Lesson 2- Evolutionary Forces
... 1. Explain what the “modern synthesis” is. How is it different from Darwin’s original theory of evolution? 2. Why does evolution have to involve the change of the genetic makeup of a population over time? 3. Explain each of the following modes of evolution in a population. For each one, describe the ...
... 1. Explain what the “modern synthesis” is. How is it different from Darwin’s original theory of evolution? 2. Why does evolution have to involve the change of the genetic makeup of a population over time? 3. Explain each of the following modes of evolution in a population. For each one, describe the ...
Evolution Recap
... Variation – differences in a trait between individuals from: – Mutation – Sex – brothers and sisters rather than clones ...
... Variation – differences in a trait between individuals from: – Mutation – Sex – brothers and sisters rather than clones ...
Natural Selection Overview
... º Within any species in a given environment the following will lead to change in a species: 1. Overproduction ¶ every generation more individuals are produced than can be supported by environment 2. Variation ¶ no 2 individuals are exactly alike 3. Selection of favorable variation ¶ those indivi ...
... º Within any species in a given environment the following will lead to change in a species: 1. Overproduction ¶ every generation more individuals are produced than can be supported by environment 2. Variation ¶ no 2 individuals are exactly alike 3. Selection of favorable variation ¶ those indivi ...
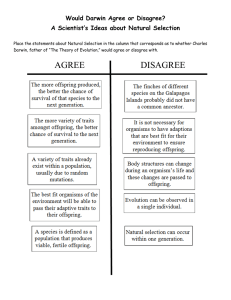
Would Darwin Agree or Disagree
... Place the statements about Natural Selection in the column that corresponds as to whether Charles Darwin, father of “The Theory of Evolution,” would agree or disagree with. ...
... Place the statements about Natural Selection in the column that corresponds as to whether Charles Darwin, father of “The Theory of Evolution,” would agree or disagree with. ...
Document
... A. Characteristics that are acquired during life are passed to offspring by sexual reproduction. B. Evolution is the result of mutations and recombination, only. C. Organisms best adapted to a changed environment are more likely to reproduce and pass their genes to offspring. D. Asexual reproduction ...
... A. Characteristics that are acquired during life are passed to offspring by sexual reproduction. B. Evolution is the result of mutations and recombination, only. C. Organisms best adapted to a changed environment are more likely to reproduce and pass their genes to offspring. D. Asexual reproduction ...
Evolution Notes
... ▫ collected plants and animals. Noticed they were suited to diverse environments. ▫ Also found species resembled others around the world ▫ Influenced by geology (Lyell) Earth shaped by slow-acting forces that are still in work today ...
... ▫ collected plants and animals. Noticed they were suited to diverse environments. ▫ Also found species resembled others around the world ▫ Influenced by geology (Lyell) Earth shaped by slow-acting forces that are still in work today ...
Natural Selection Picture Vocabulary
... A process by which the heritable characteristics of a population change such that the organisms in the population become better able to survive and reproduce in their environment. ...
... A process by which the heritable characteristics of a population change such that the organisms in the population become better able to survive and reproduce in their environment. ...
File
... All of the finches were descended from the same species, and adapted differently to occupy different niches over time 5. What conditions must be met for natural selection to occur? 1. natural selection occurs on genetically based traits (inherited traits) (genetically based) 2. mutations occur, whic ...
... All of the finches were descended from the same species, and adapted differently to occupy different niches over time 5. What conditions must be met for natural selection to occur? 1. natural selection occurs on genetically based traits (inherited traits) (genetically based) 2. mutations occur, whic ...
5_Week_of_February_6-11,_2012__files/Natural Selection PPT
... but have no kids, you are not doing as well as I am Say that I, I have reproduced… Assuming the traits that made me successful will help them then I amore fit NOW than the 127 year old guy ...
... but have no kids, you are not doing as well as I am Say that I, I have reproduced… Assuming the traits that made me successful will help them then I amore fit NOW than the 127 year old guy ...
Name Date Ch 16 – Darwin`s Theory of Evolution Read Ch 16 (450
... 4. Describe the three patters of biodiversity that Darwin observed during his journey on the HMS ...
... 4. Describe the three patters of biodiversity that Darwin observed during his journey on the HMS ...
DiscBio: C17 Vocabulary Definitions
... 7. process in which Earth’s continents move over time; plate tectonics 8. process in which natural selection causes distantly related organisms to evolve similar traits 9. In the struggle for survival, traits of the fittest will be better represented in future generations 10. preserved remains, or t ...
... 7. process in which Earth’s continents move over time; plate tectonics 8. process in which natural selection causes distantly related organisms to evolve similar traits 9. In the struggle for survival, traits of the fittest will be better represented in future generations 10. preserved remains, or t ...
Glenbard District 87
... number, (2) the heritable genetic variation of individuals in a species due to mutation and sexual reproduction, (3) competition for limited resources, and (4) the proliferation of those organisms that are better able to survive and reproduce in the environment. • LS4-3: Apply concepts of statistics ...
... number, (2) the heritable genetic variation of individuals in a species due to mutation and sexual reproduction, (3) competition for limited resources, and (4) the proliferation of those organisms that are better able to survive and reproduce in the environment. • LS4-3: Apply concepts of statistics ...
AP Biology 2011 Christmas Break Assignment
... prepared for a test over this material the first week we return to school. A. Reading Guide Questions: As you study this chapter, read several paragraphs at a time to catch the flow of ideas and understand the reasoning that is being described. In some places, the text describes a narrative or story ...
... prepared for a test over this material the first week we return to school. A. Reading Guide Questions: As you study this chapter, read several paragraphs at a time to catch the flow of ideas and understand the reasoning that is being described. In some places, the text describes a narrative or story ...
Ch. 13 How Populations Evolve packet-2007
... million years ago, but they have been extinct for millions of years. ...
... million years ago, but they have been extinct for millions of years. ...
Ch 8 Notes
... Coat color variation affects fitness • Light coat color evolved independently in different populations Evolution in response to natural selection is inevitable if: – There is variation in a trait – Variation is heritable – Some variants reproduce more than others Specific features of the environment ...
... Coat color variation affects fitness • Light coat color evolved independently in different populations Evolution in response to natural selection is inevitable if: – There is variation in a trait – Variation is heritable – Some variants reproduce more than others Specific features of the environment ...
Section 7-1
... similar traits to those on mainland – Traits seemed to match environment – Iguanas on mainland were green (match jungle) and grey on islands (match rocks) ...
... similar traits to those on mainland – Traits seemed to match environment – Iguanas on mainland were green (match jungle) and grey on islands (match rocks) ...
Chapter 2 the Development of Evolutionary Theory
... Individuals that possess favorable traits or variations are more likely to survive and produce offspring. Environmental context determines whether a trait is beneficial. Traits are inherited and passed on to the next generation. ...
... Individuals that possess favorable traits or variations are more likely to survive and produce offspring. Environmental context determines whether a trait is beneficial. Traits are inherited and passed on to the next generation. ...
Natural Selection and Evolution notes
... *He proposed the idea of Natural Selection NATURAL SELECTION—a mechanism for change in a population -Occurs when organisms in a population with favorable variations survive, reproduce and pass their variations to the next generation *Darwin’s theory proposes adaptations in species develop over many ...
... *He proposed the idea of Natural Selection NATURAL SELECTION—a mechanism for change in a population -Occurs when organisms in a population with favorable variations survive, reproduce and pass their variations to the next generation *Darwin’s theory proposes adaptations in species develop over many ...
Evolution Powerpoint
... Charles Darwin • 4 principles of natural selection: 1. Variation - Differences among organisms 2. Overproduction - More offspring increases chance for survival 3. Adaptation - Certain variations allow to survive better 4. Descent with Modification - Over time, more individuals in the population wil ...
... Charles Darwin • 4 principles of natural selection: 1. Variation - Differences among organisms 2. Overproduction - More offspring increases chance for survival 3. Adaptation - Certain variations allow to survive better 4. Descent with Modification - Over time, more individuals in the population wil ...
Species
... Finches that ate insects have strong, wide beaks. T Adaptation is a trait that helps an organism survive and reproduce. Evolution ...
... Finches that ate insects have strong, wide beaks. T Adaptation is a trait that helps an organism survive and reproduce. Evolution ...
Darwin`s Theory: Natural Selection
... manuscript from Alfred Russell Wallace proposing similar ideas, he finally decided to publish. Book was released in 1859 ...
... manuscript from Alfred Russell Wallace proposing similar ideas, he finally decided to publish. Book was released in 1859 ...
Evolution and Natural Selection PowerPoint
... Adaptation: an inherited trait that increases an organism’s chances of survival ...
... Adaptation: an inherited trait that increases an organism’s chances of survival ...
Natural selection

Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype; it is a key mechanism of evolution. The term ""natural selection"" was popularised by Charles Darwin, who intended it to be compared with artificial selection, now more commonly referred to as selective breeding.Variation exists within all populations of organisms. This occurs partly because random mutations arise in the genome of an individual organism, and these mutations can be passed to offspring. Throughout the individuals’ lives, their genomes interact with their environments to cause variations in traits. (The environment of a genome includes the molecular biology in the cell, other cells, other individuals, populations, species, as well as the abiotic environment.) Individuals with certain variants of the trait may survive and reproduce more than individuals with other, less successful, variants. Therefore, the population evolves. Factors that affect reproductive success are also important, an issue that Darwin developed in his ideas on sexual selection, which was redefined as being included in natural selection in the 1930s when biologists considered it not to be very important, and fecundity selection, for example.Natural selection acts on the phenotype, or the observable characteristics of an organism, but the genetic (heritable) basis of any phenotype that gives a reproductive advantage may become more common in a population (see allele frequency). Over time, this process can result in populations that specialise for particular ecological niches (microevolution) and may eventually result in the emergence of new species (macroevolution). In other words, natural selection is an important process (though not the only process) by which evolution takes place within a population of organisms. Natural selection can be contrasted with artificial selection, in which humans intentionally choose specific traits (although they may not always get what they want). In natural selection there is no intentional choice. In other words, artificial selection is teleological and natural selection is not teleological.Natural selection is one of the cornerstones of modern biology. The concept was published by Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace in a joint presentation of papers in 1858, and set out in Darwin's influential 1859 book On the Origin of Species, in which natural selection was described as analogous to artificial selection, a process by which animals and plants with traits considered desirable by human breeders are systematically favoured for reproduction. The concept of natural selection was originally developed in the absence of a valid theory of heredity; at the time of Darwin's writing, nothing was known of modern genetics. The union of traditional Darwinian evolution with subsequent discoveries in classical and molecular genetics is termed the modern evolutionary synthesis. Natural selection remains the primary explanation for adaptive evolution.