ...
... light ejects more electrons but does not change energy. Light on photons hit metal and collide with electrons and let them fly off. Higher energy harder collision. Brighter light more electron collisions. When solids are heated, they emit electromagnetic radiation over a wide range of waveleng ...
1B11 Foundations of Astronomy Star names and magnitudes
... Total flux emitted by a blackbody, F = sT4 W m-2 where s = Stefan’s constant = 5.67 x 10-8 W m-2 K-4 For astronomers: ...
... Total flux emitted by a blackbody, F = sT4 W m-2 where s = Stefan’s constant = 5.67 x 10-8 W m-2 K-4 For astronomers: ...
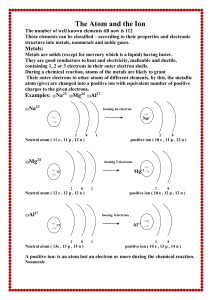
The Atom and the Ion
... atom (give) are changed into a positive ion with equivalent number of positive charges to the given electrons. ...
... atom (give) are changed into a positive ion with equivalent number of positive charges to the given electrons. ...
Hydrogen atom
A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen. The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively charged proton and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the Coulomb force. Atomic hydrogen constitutes about 75% of the elemental (baryonic) mass of the universe.In everyday life on Earth, isolated hydrogen atoms (usually called ""atomic hydrogen"" or, more precisely, ""monatomic hydrogen"") are extremely rare. Instead, hydrogen tends to combine with other atoms in compounds, or with itself to form ordinary (diatomic) hydrogen gas, H2. ""Atomic hydrogen"" and ""hydrogen atom"" in ordinary English use have overlapping, yet distinct, meanings. For example, a water molecule contains two hydrogen atoms, but does not contain atomic hydrogen (which would refer to isolated hydrogen atoms).