* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download instruction2.mtsac.edu
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Microtubule wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
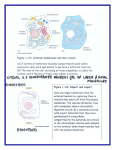
Cytoplasm and Cytoskeleton Biology 4 Honors Grace Kor Mery Wang The Cytosol Fluid within the cell 70% of cell’s volume Contains cytoskeleton Cytosol + Organelles = Cytoplasm “cytoplasm matrix” What does cytosol do? site of metabolism for prokaryotes majority for eukaryotes glucose (mitochondria can’t use) → cytosol → pyruvate (mitochondria can use) waste is dissolved here protects lysosomes transports material The Cytoskeleton Reinforces the cell’s shape Made up of proteins: Microtubules, Microfilaments, Intermediate Filaments Present in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Microtubules in the Cell Made of tubulin polymers “Tracks” on which organelles can navigate through the cell Found in centrosomes and centrioles Role in cell division Make up the inner structure of cilia and flagella in eukaryotic cells Intermediate Filaments Can be made of a variety of proteins (keratin) Cell’s support structure Specialized in bearing tension “Sturdy” Functions in the anchoring of the nucleus and other organelles Microfilaments thread-like protein fibers composed of actin (contractile protein) responsible for muscle contraction carry out cellular movement (gliding, contraction, cytokinesis)