4.2 Test Review File - Northwest ISD Moodle
... If the organism is extremely well adapted to withstand changes in the environment, would it change? ...
... If the organism is extremely well adapted to withstand changes in the environment, would it change? ...
Script 3
... others don’t—natural selection. / And unless they are affected by some chance event, the creatures most likely to survive and reproduce are those with the most favorable traits that can be passed on to their offspring. [15] Have you ever heard the phrase “survival of the fittest?” This refers to the ...
... others don’t—natural selection. / And unless they are affected by some chance event, the creatures most likely to survive and reproduce are those with the most favorable traits that can be passed on to their offspring. [15] Have you ever heard the phrase “survival of the fittest?” This refers to the ...
Natural selection
... No, it just means that the genes they have are best suited for a particular area. ...
... No, it just means that the genes they have are best suited for a particular area. ...
Name: Gr.12 Biology Unit 3: Evolution (Ch.27) Section A: Multiple
... 1. Darwin’s theory of evolution is based on: a. Natural selection and survival of the fittest b. Natural selection and survival of the most weak c. Nothing. Nothing at all. After all, it’s just a theory. d. Natural selection only 2. The Miller-Urey experiments used the following reactants: a. CH4, N ...
... 1. Darwin’s theory of evolution is based on: a. Natural selection and survival of the fittest b. Natural selection and survival of the most weak c. Nothing. Nothing at all. After all, it’s just a theory. d. Natural selection only 2. The Miller-Urey experiments used the following reactants: a. CH4, N ...
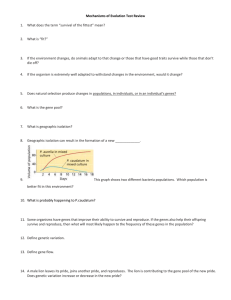
Natural Selection and Population Genetics Review
... intelligence--it is a measure of reproductive capacity: how many fertile offspring will an organism leave behind? ...
... intelligence--it is a measure of reproductive capacity: how many fertile offspring will an organism leave behind? ...
Evolution
... best adapted & strongest tend to survive longer & produce 2. Variation- animals of more offspring the same species are 6. Inheritance- favored/best different fit/selected variations 3. Change in (characteristics) are passed on to offspring. environment7. New species arise- “selected” a) Biological - ...
... best adapted & strongest tend to survive longer & produce 2. Variation- animals of more offspring the same species are 6. Inheritance- favored/best different fit/selected variations 3. Change in (characteristics) are passed on to offspring. environment7. New species arise- “selected” a) Biological - ...
Ch01
... • Evolution is consistent with known genetic mechanisms and the observational evidence from field research. • Evolution is gradual: small genetic changes regulated by natural selection accumulate over long periods and many genes can “drift” through a population at a given time. Discontinuities among ...
... • Evolution is consistent with known genetic mechanisms and the observational evidence from field research. • Evolution is gradual: small genetic changes regulated by natural selection accumulate over long periods and many genes can “drift” through a population at a given time. Discontinuities among ...
Darwin and Evolution - Ms. Oldendorf`s AP Biology
... The idea of Acquired Characteristics Involves descent with modification Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics – organisms became adapted to their environment during their lifetime and pass these adaptations to their offspring ...
... The idea of Acquired Characteristics Involves descent with modification Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics – organisms became adapted to their environment during their lifetime and pass these adaptations to their offspring ...
Darwin`s Voyage
... Peppered Moths • Before the industrial revolution, England – Trees were light in color from lichen growing on them ...
... Peppered Moths • Before the industrial revolution, England – Trees were light in color from lichen growing on them ...
Chapter 7 Questions
... differences. Biotic factors are alive. They require a source of energy and use energy. They are influences of other living organisms on survival of a particular species. 2. Define biological fitness. What role does fitness play in selection? Biological fitness is the relative reproductive success of ...
... differences. Biotic factors are alive. They require a source of energy and use energy. They are influences of other living organisms on survival of a particular species. 2. Define biological fitness. What role does fitness play in selection? Biological fitness is the relative reproductive success of ...
Ch 10 Principles of Evolution
... proposed the Theory of Catastrophism - natural disasters have shaped landforms and caused species to become extinct. ...
... proposed the Theory of Catastrophism - natural disasters have shaped landforms and caused species to become extinct. ...
1. During his voyage on the Beagle, Charles Darwin made many
... Charles Darwin’s observation that finches of different species on the Galápagos Islands have many similar physical characteristics supports the hypothesis that these finch species ...
... Charles Darwin’s observation that finches of different species on the Galápagos Islands have many similar physical characteristics supports the hypothesis that these finch species ...
Chapter 4 - De Anza College
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
Outline for Jan. 17
... (population genetics) with everything known about macroevolution (origin of species). Contributing factors: acquired characteristics not inherited Mendelian basis of continuous variation -variation among races has genetic basis -development of biological species concept -population genetics Major Te ...
... (population genetics) with everything known about macroevolution (origin of species). Contributing factors: acquired characteristics not inherited Mendelian basis of continuous variation -variation among races has genetic basis -development of biological species concept -population genetics Major Te ...
Lecture 2
... Selection at any higher level than that of an individual is essentially "impotent“ and is "not an appreciable factor in evolution" (1966:8; cf., Williams 1992). “Many, perhaps most, evolutionary biologists believe that it [group selection] is only rarely an important force of evolution.” (Futuyma 19 ...
... Selection at any higher level than that of an individual is essentially "impotent“ and is "not an appreciable factor in evolution" (1966:8; cf., Williams 1992). “Many, perhaps most, evolutionary biologists believe that it [group selection] is only rarely an important force of evolution.” (Futuyma 19 ...
Which rabbit is best adapted?
... Wild mustard has been bred by farmers into numerous other foods Dog traits have been selected by breeders for centuries to enhance certain traits. ...
... Wild mustard has been bred by farmers into numerous other foods Dog traits have been selected by breeders for centuries to enhance certain traits. ...
Natural selection

Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype; it is a key mechanism of evolution. The term ""natural selection"" was popularised by Charles Darwin, who intended it to be compared with artificial selection, now more commonly referred to as selective breeding.Variation exists within all populations of organisms. This occurs partly because random mutations arise in the genome of an individual organism, and these mutations can be passed to offspring. Throughout the individuals’ lives, their genomes interact with their environments to cause variations in traits. (The environment of a genome includes the molecular biology in the cell, other cells, other individuals, populations, species, as well as the abiotic environment.) Individuals with certain variants of the trait may survive and reproduce more than individuals with other, less successful, variants. Therefore, the population evolves. Factors that affect reproductive success are also important, an issue that Darwin developed in his ideas on sexual selection, which was redefined as being included in natural selection in the 1930s when biologists considered it not to be very important, and fecundity selection, for example.Natural selection acts on the phenotype, or the observable characteristics of an organism, but the genetic (heritable) basis of any phenotype that gives a reproductive advantage may become more common in a population (see allele frequency). Over time, this process can result in populations that specialise for particular ecological niches (microevolution) and may eventually result in the emergence of new species (macroevolution). In other words, natural selection is an important process (though not the only process) by which evolution takes place within a population of organisms. Natural selection can be contrasted with artificial selection, in which humans intentionally choose specific traits (although they may not always get what they want). In natural selection there is no intentional choice. In other words, artificial selection is teleological and natural selection is not teleological.Natural selection is one of the cornerstones of modern biology. The concept was published by Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace in a joint presentation of papers in 1858, and set out in Darwin's influential 1859 book On the Origin of Species, in which natural selection was described as analogous to artificial selection, a process by which animals and plants with traits considered desirable by human breeders are systematically favoured for reproduction. The concept of natural selection was originally developed in the absence of a valid theory of heredity; at the time of Darwin's writing, nothing was known of modern genetics. The union of traditional Darwinian evolution with subsequent discoveries in classical and molecular genetics is termed the modern evolutionary synthesis. Natural selection remains the primary explanation for adaptive evolution.