* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 35.3 Notes PP
Vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Social immunity wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Anti-nuclear antibody wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Herd immunity wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
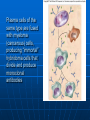
35.3 Notes PP Mitch, David, Samir, Liyana, Lori Active Immunity Develops naturally after a person is infected with a pathogen such as measles or chickenpox Induced when a person is well so that possible future infection will not take place Immunization- involves the use of vaccines, or substances that contain an antigen to which the immune system responds Active Immunity can be induced by the use of vaccines and depends on the presence of memory B cells and Memory T cells in the body Passive Immunity Passive Immunity occurs when an individual is given prepared antibodies to combat a disease Passive immunity is short lived, lasts for a short time Even though it does not last it sometimes is used to prevent illness in a patient who has been unexpectedly exposed to an infectious disease Artificial Passive Immunity is used in the emergency treatment of rabies, measles, tetanus, diptheria, botulism, Hepatitis A, and snake bites These patients receive a serum that contains antibodies and 50% become ill from serum sickness Cytokines and Immunity Cytokines are signaling molecules produced by limphocytes and monocytes or other cells They regulate white blood cell formation Inteleukines are cytokines produced by various white blood cells Interferon and Inteleukins are used as immonotherapeutic drugs to fight T-cells Interferon is produced by leukocytes, fibroblasts and probably most cells in response to a viral infection Cytokines and Immunity Cytotoxic T-cells attack and destroy cancer cells when they carry an altered protein on their cell surface If the cytotoxic T-cells have not been activated, cytokines might awaken the immune system and lead to the destruction of cancer Scientists who are engaged in interleukin research believe the interleukins soon will be used as adjuncts for vaccines for the treatment of chronic infectious diseases and for the treatment of cancer Interleukin antagonists may also be helpful in preventing: skin and organ production, autoimmune diseases, and allergies Monoclonal Antibodies Monoclonal Antibodies are one of many antibodies produced by a clone of hybridoma cells that are all bined to the same antigen One method of producing them is B-cells being romoved from an animal and exposed to a particular anitgen The few cells are called hybridomas, used for quick and certain diagnosis of various conditions Plasma cells of the same type are fused with myeloma (cancerous) cells, producing “immortal” hybridoma cells that divide and produce monoclonal antibodies