* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Classical Conditioning
Bullying and emotional intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Symbolic behavior wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral modernity wikipedia , lookup
Psychophysics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Thin-slicing wikipedia , lookup
Transtheoretical model wikipedia , lookup
Insufficient justification wikipedia , lookup
Attribution (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Theory of planned behavior wikipedia , lookup
Applied behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Learning theory (education) wikipedia , lookup
Adherence management coaching wikipedia , lookup
Observational methods in psychology wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Theory of reasoned action wikipedia , lookup
Descriptive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Verbal Behavior wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Classical conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Social cognitive theory wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
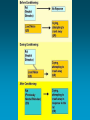
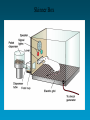
Learning Table of Contents71. Chapter 6 Concepts 72. Classical Conditioning Practice Homework- Review Chapter 6 Concepts- Quiz Thursday! Conditioning • Type of learning that involves stimulusresponse connections • Two types: – Classical Conditioning – Operant Conditioning Pavlov -Pavlov set out to discover how learning occurred -Created a study using dogs where he tried to condition the dogs to have a biological response (salivation) to a neutral stimulus. (ringing a bell) 1. UcS- Unconditioned Stimulus- food given to dogs UcR- Unconditioned Response- dog salivates and eats 2. Introduce NSNeutral Stimulus (ring bell when placing food down) 3. CS- Conditioned Stimulus- bell CR- Conditioned Response- salivate when hearing bell Little Albert experiment- John Watson • Watson wanted to apply Pavlov’s study to humans • Believed that human behavior (even things we thought were instinct) were a result of the environment (could be LEARNED) • Emotionally and physically healthy 9-month old male raised in a hospital environment • Seeks to condition this baby to have an extreme fear (response) to a small white rate (stimulus) Watson Anybody have issues with his experiment… Methodology? Ethics? Data? Watson’s Contributions • One of the First American Psychologist to apply Pavlov’s work to humans (emotions) • Brought the study of behavior (Psych) into a more “scientific” and observable discipline • Little Albert in every Psych Textbook •Convinced other Psychologist that there was an alternative to Freudian Psychoanalysis •Neurotic symptoms (Phobias could be controlled via CC)…Major applied significance Contributions to Psychology • Generalization of fears • Showed that emotions can be learned Use Classical Conditioning to explain behavior: Scenarios (group discussions) 1. Sound of drill, dentist visit 2. Hospital smell, visiting the hospital 3. Band-aids, visiting the doctor Neutral Stimulus (NS) Unconditioned Stimulus (UCS) Unconditioned Response (UCR) Conditioned Stimulus (CS) Conditioned Response (CR) Real-Life Examples of Classical Conditioning Mowrer & Mowrer (1938) Treatment for enuresis (bed-wetting) -Child sleeps on a pad (a wire mesh that is connected to a bell has been sewn) - Child wets the bed electrical circuit causes bell to ring (UCS) -Child wakes up (UCR) After several repetitions of this cycle (bed-wetting causes him to be awakened by the bell), the child begins to associate the sensation of pressure in his bladder (a previously neutral stimulus) with waking up -In a short time, the need to urinate (now a CS) becomes sufficient in itself to awaken the child (now a CR) so he or she can get up and go to the bathroom - no need for PAD with Bell In A Clockwork Orange, a brutal sociopath, a mass murderer, is strapped to a chair and forced to watch violent movies while he is injected with a drug that nauseates him. So he sits and gags and retches as he watches the movies. After hundreds of repetitions of this, he associates violence with nausea, and it limits his ability to be violent. Operant Conditioning- Skinner Box Operant Conditioning- People and animals can learn to do certain things (and not do others) by learning from the results of their behaviorVOLUNTARY responses • B.F. Skinner (19041990) – elaborated Thorndike’s Law of Effect <people keep doing things that feel good> – developed behavioral technology Thorndike’s Law of Effect Rewarded behavior is likely to recur. Behavior followed by a negative consequence is less likely to recur. Operant Conditioning • Operant Chamber (“Skinner Box”) – soundproof chamber with a bar or key that an animal can manipulate to obtain a food or water reinforcer – contains a device to record responses Skinner Box Reinforcer Increases the Probability of the Behavior It Follows • The fundamental principle of behaviorism is that rewarded behavior is likely to be repeated. • This is known as a positive reinforcement in operant conditioning. ex: Your teacher praises you when you get an “A” • A negative reinforcement is when you want a bad feeling/thing to stop so you exhibit a behavior – Ex: You put on your seat belt to make the ringing sound stop. OR You take an aspirin to make a headache stop. Punishment • When you get a consequence for a negative behavior so you stop doing the negative behavior – Ex: You get grounded for coming home after curfew. Positive and Negative Reinforcement, Positive and Negative Punishment Social Learning Theory Social Learning • Aka Observational Learning • learning by observing and imitating the behavior of others – The others whom we observe and imitate are called models. – They teach us by modeling behavior Observational learning helps children learn how to behave in their families and in their cultures without requiring direct experience Children Can Learn Aggressive Behavior through Observation • Albert Bandura • Bobo doll studies: the first set of experiments demonstrating the power of observational learning in eliciting aggression. • Research demonstrates that children are less likely to imitate the actions of punished aggressors. Children Can Learn Aggressive Behavior through Observation – Bandura believes children observe and learn aggression through many avenues, but the three principal ones are: • Families: where adults use violence • Communities: where aggression is considered to be a sign of manhood, especially among males • Media: principally television and the movies