* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Brain Notes Most complex organ in the body It allows us to think
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of human intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Mind uploading wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
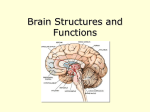
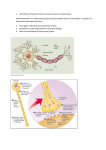
Brain Notes I. Most complex organ in the body II. It allows us to think, have emotions, move, and dream III. The brain’s job: 1. receiving information from the rest of the body 2.interpreting that information 3.guiding the body’s response to it II. Types of input (information received): 1. odors 2. light 3. sounds 4. pain III.Preforms vital operations such as 1. breathing 2. maintaining blood pressure 3. releasing hormones IV. Divided into 3 main sections : 1. Hindbrain 2. Limbic System 3. Neocortex A.Each section is responsible for doing a portions of the brain’s job. Different areas often share responsibility for the same task B. The larger areas of the brain are divided into smaller areas that handle smaller portions of the work The Hindbrain - oldest part of the brain - we share this piece of the brain with reptiles - in charge of our primal instincts and most basic functions 1. Spinal Cord a. information superhighway of the body b. carries information up to the brain and instructions back down 2. Medulla Oblongata a. part of the Brain Stem a. Job: 1.Helps control the body's autonomic functions (things you don't need to think about to perform) like respiration, digestion and heart rate. 2.Also acts as a relay station for nerve signals going to/from the brain 3. Pons a. part of the Brain Stem b. Job: 1. Also controls body’s autonomic functions 2. also a relay station for sensory information 3. plays a role in your sleep habits 4.Cerebellum a. is below and behind the cerebrum, attached to the brain stem b. Job: 1.motor function 1. the body’s ability to balance 2. ability to interpret information sent to the brain by the ears, eyes, and other sensory organs The Limbic System - sometimes called the “emotional brain” - in more primitive mammals - Where our emotions reside and our memory begins - Where our unconcious value judgements are made - information going through the Limbic System are filed under “agreeable and disagreeable” - plays a role in salience (what grabs your attention), spontaneity, and creativity 1. Diencephalon a. inside the cerebrum, above the brain stem. b. Job: 1. sensory function 2. food intake control 3. body’s ability to sleep c. Divided into sections: 1. thalamus: the relay station of the brain. Most sensory signals pass through here on their way to other parts of the brain. Also plays a part of motor control 2. hypothalamus: controls many of the body’s functions. - monitors and controls your circadian rhythms (your daily sleep/wake cycle) - homeostasis (making sure your body is running smoothly) - appetite - thirst 3. epithalamus: the connection between the limbic system and other parts of the brain 2. Amygdala a. latin name for almond, which is it’s shape b. storing and classifying emotionally charged memories c. produces our emotions, especially fear d. triggers responses such as sweaty palms, freezing, increased heart-beat/ respiration and stress hormone release 3. Hippocampus (RAM on the computer) a. memory formation b. classifying information c. long-term memory The Neocortex - most advanced part of the brain - shared with primates and dolphins - human has the largest neocortex - power to develop language, abstract thought, consciousness, and imagination - divided into two hemispheres - the right side of the brain controls the left side of the body - the left side of the brain controls the right side of the body - right side of the brain: artistic, spatial, and musical - left side of the brain: colder, linear, rational, and verbal aspects 1.Cerebrum a. largest part of the brain (wrinkly gray blob) b. wrinkles are called cortex i. where the majority of brain cells (neurons) are c. Job: i. speech ii. senses iii. emotional response iv. memory d. divided into several sections called lobes i. Frontal Lobe(white house): reasoning, problem solving, judgement, impulse control 1. last thing to develop- occurs when we are young adults 2. higher emotions such as empathy and altruism 3. motor control and memory ii. Temporal Lobe: process sounds and form memories iii. Parietal Lobe: make sense of all of the different bits of information that is bombarding your brain 1. processing pain and touch sensation 2. movement, orientation, recognition, and speech 3. Wernicke’s Area: language recognition iv. Occipital Lobe: process all the things you see 2. Broca’s Area a. controls speech, languge recognition, and facial nerves 3. Corpus Callosum a. Neural bridge that connects the two hemispheres to each other, located centrally in the brain