* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download subcortical white matter (centrum semiovale)
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Orbitofrontal cortex wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Basal ganglia wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Superior colliculus wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
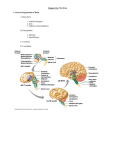
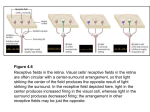
dispersion of internal capsule as the corona radiata ► ▲ optic radiation auditory radiation ► subcortical white matter (centrum semiovale) - projection tracts - axonal tracts connecting the brain to or from the ‘outside’ of the brain - internal capsule - projection tracts between the cerebral cortex, and thalamus and spinal cord - in horizontal cross-section, internal capsule is a V-shaped collection of axonal tracts, with the angle of the ‘V’ (the “genu”) pointing medially, separating the lenticular nucleus (globus pallidus and putamen) (laterally) from the caudate nucleus (located medially and anteriorly) and also from the thalamus (located medially and posteriorly) - located posterior to the genu are corticobulbar tracts from the motor cortex to cranial nerve motor nuclei in brainstem and corticospinal tracts in spinal cord - located both anterior and posterior to corticobulbar and corticospinal tracts in internal capsule are corticopontinecerebellar tracts from premotor/motor cortex, and other cortex, to cerebellum (via cerebral peduncles, then pons) - thalamocortical tracts go to sensory cortex from thalamus neurons receiving synapses from neurons in spinothalamic tracts and dorsal columns - note: tracts from the most posterior thalamic nuclei are not in the internal capsule, but go under lenticular nucleus: - medial geniculate nucleus (of thalamus) → → auditory radiation → → auditory cortex - lateral geniculate nucleus (of thalamus) → → optic radiation → → visual cortex (continued, next page) ©