Evolution Review
... Frequent and vigorous use of a body part led to a slight increase in its size. These changes were heritable and could lead to an entire population to transform gradually over time. ...
... Frequent and vigorous use of a body part led to a slight increase in its size. These changes were heritable and could lead to an entire population to transform gradually over time. ...
Mechanisms for Evolution
... species vary. Only individuals with the characteristics best suited to the environment will survive to reproduce. Over time characteristics will increase in the population. (Now called Natural Selection) ...
... species vary. Only individuals with the characteristics best suited to the environment will survive to reproduce. Over time characteristics will increase in the population. (Now called Natural Selection) ...
Natural Selection
... theorized that periodically all life was destroyed by natural disasters. Lamarck 1. organisms strive to improve 2. use it or lose it 3. modifications are inherited ...
... theorized that periodically all life was destroyed by natural disasters. Lamarck 1. organisms strive to improve 2. use it or lose it 3. modifications are inherited ...
Ch 13 - Evolution
... BIOLOGY Ch 13 – The Theory of Evolution Mrs. Stolipher VOCABULARY Population, natural selection, adaptation, vestigial structure, homologous structure, artificial selection, reproductive isolation, evolution, Darwin, Lyell, Malthus, Wallace ...
... BIOLOGY Ch 13 – The Theory of Evolution Mrs. Stolipher VOCABULARY Population, natural selection, adaptation, vestigial structure, homologous structure, artificial selection, reproductive isolation, evolution, Darwin, Lyell, Malthus, Wallace ...
Natural Selection - Northwest ISD Moodle
... in populations over time. • Natural Selection is also known as descent with modification because each species has descended with changes from other species over time. ...
... in populations over time. • Natural Selection is also known as descent with modification because each species has descended with changes from other species over time. ...
Document
... 2. Micro – small changes in genes, chromosome, and allele frequencies in a population II. Natural Selection A. Differences in survival and reproduction among individuals in a population that differ in heritable traits B. Individuals with higher fitness (superior phenotypes) will survive, reproduce, ...
... 2. Micro – small changes in genes, chromosome, and allele frequencies in a population II. Natural Selection A. Differences in survival and reproduction among individuals in a population that differ in heritable traits B. Individuals with higher fitness (superior phenotypes) will survive, reproduce, ...
Darwin`s Evolution
... • Each bird was very similar except for its beak which appeared to be adapted for each specific type of food for the finches • Darwin believed that these finches had a common ancestor which had probably flown there after the islands had formed. ...
... • Each bird was very similar except for its beak which appeared to be adapted for each specific type of food for the finches • Darwin believed that these finches had a common ancestor which had probably flown there after the islands had formed. ...
C. The Origin of Species
... 1. All plants and animals produce more offspring than are needed to simply replace the parents. (#1 Overproduction in Environment, p 65) a. Are humans an exception? Maybe not. 2. All the young are different from one another, and some are better suited for survival & reproduction than others. (#2 Var ...
... 1. All plants and animals produce more offspring than are needed to simply replace the parents. (#1 Overproduction in Environment, p 65) a. Are humans an exception? Maybe not. 2. All the young are different from one another, and some are better suited for survival & reproduction than others. (#2 Var ...
PDF file
... (infections, poisons) can affect how well the embryo develops and leave asymmetries. The fewer the insults, or the better the embryo deals with them, the more symmetric the individual will be. So, symmetry reflects genes and the environment. The important point about natural selection is that there ...
... (infections, poisons) can affect how well the embryo develops and leave asymmetries. The fewer the insults, or the better the embryo deals with them, the more symmetric the individual will be. So, symmetry reflects genes and the environment. The important point about natural selection is that there ...
Frantzer AP bio 12/31/12 DARWIN`S HISTORICAL REPORT
... to be a common ancestor. Darwin's finches look very similar; it is the variations in beak structure which set them apart. One of the aspects of Darwin’s theory of evolution is natural selection. Natural selection is the gradual, non-random process by which biological traits become either more or les ...
... to be a common ancestor. Darwin's finches look very similar; it is the variations in beak structure which set them apart. One of the aspects of Darwin’s theory of evolution is natural selection. Natural selection is the gradual, non-random process by which biological traits become either more or les ...
PowerPoint: Artificial Selection
... Natural Selection vs. Artificial Selection Natural Selection: ...
... Natural Selection vs. Artificial Selection Natural Selection: ...
Darwin Today exhibition - Understanding how evolution
... The earliest farmers collected seeds from the wild plants that they liked to eat. Year on year, they selected seeds from the plants that produced the best yields, the best tasting food or were the easiest to process. Farmers sowed seeds from these ‘better’ plants to produce next year’s crop and, sin ...
... The earliest farmers collected seeds from the wild plants that they liked to eat. Year on year, they selected seeds from the plants that produced the best yields, the best tasting food or were the easiest to process. Farmers sowed seeds from these ‘better’ plants to produce next year’s crop and, sin ...
History of Evolution
... Life forms continually become more complex or more perfect as they transform into new species ...
... Life forms continually become more complex or more perfect as they transform into new species ...
Mutation, Evolution, and Natural Selection
... •The continents split and populations were separated. •This increased the variety of living things because they were in new environments,which would select for specific adaptations and isolated these species from reproducing with original form. ...
... •The continents split and populations were separated. •This increased the variety of living things because they were in new environments,which would select for specific adaptations and isolated these species from reproducing with original form. ...
Theory of Natural Selection
... Ideas that Shaped Darwin’s Thinking Selective Breeding The process of humans selecting traits they want to appear in offspring to produce desired traits Used in farming to create sheep with fine ...
... Ideas that Shaped Darwin’s Thinking Selective Breeding The process of humans selecting traits they want to appear in offspring to produce desired traits Used in farming to create sheep with fine ...
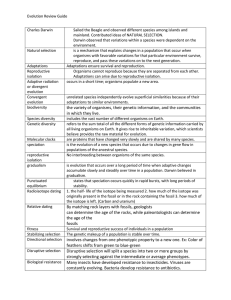
Evolution Review Guide Charles Darwin Sailed the Beagle and
... Sailed the Beagle and observed different species among islands and mainland. Contributed ideas of NATURAL SELECTION. Darwin observed that variations within a species were dependent on the environment. is a mechanism that explains changes in a population that occur when organisms with favorable varia ...
... Sailed the Beagle and observed different species among islands and mainland. Contributed ideas of NATURAL SELECTION. Darwin observed that variations within a species were dependent on the environment. is a mechanism that explains changes in a population that occur when organisms with favorable varia ...
Name: #1. Use the circle graphs below to answer the question. The
... #2. In North America, the eastern spotted skunk mates in late winter, and the western spotted skunk mates in late summer. Even though their geographic ranges overlap, the species do not mate with each other. What most likely prevents these two species from interbreeding? A. habitat isolation B. game ...
... #2. In North America, the eastern spotted skunk mates in late winter, and the western spotted skunk mates in late summer. Even though their geographic ranges overlap, the species do not mate with each other. What most likely prevents these two species from interbreeding? A. habitat isolation B. game ...
Evolution - LincolnLions.org
... Took lengthy observations of the different species found on the Galapagos Islands. Mainly of the different beaks of finches, and shapes of tortoise shells found on various ...
... Took lengthy observations of the different species found on the Galapagos Islands. Mainly of the different beaks of finches, and shapes of tortoise shells found on various ...
Evolution by Natural Selection
... What did he say? 3. Selection: In an environment, having a particular trait can make individuals more or less likely to survive and have successful reproduction. So, some individuals leave more offspring than others. 4. Adaptation: Over time, those traits that improve survival and reproduction ...
... What did he say? 3. Selection: In an environment, having a particular trait can make individuals more or less likely to survive and have successful reproduction. So, some individuals leave more offspring than others. 4. Adaptation: Over time, those traits that improve survival and reproduction ...
disruptive selection
... never acts directly on genes, only the entire organism • If an individual dies without reproducing, it does not contribute its alleles to the gene pool ...
... never acts directly on genes, only the entire organism • If an individual dies without reproducing, it does not contribute its alleles to the gene pool ...
LECTURE 7 Natural Selection and Evolution
... 3. Returns believing that organisms are the product of their environment, and can change over time. II. MODES OF EVOLUTION A. Charles Darwin wasn’t the first to come up with the idea of evolution. 1. However, his contribution was the METHOD by which it occurred. Evolution by NATURAL SELECTION. a. Co ...
... 3. Returns believing that organisms are the product of their environment, and can change over time. II. MODES OF EVOLUTION A. Charles Darwin wasn’t the first to come up with the idea of evolution. 1. However, his contribution was the METHOD by which it occurred. Evolution by NATURAL SELECTION. a. Co ...
Natural selection

Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype; it is a key mechanism of evolution. The term ""natural selection"" was popularised by Charles Darwin, who intended it to be compared with artificial selection, now more commonly referred to as selective breeding.Variation exists within all populations of organisms. This occurs partly because random mutations arise in the genome of an individual organism, and these mutations can be passed to offspring. Throughout the individuals’ lives, their genomes interact with their environments to cause variations in traits. (The environment of a genome includes the molecular biology in the cell, other cells, other individuals, populations, species, as well as the abiotic environment.) Individuals with certain variants of the trait may survive and reproduce more than individuals with other, less successful, variants. Therefore, the population evolves. Factors that affect reproductive success are also important, an issue that Darwin developed in his ideas on sexual selection, which was redefined as being included in natural selection in the 1930s when biologists considered it not to be very important, and fecundity selection, for example.Natural selection acts on the phenotype, or the observable characteristics of an organism, but the genetic (heritable) basis of any phenotype that gives a reproductive advantage may become more common in a population (see allele frequency). Over time, this process can result in populations that specialise for particular ecological niches (microevolution) and may eventually result in the emergence of new species (macroevolution). In other words, natural selection is an important process (though not the only process) by which evolution takes place within a population of organisms. Natural selection can be contrasted with artificial selection, in which humans intentionally choose specific traits (although they may not always get what they want). In natural selection there is no intentional choice. In other words, artificial selection is teleological and natural selection is not teleological.Natural selection is one of the cornerstones of modern biology. The concept was published by Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace in a joint presentation of papers in 1858, and set out in Darwin's influential 1859 book On the Origin of Species, in which natural selection was described as analogous to artificial selection, a process by which animals and plants with traits considered desirable by human breeders are systematically favoured for reproduction. The concept of natural selection was originally developed in the absence of a valid theory of heredity; at the time of Darwin's writing, nothing was known of modern genetics. The union of traditional Darwinian evolution with subsequent discoveries in classical and molecular genetics is termed the modern evolutionary synthesis. Natural selection remains the primary explanation for adaptive evolution.