* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nickel affinity chromatography in Protein purification
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Expression vector wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
Ancestral sequence reconstruction wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Bimolecular fluorescence complementation wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Ligand binding assay wikipedia , lookup
Chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
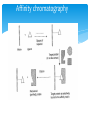
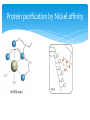
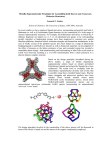
Nickel affinity chromatography in Protein purification Date: 26/03/2015 Awaji-kansan Obediah Contents Affinity Chromatography Protein purification by Nickel affinity Types of Ligands used Advantages of some of the Ligands used Applications References Affinity chromatography Affinity chromatography has to do with the immobilisation of a metal ion, usually a transition metal to a ligand which is then used to separate or purify protein or other biomolecules. Nickel just like any other transition metal has affinity for protein, specifically protein molecules containing Histidine residue. Affinity chromatography In order for affinity chromatography to work perfectly the right choice of the ligand to be used is very crucial, The metal ion should have a strong coordination with the ligand as well as the protein of interest. Affinity chromatography Points to note when choosing a ligand: Stability of the ligand under the condition of operation. The interaction with the protein of interest should be reversible. This is important because the protein has to be separated from the ligand after purification Affinity chromatography Protein purification by Nickel affinity Nickel affinity is specific for purification of protein molecule containing histidine residue. One method used is IMAC (Immobilised-metal affinity chromatography), with a centrally placed nickel ion. Protein purification by Nickel affinity Types of Ligands used Nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA), Iminodiacetic acid (IDA) both could be used to purify proteins with histidine molecules. NTA coordinates the Ni2+ with four valences and two valences are available for interaction with imidazole rings of histidine. Types of Ligands used IDA coordinates Nickel with 3 valences while 3 other electrons on Nickel are left to interact with the protein. Advantages/Disadvantages of some of the ligands used high level of purity obtained with NTA This is due to the strong coordination between the ligand and Ni2+ as well as the protein under consideration. IDA has shown poor purity of protein this is due to the fact that it has 3 coordination points with the ligand and 2 with the protein Advantages/Disadvantages of some of the ligands used One of the electrons remains free and this leads to leaching of Ni2+ which could bind to the surface of the purified protein and lower the purity of the protein after elution. A penta-dentate ligand can be used, this has lower metal leaching but protein recovery is very low. Applications Some of the applications of IMAC: IMAC can be used to separate structurally intact and soluble His-tagged antigens. It can also be used to separate denatured protein from the ones that are not denatured References Jerker, P. and Bright, O. (1983). Immobilised metal affinity adsorption and immobilised metal affinity chromatography of biomolecules. 22(7), 1621-1630 Sigma-Aldrich (). His-select Nickel affinity Gel. Retrieved from https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/content/dam/sigmaaldrich/docs/Sigma/Bulletin/p6611bul.pdf http://www.iba-lifesciences.com/Double-tag_His-tag.html http://info.gbiosciences.com/blog/bid/200711/What-You-Need-toKnow-About-NTA-and-IDA-Ligands Questions Thank you for your time