* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download I + rel + - UCSF Biochemistry & Biophysics
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Ancestral sequence reconstruction wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Oligonucleotide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Expression vector wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
De novo protein synthesis theory of memory formation wikipedia , lookup
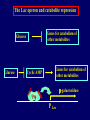
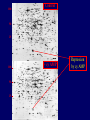
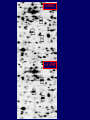
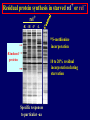
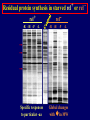
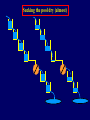
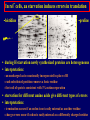
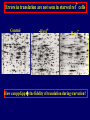
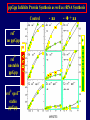
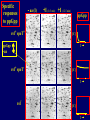
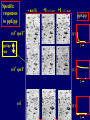
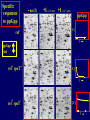
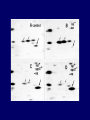
Pat O’Farrell Dept. Biochem and Biophys. UCSF San Francisco 2D Gels/proteomics - what is it good for Characterizing Characterizingexpression expressiondifferences differences for ONE difference (needle in the hay stack) Looking Looking for ONE difference (needle in the hay stack) Assaying ONE difference Assaying ONE difference Defining Defininga acomplex complex(pleiotropic) (pleiotropic)response response 2D Gels/proteomics - what is it good for Characterizing expression differences Looking for ONE difference (needle in the hay stack) Assaying ONE difference Defining a complex (pleiotropic) response ? Assessing & comparing protein levels/tissues/secretions Regulation of protein levels by turnover Assessing modification of proteins Finding surprises The Lac operon and catabolite repression Genes for catabolism of other metabolites Glucose Glucose Cyclic AMP Genes for catabolism of other metabolites -galactosidase Crp P Lac 100 Control 50 25 100 50 25 + cy AMP Repression by cy AMP +Control cy AMP + cy AMP The catabolite repression (cyAMP) domain Size: -about 10% of all genes respond to cyclic AMP Heterogeneity: -responses vary - in direction (~1% repression 9% induction) - and magnitude Mechanism: - all responses depend on the same receptor • i.e. crp mutants show no response to cyclic AMP - the receptor is inactive without cyclic AMP • i.e. adenyl cyclase mutants = crp mutants Overlap - cyclic AMP responsive genes are downregulated by limitation for an amino acid Warning! The analysis is EXTREMELY sensitive to conditions • strains must be congenic • culture conditions must be precisely reproduced Coordinating growth • Synthesis of ribosomes is a major part of bacterial growth • Ribosomes are half RNA and half protein • Stringent E. coli strains rRNA synthesis when short of aa • Relaxed strains lack the ability to down regulate rRNA rel+ coordinate rRNA & r-protein synthesis rel- lack coordination of rRNA & r-protein synthesis A system that detects shortage of aa & signals starvation AMP + ppGppp rel ATP + GTP ppGpp GDP spoT G tetraphos & G pentaphos Signals for aa starvation rRNA synthesis Experiment to test effect of ppGpp on protein expression • ppGpp does not get into cells I could not just add it a test the consequences • My Plan rel+ strain rel- strain Restrict amino acids Restrict amino acids Residual protein synthesis occurs in the presence of ppGpp Residual protein synthesis occurs in the absence of ppGpp +ppGpp Compare -ppGpp Residual protein synthesis in starved rel+ or rel rel + -R -H -P -L 35S-methionine incorporation -R induced proteins 10 to 20% residual incorporation during starvation Specific responses to particular -aa Residual protein synthesis in starved rel+ or rel rel + rel -R -H -P -L Specific responses to particular -aa -R -H -P -L Global changes with in MW The “Hungry Codon” • simple thought experiment • a 20 residue protein with each of the aa • a step time, ST, is the time it normally takes to add one aa • its synthesis would take 20 ST A C D E F G H I K L M N P Q R S T V W Y 1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 • starvation for histidine reduces protein synthesis to 10% The “Hungry Codon” • simple thought experiment • a 20 residue protein with each of the aa • a step time, ST, is the time it normally takes to add one aa • its synthesis would take 20 ST A C D E F G H I K L M N P Q R S T V W Y 1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 • starvation for histidine reduces protein synthesis to 10% • rate of synthesis of average peptide is reduced 10x A C D E F G H I K L M N P Q R S T V W Y 1 +1 • • • • +1 +1 +1 +1 +181 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 it takes 10x as long to synthesis the average peptide it takes 10x20=200 ST to make our 20 aa peptide 19 of aa are normal and are added in 19 step times translation of the hungry codon takes 200-19=181 ST +1 +1 A steady state determines pool size A B C D F G Sucking the pool dry (almost) In rel cells, aa starvation induces errors in translation -histidine ••••• • -proline • • during H starvation newly synthesized proteins are heterogeneous • interpretation: - an uncharged aa is occasionally incorporated in place of H - each substituted position removes a basic residue - the trail of spots is consistent with 3% misincorporation • starvation for different amino acids give different types of errors • interpretation: - termination occurs if an codon is not easily misread as another residue - charge errors occur if codon is easily misread as a differently charged residue Errors in translation are not seen in starved rel+ cells Control -H rel+ -H rel How can ppGpp the fidelity of translation during starvation? Starved rel+ cells behave as if they are not missing an aa • ribosomal proteins L7 has no histidine Relative L7 expression control rel- - H rel- - I rel+ - H rel+ - I +++ +++++ + +++ +++ Difference consistent with the difference in H and I abundance in the protein Expression insensitive to aa abundance ppGpp Inhibits Protein Synthesis as well as rRNA Synthesis Control - aa - + aa rel+ unstable ppGpp - rel+ spoT stable ppGpp Prot ein relno ppGpp Sharing the burden • in a rel- strain all the slowing of translation occurs at the “hungry codon” A C D E F G H I K L M N P Q R S T V W Y 1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +181 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 • ppGpp slows down translation at multiple steps of translation • The aa-tRNA for the hungry codon is only reduced enough to generate a signal A C D E F G H I K L M N P Q R S T V W Y 10 +10 +10 +10 +10 +10 +10 +10 +10 +10 +10 +10 +10 +10 +10 +10 +10 +10 +10 +10 Conclusions 1. Protein synthesis has a precarious relationship with its substrates • imbalances in substrates are exaggerated as residues are incorporated according to the dictates of the code not availability 2. Substrate imbalance severely compromises fidelity • 3% missincorporation, tuncation & inactive enzymes 3. ppGpp makes translation more robust and accurrate • it acts as governor to coordinate translation with substrate supply • it adjusts protein synthesis rates to availability of the limiting aa (the weakest link) Generalization • balanced substrate supply is universally important for translation Global requirement • a specific signaling system that senses substrate levels and modulates translation accordingly The basis of this regulation outside of E coli is not known. It is not based on ppGpp, which is absent in eukaryotes. Specific responses to ppGpp rel+ spoT+ - aa (I) +I (0-5 min) +I (12.5 min) ppGpp [C] ppGpp -aa t rel+ spoT- [C] t rel- [C] t Specific responses to ppGpp rel+ spoT+ - aa (I) +I (0-5 min) +I (12.5 min) ppGpp [C] ppGpp -aa t rel+ spoT- [C] t rel- [C] t Specific responses to ppGpp rel- - aa (I) +I (0-5 min) +I (12.5 min) ppGpp [C] t ppGpp -aa rel+ spoT+ [C] t rel+ spoT- [C] t Pat O’Farrell Dept. Biochem and Biophys. UCSF San Francisco