* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Life Science
Survey
Document related concepts
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Microtubule wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
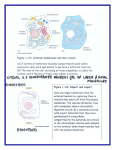
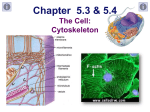
Chapter 5, Lesson 6 Notes The Cytoskeleton Cytoskeleton Structure Composed of a network of protein fibers called microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules. Cytoskeleton Function 1. gives cells support and helps the cell keep its shape 2. anchors organelles into a certain position or allows them to move around in the cell 3. allows cells to move by functioning as a muscle Types of Cytoskeleton Fibers 1. Microfilaments – made of strings of ball-shaped proteins called actin. The actin are twisted together to make long fiber molecules. They are mainly responsible for moving the whole cell around. 2. Intermediate filaments – made from long, string-like proteins, they coil together like rope to form rods that add strength to the shape of the cell. 3. Microtubules – made from units of a ball-shaped protein called tubulin. The tubulin molecules come together to form a hollow tube that supports the cell’s shape. Microtubules’ Function Outside the Cell Outside the cell, the microtubules anchor to and extend out of the plasma membrane. They form two types of structures—cilia and flagella. Both cilia and flagella are made of microtubules. (draw and label the picture of the eukaryotic cell on p. 155)