* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Actin filaments
Survey
Document related concepts
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Microtubule wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
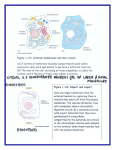
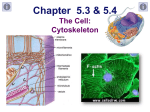
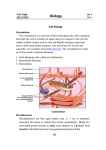
Cytoskeleton The cytoskeleton (also CSK) is a cellular "scaffolding" or "skeleton" contained within the cytoplasm that is made out of protein. The cytoskeleton is present in all cells; it was once thought this structure was unique to eukaryotes, but recent research has identified the prokaryotic cytoskeleton. It is a dynamic structure that maintains cell shape, protects the cell, enables cellular motion (using structures such as flagella, cilia and lamellipodia), and plays important roles in both intracellular transport (the movement of vesicles and organelles, for example) and cellular division. The concept and the term (cytosquelette, in French) was first introduced by French embryologist Paul Wintrebert in 1931. Cells contain elaborate arrays of protein fibers that serve such functions as: establishing cell shape providing mechanical strength locomotion Cell division intracellular transport of organelles The cytoskeleton is made up of three kinds of protein filaments: Actin filaments (also called microfilaments) Intermediate filaments and Microtubules Actin Filaments is composed of two intertwined actin chains most concentrated just beneath the cell membrane, and are responsible for resisting tension and maintaining cellular shape. Microtubules Microtubules are cylindrical tubes, 20-25 nm in diameter. They are composed of subunits of the protein tubulin-these subunits are termed alpha and beta. Microtubules act as a scaffold to determine cell shape, and provide a set of "tracks" for cell organelles and vesicles to move on. Microtubules also form the spindle fibers for separating chromosomes during mitosis. When arranged in geometric patterns inside flagella and cilia, they are used for locomotion. Intermediate Filaments Intermediate filaments are about 10 nm diameter and provide tensile strength for the cell. Different intermediate filaments are: made of vimentins, being the common structural support of many cells. made of keratin, found in skin cells, hair and nails. neurofilaments of neural cells. made of lamin, giving structural support to the nuclear envelope.