* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Biology of depression wikipedia , lookup
History of anthropometry wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
State-dependent memory wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Mind uploading wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of human intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
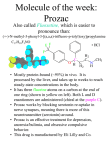
OCR 21st Century Science Unit B6 Statements Learning and conditioning 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 the cerebral cortex is the part of our brain most concerned The Prozac molecule blocks the re-uptake of serotonin from a synapse. scientists can map the regions of the brain to particular functions (including studies of patients with brain damage, studies in which different parts of the brain are stimulated electrically, Serotonin is a chemical released in the brain that gives feelings of pleasure. Whenever we have a new experience, a new pathway in the brain is used. Each new experience changes our behaviour - this is called learning. evolution of a larger brain gave with intelligence, memory, language and consciousness Prozac is an anti-depressant drug that causes serotonin concentration to build up in synapses. The human brain consists of billions of neurons. These neurons are connected together to form even more billions of different pathways. Lack of this chemical can lead to feelings of depression. humans are more likely to remember information if: and brain scans such as MRI, showing brain structure and activity). early humans a better chance of survival 1. The dog salivates naturally when given food 2. Pavlov rings a bell every time the dog eats 3. After much repetition the dog salivates when the bell rings, even when there is no food. a. they can see a pattern in it (or impose a pattern on it) b. there is repetition of the information, especially over an extended period of time c. there is a strong stimulus associated with it, including colour, light, smell, or sound a loss of short-term memory. They may not remember what day of the week it is, but they can remember details of their childhood. 8 A Russian scientist called Pavlov trained dogs to expect food whenever he 9 Short term memory is capable of storing a limited amount of information for 10 11 12 Long term memory is when more a limited amount of time. People with Alzheimer's disease suffer The food is the primary stimulus, the human entering the room is the secondary stimulus. information is stored over a much longer time. rang a bell. The dogs eventually produced saliva when they heard the bell ring. Another example of conditioning is a goldfish expecting food when seeing a human in the room. A goldfish swims to the front of the bowl when the human appears. OCR 21st Century Science Unit B6 Statements Learning and conditioning 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 the cerebral cortex is the part of our brain most concerned The Prozac molecule blocks the re-uptake of serotonin from a synapse. 5 scientists can map the regions of the brain to particular functions (including studies of patients with brain damage, studies in which different parts of the brain are stimulated electrically, Serotonin is a chemical released in the brain that gives feelings of pleasure. Whenever we have a new experience, a new pathway in the brain is used. Each new experience changes our behaviour - this is called learning. 6 and brain scans such as MRI, showing brain structure and activity). 2 evolution of a larger brain gave with intelligence, memory, language and consciousness 1 Prozac is an anti-depressant drug that causes serotonin concentration to build up in synapses. The human brain consists of billions of neurons. These neurons are connected together to form even more billions of different pathways. Lack of this chemical can lead to feelings of depression. 3 early humans a better chance of survival 4 humans are more likely to remember information if: 1. The dog salivates naturally when given food 2. Pavlov rings a bell every time the dog eats 3. After much repetition the dog salivates when the bell rings, even when there is no food. a. they can see a pattern in it (or impose a pattern on it) b. there is repetition of the information, especially over an extended period of time c. there is a strong stimulus associated with it, including colour, light, smell, or sound a loss of short-term memory. They may not remember what day of the week it is, but they can remember details of their childhood. 8 7 8 A Russian scientist called Pavlov trained dogs to expect food whenever he 9 Short term memory is capable of storing a limited amount of information for 10 11 12 Long term memory is when more a limited amount of time. 9 People with Alzheimer's disease suffer The food is the primary stimulus, the human entering the room is the secondary stimulus. information is stored over a much longer time. 12 rang a bell. The dogs eventually produced saliva when they heard the bell ring. Another example of conditioning is a goldfish expecting food when seeing a human in the room. A goldfish swims to the front of the bowl when the human appears. 11 10